Significance To Nursing
Significance of Integrating smoking cessation into daily nursing practice are:
- Support the global movement to reduce tobacco use.
- Motivate nurses and support them in identifying their clients tobacco use status.
Globally, different governments are on the move to reduce the use of tobacco. They have employed strategies like increasing the prices of tobacco practices. These strategies have worked to some extent, but are also limited. Use of smoking cessation strategy is the best method to reduce the use of tobacco products (Registered Nurses’ Association of Ontario, 2007). therefore, practicing these guidelines will ensure that nurses supports the fight against tobacco use.
smoke cessation is best delivered when evidence is included. Tobacco users are likely to quit smoking on use of smoke cessation strategies that supported by evidence. Through the use of nurse, it is easy to develop strategies that employ evidence. For instance, before implementing any evidence based strategy, it is advisable that a client should first obtain help from a doctor. The purpose of brief interventions is to help the client find confidence in the strategy to use in quitting smoking. Studies indicate that nurses have an influence on the client ability to quit nursing. Nurses relationships and trusts built on them by clients can be used as an advantage to help a person quit smoking. Using this opportunity, it is beneficial when a smoking cessation program is implemented in the nursing daily practice. Nurses exposure to opportunities that will help reduce tobacco use makes smoking cessation implementation reasonable in daily nursing practice.

Standardized Specific Guidelines
- Regular tobacco use is an addiction that require repeated intervention.
- Assistance to stop smoking benefit every smoker.
- A client can refuse or accept smoke cessation intervention.
- Smokers should be treated with dignity as they receive smoke cessation intervention.
- Public values and trusts nurses interventions.
- Nurses have multiple opportunities to identify smokers and implement cessation strategy.
- Active implementation of smoking cessation strategy will lead to successful quitting.
- Smoking nurses have a professional responsibility to implement smoking cessation.
- Nursing students should be educated on evidence based practice strategies.
- Nurses are positioned to leadership in smoking cessation implementation.
These guidelines are vital to ensure that the implementation of smoke cessation strategy is successful. In addition, they ensure that stakeholders involved understand their role and responsibility. Standardized guidelines can be perceived as universal laws. They direct the entire process of developing clinical guidelines in any circumstance. In addition, they stand as a basis for developing other practical guidelines. These guiding principles are assumptions made to guide the development of evidence based clinical guidelines (Registered Nurses Association of Ontario, 2007).
The standardized guidelines indicates a gap that require action. For instance, the above guidelines indicates the need to have a guideline that would help in reducing the use of tobacco. Further, the guidelines identifies opportunities in which the smoking cessation strategy can be implemented. Therefore, using these assumptions, it becomes easier to provide a logical guideline.

Clinical Guideline Working Link
The link provides the clinical guideline for integrating smoking cessation in daily nursing practice. The guideline contains the recommendations for implementing a smoking cessation program into daily nursing practice. In summary, the guideline is authored by the Registered Nurses Association of Ontario (2007). It is a revision of the previous smoking cessation guidelines, written by the similar author in 2003. the revision concentrates on recommendations and more evidence.

Author and Guideline development description
The guideline was developed by Registered Nurses Association of Ontario.
The author developed this guideline by revising the original guideline focusing on smoking cessation published in 2003.
The development focused on four areas. First, the development gave recommendations directed for nurses in their practice. Second, the guideline made education recommendations and competencies necessary for smoking cessation. Third, organizational recommendations were made. Finally, the method for evaluation and monitoring criteria is suggested (Registered Nurses Association of Ontario, 2007).

Credentials and credibility of Guideline developers
- A professional association in charge of registered nurse in Ontario, Canada.
- Participates in development of Best Practice Guidelines Program.
Registered Nurses Association of Ontario has influenced the development of public health. The association is strongly and credible in voicing the needs of nurses. Being a professional association, it is more credible in implementing professional programs affecting nursing. This body has a mission of representing nurses in Canada. It has well laid down strategies and is governed by a board of directors. In summary, this body has made much contributions to the professionalization of nursing in Ontario.

Analysis of the Research
- 16,000 people die each year in Ontario for using tobacco.
- Tobacco economic cost was $6.1 billion in 2002.
- Smoke cessation promotes change in an individual lifestyle.
The increase in the use of tobacco is worrying. This substance has led to an increase in number of death in Canada. Use of tobacco has also increased the economic expenditure. With smoke cessation, it becomes easier to combine a multiple of strategies to control the use of tobacco. Studies indicate that using multiple strategies is reliable in the control of tobacco (Registered Nurses Association of Ontario, 2007).

