Abstract
Though some businesses have thrived in the 21st century without creating business strategies or innovating, for the proposed study, the author asserts that many have taken a beating, and the fiscal crises that have continued to strike many business sectors increase the odds that the effects of the existing recession will be felt over the long term. The effects of globalization have tasked management by identifying the best strategies to address the reducing share markets. The use of technology and information or simply information technology to advance business operations has emerged as the best option.
As such, the author adapts from the above framework and asserts that the study will aim to study how information technology has been at the forefront of supporting and proactively enabling the establishment of business strategy in the Nigerian telecom industry and recommend measures that can be utilized by service providers to tap on this. The proposed study will address the following key aspects:
The introductory section will set the paper’s context by articulating the paper’s proposed objectives, research questions, problem statement, and the justification for undertaking this topic at a dissertation level. The proposal’s main section (the literature review) identifies the key concepts that have been advanced by previous and current scholars on the topic, albeit in brief. In the succeeding section, the author proposes and mentions details of the pertinent issues used in the collection and analysis of the collected data. To conclude, the author reflected on the ethical issues.
The Introductory section
Proposed Objectives
The following proposed objectives were derived from the study’s proposed aim
General Objective
To demonstrate that IT plays vital roles that aid in establishing competitive advantages in the Nigerian Telecom Sector.
Specific Objectives
- To identify barriers and challenges experienced when adopting or implementing IT-oriented strategies in the Nigerian Telecom sector.
- To clearly state the reasons why it is significant and justified to use the rapid advancements in IT to establish competitive strategies in the Nigerian Telecommunication Sector.
- To review some of the rapid or dynamic technological advancements that have taken place with regard to the telecom sector.
- To clearly explain the roles that IT has effected in enabling the establishment of competitive strategies in the Nigerian telecom sector.
- To examine the measures that can be adopted and implemented by mobile phone service providers in Nigeria to improve on their adoption of IT for competitive advantage.
Research Questions
The following research questions were derived from the study’s proposed aim and objectives statements;
- What are some of the barriers and challenges experienced when adopting or implementing IT-oriented strategies in the Nigerian Telecom sector?
- State clearly some of the reasons why it is significant and justified to adopt and implement the rapid advancements in IT for competitive positioning in the Nigerian telecom industry.
- Identify and provide a brief description of some of the dynamic technological advancements in the context of the telecom sector.
- Briefly explain a number of roles that IT plays in enabling establishing of innovative and competitive strategies in the Nigerian telecom sector.
- Which measures can be implemented by Nigerian telecom firms to improve on competitive positioning?
Problem statement
The problem statement emanates from the fact that despite the Nigerian telecoms market being the leading in Africa (Chanakira p.10) and offering a clear and exciting opportunity for a number of telecom providers (Willis & Daniels 2003, p.2), many service providers have found it tough to compete effectively in this fully liberalized market where the law of competition has of late replaced the law of the jungle. A report by Africa’s Technology News Leader (2011) documented statistics that revealed that about 65 Nigerian telecom firms had closed some of their shops as a result of prevailing harsh business environment in Africa’s most populous nation.
On their part, Achimugu and others (2009, p.37) went ahead to assert that only a few telecom firms in Nigeria had adopted IT changes to achieve competitive advantages successfully. This has therefore created a widening IT gap (or digital divide). Moreover, the author established that the evolvement of information technology and its capabilities have continued to assume a dizzying pace, thus becoming a challenge for management to compete in incorporating the technology in their operations. With these facts in mind, this proposed study will, therefore, look at the roles that IT advances in supporting and proactively enabling business strategy in the Nigerian telecom context.
Justification
The aspects discussed will be relevant and justified both from an organizational and learning perspective. On the organizational side, the author notes that the study will help telecom managers to identify and familiarize themselves with the opportunities and challenges that are IT related or oriented. Then they can go ahead to adopt and implement some of the findings and recommendations to establish competitive advantages for their telecom firms. From a learning perspective, the researcher points out that the study is justified in advancing future learning since its concepts will be borrowed by scholars for future research.
Literature Review
This section will discuss the theoretical framework on which the study will be based and, at the same time, review themes related to roles of IT in the telecom sector. The following is a review of literature on a number of identified debates.
The competitive nature of any telecom Industry
Willis and Daniels (2003) set the stage by acknowledging that the telecommunications market had undergone rapid changes over the past few years; driven primarily by the effect of globalization. To support this, according to two studies by Kohler and Chaves (2003, p.6) and Boulle (2009, p.11), globalization has led to the removal of barriers that restricted market entry and instead opened the way for the ‘natural market forces’ which in return determine the market sustainability.
On the other hand, in a study that assessed the implementation of the corporate strategic action and the performance of various telecom firms in the US, Lee (2008) articulated facts that supported the notion that the competitive environment defined any telecom market. In his widely acknowledged research article, this renowned US scholar asserted that the decade ranging from the mid-1980s to 2004 was defined by an explosion in demand for new telecom services and products (Lee 2008, p.25).
This scholar expounded on his findings by pointing out that the improvements in existing technologies, the rapid growth in telecom markets and the surfacing of new substitutes had intensified competition and facilitated the entry of new players into the telecom industry (Lee 2008, p.25).
Tellingly, different researchers continue to postulate that as competition becomes more intense in the telecom industry, more diverse and frequent corporate strategic activities will be sought after by the many telecom firms all over the world for their profitability. To justify the claim, a study by Khosrowpour (2006, p.255) on the Philippines’ telecom industry established how a lesser telecom firm (Globe Telecom) had innovated, competed and survived in a market that had been monopolistically dominated by one player (PLDT). According to this study, Globe Telecom had formed partnerships with lesser telecommunication firms and built additional and cost-effective networks across the nation thus increasing their profits and enhancing customer satisfaction (Khosrowpour, 2006, p.255).
Moreover, the researcher came across interesting and fascinating statistics for a fastest growing Nigerian telecom firm (Visafone Ltd) that had been born out of a strategic merger of three underperforming telecom firms in the year 2007. According to the facts presented on its website, this successful Nigerian telecom firm strategized by offering exciting bouquets of superior telecommunication services (Visafone 2011). These encompassed the very best of high-speed 3G data, internet, voice and highly innovative value-added services. This new strategy had seen the company record a milestone when it amassed three million new subscribers in its first 16 months. This led to it being voted the best telecom and ICT brand in Nigeria in the same year of its launch, 2008 (Visafone Homepage 2011).
The findings in this subsection will be used to inform the research that strategizing and attaining diversity in the telecom sector is neither achieved on a silver platter nor easily incorporated under existing business models unless there is a true commitment from the concerned managers.
Challenges facing the telecom industry
Several scholars have come to agree that many challenges face the modern-day telecom industry. To define the content in this subsection, Willis and his friend Daniels (2003) averred in their concluding remarks that the days of deploying the technology on the assumption that subscribers will highly embrace it has been assigned to the annals of history as is the case with many telecom operators. To help us understand the meaning of their statement, this important scholars went on to clarify that in the Modern Day, the market demands were the ones tasked with setting the pace for the deployment of technology.
On a slightly contrasting note, PWC (2012) surveyed and named the failure to enact a flourishing business framework to help in the provision of intermediary financial services of the nature of mobile banking as a key challenge that faced the telecom industry. The same report went ahead to name the un-exploration of the scope for the mobile-commerce application as an additional challenge that hampered growth in the telecom industry, especially in the developing countries (PWC 2012).
On a rather surprising and very different note, policy changes such as the issuing of new licences to new players were cited as a factor that opened the way for the entry of many players in Indian telecom market (India Telecom Online 2010). The end result of this has seen many players creating stiff competition that has led to huge pressure on the profit margin as well as the slowdown in revenue growth (India Telecom Online 2010).
The findings in this subsection will inform the proposed research on the nature of challenges that are already affecting or will come to affect the telecom firms at a future date. The users of the study can go-ahead to carry out control or mitigation measures for the reviewed challenges.
Definition of IT, its importance and its adoption in developing countries
Achimugu and his group of three scholars (2009) defined Information Technology (IT) as forms of information exchange amongst more computers using any of the several methods of interconnection, principally the internet” (p.37). From another perspective, Tansey (2003) went ahead to adopt the definition that had been employed by Flowers to define the term as the application of telecoms and computers to the processing, storage and dissemination of the text, voice, numerical information and graphics (p.3). Nonetheless, Betz (2011) provided the latest and summarized definition of IT by saying that it was about the computing software and hardware applications which were in return applied to enterprise needs (p.2).