Links to the Guidelines National Standards
Establishing links helps nurses find many opportunities for implementing smoking cessation strategy.
The links provide the nurse in practice with opportunities to find ways of interacting with clients. The links also helps the nurses increase their understanding of the

Best Evidence: Supporting The Guideline
- Existence of initial and ongoing smoking cessation services.
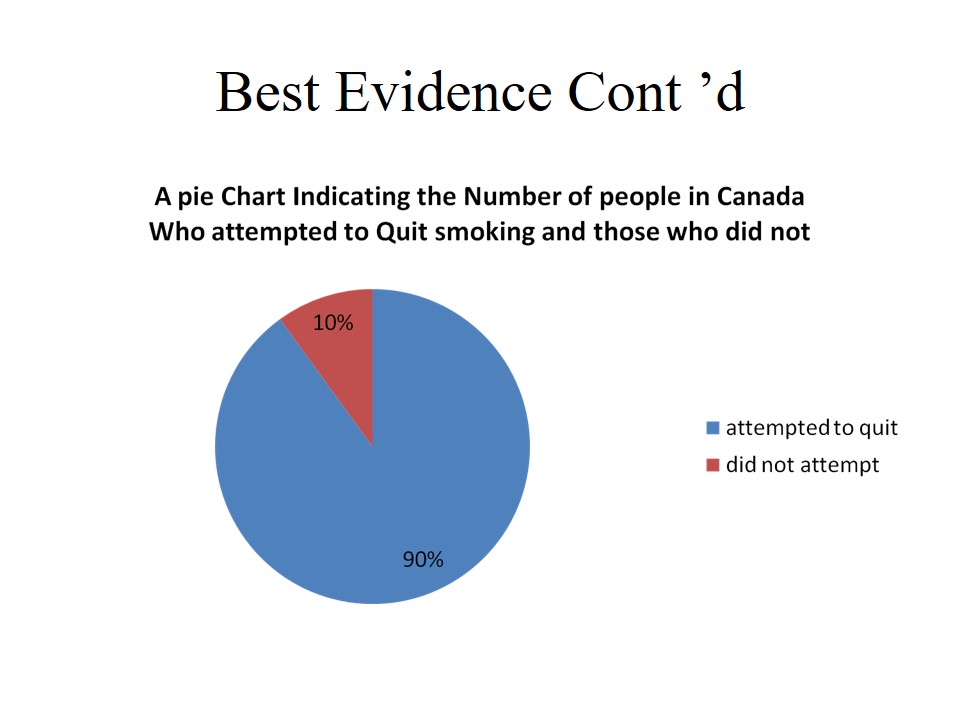
- 90% of smoking Canadian attempted to quit smoking.
- People can successfully quit smoking when they use several efforts.
- Ineffectiveness of using NRT and other Pharmacological strategies.
- Increase in total economic cost to almost $6.1 billion.
- Smoking cessation can be utilized in most opportunities.
- Short and long term of smoking cessation.
There exist a number of evidences supporting the implementation of smoking cessation program in the daily nursing practice. First, smoking cessation strategies already exist in the society. Examples include individual behavioral support and telephone support (Baxter et al., 2009). Considering the benefits of quitting smoking, 90% of smokers in Canada have worked their way out to drop the habit (Pfizer Canada Inc., 2006). However, they fail for lacking consistent efforts and support. According to Canadian Lung Association (2008) successful people who quit smoking use a combination of methods. This evidence makes smoke cessation a suitable strategy because it provide room for a variety of methods. Early methods eased to quit smoking like Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) and other related pharmacological strategies ineffectiveness calls for the implementation of smoking cessation. For instance, NRT products need to be used in a certain way for admirable results. Improper use of these products will make the process of quitting smoking ineffective. In addition, NRT products can be addictive and costly (Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, CAMH, 2007). Smoking cessation will help reduce the economic cost emanating from tobacco use. For instance in Ontario, in 2002, $6.1 billion was spent on tobacco related issues. Such amount would have been used on other projects of international interests (Registered Nurses Association, 2007).
From the pie chart above, it is clear that the number of people who attempted top quit smoking was high that those who did not attempt. For instance, 90 percent of smokers in Canada attempted to quit smoking. Conversely, a small percentage (10%) did not try attempt to quit smoking (Registered Nurses Association of Ontario, 2007). The a study indicated that those who tried to quit received pressure from the public. Unfortunately, they did not complete quit smoking as a result of poor strategies being used. The quitting process is based when done in a group and by use of a multiple strategies.