While reviewing the importance of IT in the competitive business environment, Achimugu and his group of scholars postulated that IT provided inexpensive, speedy and convenient means of communication (p.37). The four scholars expounded on their findings by highlighting that the diffusion of IT-oriented technologies provided direct positive effects on a firm’s operational efficiency thus leading to the rapid acceleration of growth to the affected nation’s economy.
On the other hand, Tansey (2003, p.4) studied the impacts of IT and stated that when applied, technology brought inevitable, far-reaching and widespread impacts, some of which included the creation of new services and products, new production methods, and transformations in communication and information processing. Furthermore, Agboh (2000) wrote to acknowledge the importance of IT by stating that IT applications had the potential of bringing significant and competitive advantages to development and trade, and were thus deemed critical in determining the success of any organization.
Notably, in analyzing how management has increased their involvement with information technology through the use of various methodologies, the author found out that IT has called on the need for organizations to introduce strategic management, outsourcing and corporate governance amongst others as answers to their profit motives (Orcullo 2007, p.25).
Conversely, while reviewing the status of IT adoption in developing countries, Achimugu and his friends (2009, p.37) begun by averring in their introductory section that preliminary investigations showed that precisely, a few organization had made efforts to adopt IT. On his part, Agboh (2000) noted that despite IT having changed rapidly and causing variations and radical opportunities to several spheres of life, few inhibitors for managers and other users had proved difficult to cope with especially in Africa’s less-developed nations. This scholar went ahead to identify these inhibitors as inadequate capital, lack of modern telecom infrastructure, and lack of technical know-how, all of which have proved deficient in most parts of Africa.
Roles of IT in the telecom sector
The important roles of innovative information technology continue to be felt across many telecom firms.
Strategic branding of telecom firms
The first analysis of how insights into technology have been valuable to designing and enabling business strategy can be well explained by analyzing the current trends in digital branding. Branding was defined by Balakrishnan (2009) as “selecting a consistent brand element mix to identify and distinguish a business brand through positive image building”. Until recently, few success stories had existed in branding strategies (Balakrishnan 2009).
Morrison and Anderson averred that this was so because they contained a mixture of varying components (commonly referred to as marketing mix). However, the trend has changed today thanks to the important role played by technology in enhancing the designing of appropriate business strategies.
This has been so because on project-based co-operations, designers have been able to manage the translation of business goals and brand stories into sentiments and visuals that touch specific target audiences. The advanced technology has thus facilitated the implementation of concept, research, design and strategy. This has been achieved by the use of technological tools such as Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), Marketing Platforms and other additional data services.
Figure 1 demonstrating how a designer made use of the advancements in technology to design and depict key factors necessary for branding strategies (Source: Balakrishnan 2009).
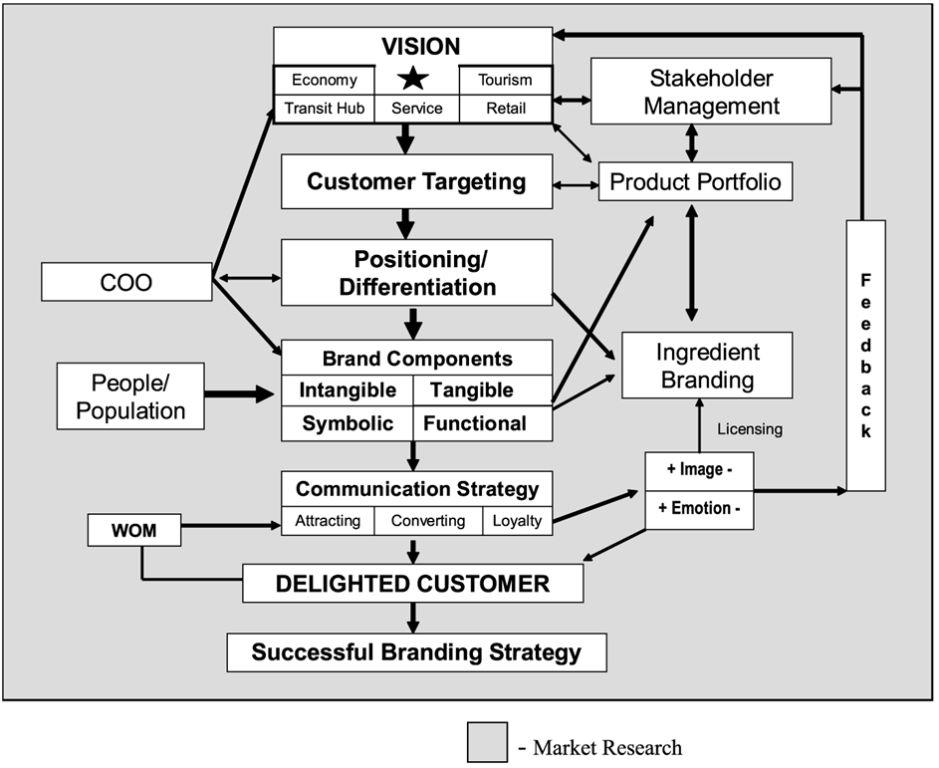
Figure 2 showing a sample of how Visafone used technology to brand itself (Source: Visafone Homepage 2011)
The findings in this subsection will be used to inform the research that IT plays significant roles in enhancing the branding of telecommunication firms. These in return, improve on their image and reputation.