Summary of Articles supporting the Guideline
- Smoke cessation strategies already exist in our society (Baxter et al., 2009).
- Benefits of smoking prompt smokers to quit (Pfizer Canada Inc., 2006).
- A combination of more than on strategy is suitable to overcome smoking (Canadian Lung Association,2008).
- NRT and Pharmacological strategies are sometimes ineffective (Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, CAMH, 2007).
- Smoking cessation is vital in healthcares (Tsoh, McClure, Skaar, et al., 1997).
- Smoke cessation is cost effective in the long run (Jit et al, 2009).
According to Baxter et al (2009), smoke cessation program is feasible because there already other methods of smoking prevention. These methods can also be integrated in a smoking cessation program. This case becomes much important for nurses in their daily practice because they are familiar with most of the methods used in smoke prevention.
Pfizer Canada Inc (2006) study has outlined that the benefits of quitting to smoke are a major motivator for one to quit smoking. Those who have attempted to stop smoking were motivated by different benefits. For instance, a person who quits smoking has an improved lifestyle, avoids the risk of contracting some diseases, and maintains his or her body weight. Other benefits include relief on budget stress and improved family relationships.
According to Canadian Lung Association (2008), combination of more than two strategies is essential for successful process of one quitting to smoke. Multiple strategies reduces the likelihood of a client smoking again, when on strategy fails. Therefore, practical guidelines that advocate for multiple strategies encourages successful smoke cessation in different contexts.
The ineffectiveness of pharmacological strategies and NRT creates an opportunity for an alternative smoke prevention alternative (CAMH, 2007). In most cases these alternatives work independently. In such a scenario, when one alternative fail or becomes ineffective, there is no another method put in place to compensate for the ineffectiveness.
Healthcares have a number of opportunities that would make it effective to implement smoke cessation program (Tsoh, McClure, Skaar, et al, 1997). Smoke cessation program should be both nurse and client centered. Within healthcares, nurses are exposed to opportunities of meeting new smoking clients in various departments. It is essential to sensitize nurses in healthcares on the ways to identify clients.

Evidence for each research study
There are a number of reasons or evidence that support the use or implementation of smoke cessation strategy. First, the existence of other smoke prevention strategies in the society promotes implementation of smoke cessation. This is because smoke cessation advocates for multiple strategies in the control of smoking. Therefore, with the existence of smoking cessation strategies, it is easier for the society to accept this program.
Implementation of smoke cessation is needed because there are people willing to quit smoking. Their quitting process was interfered by the ineffectiveness of the alternatives that they use. In addition, it is not easy to quit smoking as an individual. Quitting smoking is best achieved in a group, a characteristic developed well through smoke cessation program. Successful smokers have been proved to have used multiple strategies. Their testimonies indicate the contribution of smoking cessation in the prevention of smoking.
Evidence indicates the role of nurses in control of smoking. Nurses need to be educated or be provided with practical guidelines on preventing smoking. There position and daily practices puts them in a position to meet may people to advise on the best ways to help them quit smoking (Registered Nurses Association of Ontario, 2007).
Finally, prevention of smoking has been expensive to most governments. Governments are in need to come up with method that would help them reduce the costs of stopping smoking. Evidence indicate that cost-effectiveness is one of the long-run benefit of smoke cessation (Registered Nurses Association of Ontario, 2007).

Summary of Evidence
From the reviewed literature, it is concluded that:
- Tobacco users are prompted to quit.
- Multiple strategies are essential in smoke prevention.
- Cost will determine the effectiveness of a smoke prevention program.
The desire to quit smoking is with some smokers. Unfortunately, this smokers normally fail to quit the process. They again begin smoking for lacking effective alternatives. This failure supports the use of smoking cessation to control smoking. Last, smoke cessation is cost effective, making it a realistic program. Smoke prevention programs are normally supported by governments. For government to support a program over a long period, it should be cost friendly. Programs that require much money can be considered ineffective.

Application to Practice Setting
This smoke cessation program should be applied by Nurses because they:
- Have numerous opportunities of identifying tobacco users.
- Are familiar with other smoking prevention strategies.
Nurses are exposed to opportunities that can help them reach numerous people who are willing to quit smoking. In their daily nursing practice, they are meet new people whom they develop close relationship with. This relationships provides a good opportunity to reach clients who smoke. Nurses familiarization with different smoke prevention strategies has been equipped with different skills and techniques.