Smartening of phones
Before its current sleek design, the mobile phone design revolved around the creation of bulky, expensive and heavy gadget (Karie, 2011). Thankfully, succeeding years have seen the ever-changing technology lead to the smartening of the mobile phones. While borrowing from Goggin research, the author established that IBM became the first competing manufacturer to introduce the smartphone. This was in the year 1992. Its device was strategically designed to combine versions of the then-standard computer programs.
However, today, almost all phone manufacturers have embraced the technological innovations in the industry by designing and developing high-tech smartphones that continue to be reproduced regularly in improved versions (McDaniel 2009, pp.453-456). McDaniel (2009) went ahead to justify his finding by pointing out that the smartening of the phones through technological advancements facilitated the supporting of different modes of interaction and communication (p.453).
Figure 3 illustrating the latest iphone4s; an example of a smartened and advanced mobile phone design by the leading smartphone designer Apple (Source: Apple Homepage 2011.)

The findings in this subsection will inform the research that with the advancements in technology occurring at a fastening pace, the design of the smartphones will continue to change to reflect these changes. Therefore, telecom firms should not be left behind in embracing these technological changes in innovate strategies that will lead to the effective and efficient use of improved phones.
Proposed Methodology
This section presents the research methodology, approach and strategy that will be used to complete the study if approved. The study sites, participants, data collection methods and ethical considerations amongst others are explained in this chapter.
Proposed research methodology
The proposed study will execute a quantitative approach. This is so because this being a survey kind of study and borrowing from Terry (2011, p.68), this proposed research design will enable the researcher to analyze statistics as well as establish causal and correlation relationships amongst study variables (that include: technology, its adoption in the telecom sector, challenges and benefits associated with IT adoption amongst others).
Again, the proposed design will allow the researcher to test theoretically derived hypothesis or assumptions to arrive at logical outcomes that will possess scientific validation. Haberfeld and other two scholars (2009, p.27) documented the same justification by mentioning that quantitative research studies allowed the application of statistical analysis toward the collected data, thus providing a clear picture on the findings or results.
Study population and study area
A study population can be defined as a compilation of objects of interest in research, which if used, can provide relevant information that will help the researcher to accomplish the study objectives or aims. In this proposed study, the study population will include 100 managers drawn from 5 leading telecom firms in Abuja, Nigeria.
The following table shows the names and statistics of the selected study companies.
Sampling technique and sample population
The researcher will use purposive sampling, whereby, he/she will only choose those respondents who will have relevant experience in relation to the topic under investigation. As such, five managers will be chosen from each firm to constitute a sample population of 25 (see table above for illustration). As such, the following departments will constitute the majority of respondents in the sample: IT or ICT, marketing, operations and procurement departments.
Data Collection Method
Quantitative methods of data collection that include questionnaires and documentary sources are proposed.
Questionnaires
Questionnaires are tools often used by researchers to collect data or information on several indicators of a target population. Mugenda and Mugenda (2003) established that they are normally used in a large scale survey of well-educated people in the country or area where the research is done. The researcher proposes to use hand delivery to distribute questionnaires to the selected sample group.
Since questionnaires normally suffer from a low response rate, the researcher will make them short, open-ended with straight forward questions to improve on their response rate. They are also preferred by the researcher because of their suitability in instances where both the researcher and respondents prefer their own privacy. Findings from the questionnaire will be augmented by face to face interviews with key informants drawn from the respondents.
Documentary sources
These will be sources like journals, online books, published books, thesis and dissertations, among others; addressing the same topic. They will provide past references and findings hence revealing knowledge gaps for improvement. Secondary data will be obtained through the library and another search on the internet.
By solely employing secondary sources in the investigation, the researcher will benefit from numerous advantages that are connected with their applications. First and foremost, secondary sources are generally available and ready-made for use (Newman & Benz, 1998).
Another huge benefit of using secondary sources in this research is that these sources are not limited by space and time (Kaar, 2009). As such, the researcher will be at liberty to review these sources at own convenient time and place. Also, as was postulated by Housden (2008), secondary methods of data collection are quick and inexpensive approaches. In addition, in using this method, the researcher will particularly be interested in narrowing on specific roles that IT plays in supporting and enabling strategy in the Nigerian telecom sector. This will be achieved through the proper formulation of questions that will be searched on the internet using suitable search engines.
Data collection procedure
The researcher will obtain a research permit from the Nigerian government before proceeding with the study as per the requirement. The researcher will conduct a pilot study on the questionnaire and schedule the day for distributing the questionnaires. The pilot study will assist in ensuring that;
- The chosen questions are clear;
- The chosen questions will not consume a lot of respondents’ time;
- The questions are easily understood
Furthermore, an advance letter will be sent to the sample respondents, explaining the purpose of the study. In this letter, the information will be given to the respondents regarding the nature of the study and how the study will benefit them.
Exploration of the Issues of Validity and Reliability
Validity
The validity measurement will be based on logical judgment and external criteria such as an expert opinion as in the researcher’s case. This will be done by conducting preliminary interviews say on five respondents after which the questionnaire will critically be reviewed to ensure that there will be similarities and complements between the interviewed questions and those in the real questionnaire. This will be so bearing in mind that the study adopted a quantitative research method. The above measures will be considered in this study to ensure the validity and credibility of the quantitative data. This research will only be considered valid when conclusions will be found to be true.
Reliability
Reliability will be the extent to which the collected data will produce similar results under constant conditions, occasions and evaluation. Reliability will be achieved when the data collection process will be done repeatedly at different times using the same population to ensure consistency of the results.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Data analysis shall be done upon completion of the data collection from the sample population. The process will involve the presentation of findings and the derivation of meaningful findings.
Data analysis will employ content analysis. It is any technique for making inferences by objectively and systematically identifying specified characteristics of messages. In this approach, the analysis of documents and texts that seek to quantify content in terms of predetermined categories and in a systematic and replicable manner will be carried out. To add, descriptive statistics will be used to describe the sample results and the findings generalized to the rest of the population. After stating the findings, data will need to be presented for ease of comprehension. The researcher will use statistical techniques such as frequency distribution charts, tables, and graphical techniques to illustrate the results easily.
Reflections and Resources
This section also provides a detailed discussion on the proposed ethical considerations, action plan, an audit of the researcher’s skills and knowledge to ensure that this proposed research will be well tacked by the researcher. However, due to the nature and the format of any proposal, the audit and action plan will be incorporated under the appendices section.
Ethical Issues
The researcher will be dealing with human beings and will, therefore give attention to the ethical issues associated with carrying out research. Some of these issues include but will not be limited to:
- Voluntary participation: The researcher will obey the cardinal rule of voluntary participation amongst participants because when doing research, participants should not be coerced into taking part in the study.
- Informed consent: The researcher will ensure that his participants are informed of the procedure of the research and that they will be at liberty to consent before being part of the study sample.
- Confidentiality: For this, only the researcher and research assistant (if any) will know the identity of the respondents. The researcher must obtain full consent of the respondents
References
Achimugu, P, Oluwagbemi, O, Oluwaranti, A, & Afolabi, B 2009, ‘Adoption of information and communication technologies in developing countries: An impact analysis’, Journal of Information Technology Impact, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 37-46. Web.
Africa’s Technology News Leader 2011, Over 65 Nigerian telecom companies shut down. Web.
Agboh, DK 2000, Coping with rapidly changing information technology: Challenges facing Africa’s less-developed countries, International Journal of Computer Applications in Technology, vol. 13, nos.3/4/5, pp.107-112.
Balakrishnan, MS 2009, ‘Strategic branding of destinations: A framework’, European Journal of Marketing, vol. 43, nos. 5/6), pp. 611-629.
Betz, CT 2011, Architecture and patterns for it service management, resource planning, and governance: Making shoes for the cobbler’s children, 2nd edn., Elsevier, Massachussets.
Boulle, L 2009, The law of globalization: An introduction, Kluwer Law International, The Netherlands.
Chanakira, M n.d., The impact of the financial crisis on the telecommunications industry in Africa. Web.
Goggin, (n.d). Cellphone. Dissertation. Commonwealth of Australia.
Haberfeld, MR, King, JF & Lieberman, CA 2009, Terrorism within comparative international context: The counter-terrorism response and preparedness, Springer, New York.
Housden, M 2008, CIM coursebook marketing information and research, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford.
India Telecom Online 2010, Challenges faced by Indian telecom industry. Web.
Kaar, M 2009, A critical investigation of the merits and drawbacks of in-depth interviews, GRIN Verlag, Germany.
Karie, J 2011, The role of science and technology in future design, Nobel Prize Homepage.
Khosrowpour, M 2006, Cases on telecommunications and networking, Idea Group Inc (IGI), Hershey, Palmdale.
Kohler, G & Chaves, EJ eds. 2003, Globalization: Critical perspectives, Nova Publishers, New York.
Lee, JJ (2008), Corporate strategic action portfolios and firm performance in the US telecom industry (1984–2004), ProQuest, Michigan.
McDaniel, JG 2009, Advances in Information Technology and Communication in health, IOS Press, Amsterdam.
Mugenda, O & Mugenda, A 2003, Research methods: Quantitative and qualitative approaches, Acts Press, Nairobi.
Newman, I & Benz, CR 1998, Qualitative-quantitative research methodology: Exploring the interactive continuum, SIU Press, Illinois.
Orcullo, N 2007, Fundamentals of strategic management, Rex Bookstore, Inc., Manila.
PWC 2012, Challenges facing telecoms sector. Web.
Tansey, SD 2003, Business, information technology and society, New York, Routledge.
Terry, AJ 2011, Clinical research for the doctor of nursing practice, Jones & Bartlett Publishers, Massachusetts.
Visafone Homepage 2011, History and business of the company. Web.
Willis, A & Daniels, G 2003, Nigeria telecommunications market: A snap shot view, Africa Analysis. Web.
Appendix A: Continuation on Reflections and Resources
AI. An audit of researcher’s knowledge and skills.
AII. Proposed Action Plan
Appendix B: Introduction Letter
Dear Respondents,
I am a postgraduate student in the school of Business Administration. As part of the requirements of the Masters in information science programme, I am undertaking a research project titled, ‘Role of IT in Supporting and Proactively Enabling Business Strategy in the Nigerian Telecom Industry’
Your have been selected to assist with data collection by responding to questions in the accompanying questionnaire. Your responses will be treated with utmost confidentiality and will be analyzed for academic purposes only. You will also be provided with a copy of the final report upon your request.
Thanks for your cooperation
Yours faithfully,
Appendix C: Proposed Research Questionnaire
University of (Insert Institution Name), School of Business Administration, Proposed Research Project Questionnaire.
Instruction(s): Study the following questions and provide your own responses (Any stated or listed points should be numbered; e.g. 1.)
- List some of the barriers and challenges experienced when adopting or implementing IT oriented strategies in the Nigerian Telecom sector?
- State clearly some of the reasons why it is significant and justified to adopt and implement the rapid advancements in IT for competitive positioning in the Nigerian telecom industry.
- Briefly explain a number of roles that IT plays in enabling establishing of innovative and competitive strategies in the Nigerian telecom sector.
- Using 5 to represent the most successful results and 1 to represent least successful results, rate (by ticking in the relevant corresponding box) the level of success at which the Nigerian telecom providers have embraced IT.
- According to your own analysis, briefly explain a number of roles that IT plays in enabling establishing of innovative and competitive strategies in the Nigerian telecom sector.