Barriers and facilitators to change
- Barriers:
- Inadequate training personnel.
- other smoke prevention programs.
- Tobacco users non-commitment.
- Facilitators
- Evidence from literature.
- initial smoking cessation strategies.
- Government.
At the beginning, there would be a deficit in the people to help the nurses in implementing the strategy. It will also be hard to implement the program in organizations that already have their own smoking prevention program. In addition, at first, it would be hard to find a high level of commitment from smokers, especially when handling an individual smoker. This is because it is easier to quit smoking in a group than as an individual. Fortunately, enough evidence from the literatures will help in convincing people on the value of this program. The existing smoking cessation strategies will be helpful in explaining the program to people. In addition, the government will support the program because it has not been satisfied with some of the existing programs of smoking prevention.
The existence of other smoke prevention programs stand as a barrier to implementing a smoking cessation program in the daily nursing practice. Normally, it is hard t implement change. Different nursing settings and contexts already have smoke prevention programs. Making changes in this program can be limited by individual obstacles and organizational obstacles. The effectiveness of these programs will determine the level at which a new smoke cessation program is implemented. The implementation procedure will call for the assessment of the current programs to have enough information to convince the nurses and healthcare centers to accept the new changes.
The us of tobacco is addictive. It is important for a person attempting to quit smoking to demonstrates a high level of commitment. Lack of commitment makes the client be tempted to smoke again. This will makes the quitting process harder and irresistible. When the follow up plan fails, there are high chances of the smoker failing to adhere to the plan agreed upon. Other factors like finances and peer pressure may reduce the level of commitment of a client. Therefore, the client has to put in much sacrifice during a smoking cessation process.
Evidence from literatures facilitate the smoking cessation program. Smoking cessation strategies that are evidence based are much more successful compared to the ones without evidence. There exist a variety of literatures that calls for smoke cessation strategies that are evidence based. The purpose of evidence is to guide one in constructing logical strategies, which can be supported. Such strategies are easy to use because of their convincing power.
Existence of initial smoking cessation programs makes it easier to implement a smoking cessation program. There exist a number of smoke cessation programs in the society today. These strategies are implemented in different settings and environments. Familiar use of these strategies will make it easier in implementing a smoking cessation program. The nurses will not find it difficult in implementing the program. For instance, the existence of clients who have attempted to quit smoking is an indication that there already exists strategies that are used to quit smoking (Registered Nurses Association of Ontario, 2007). Therefore, the cost of implementing this program will be low.
Last, the government support will facilitate the implementation of smoking cessation program. The government is one of the strong stakeholders behind the control of tobacco use. The government supports the strategies that do not have much negative effects on people. Considering the importance of smoke cessation strategies, there is a high likelihood that the government will support the program. Specifically, the program is normally cost-effective, making it the most appropriate method to be supported by the government.

Decision to change practice
The decision to change is for the person using tobacco/ smoker.
For a person to stop smoking, he or she should first show the willingness to quit. This will be an internal motivation, which will help increase commitment to a smoke cessation program. A person can acquire this motivation by being sensitized on the benefits that comes when one stops smoking.

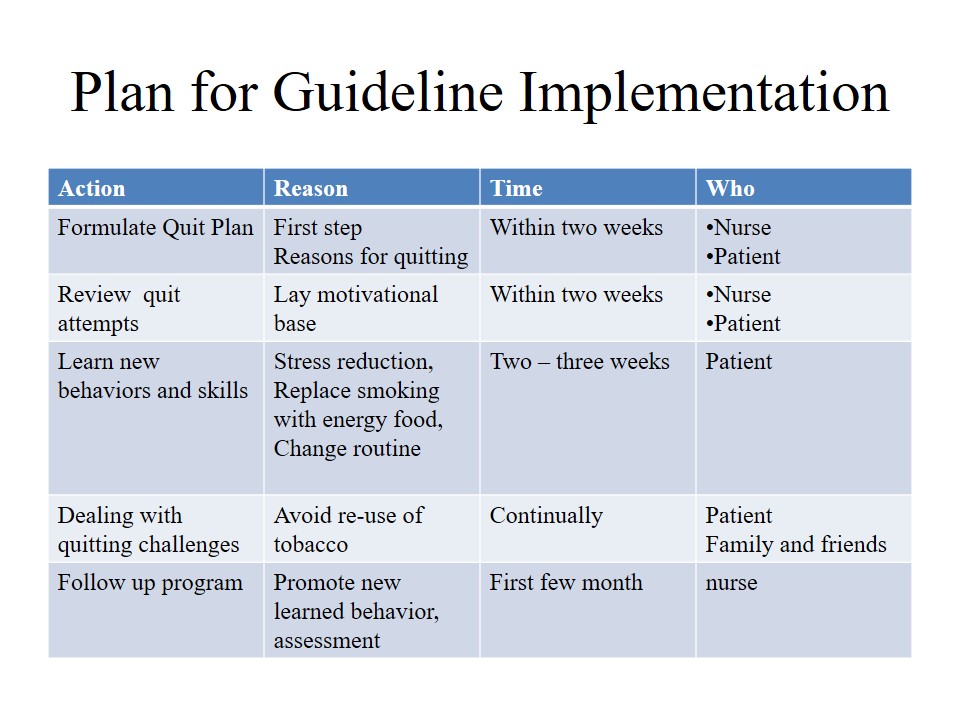
Plan for Guideline Implementation
Cost factors to Implement Change
These cost factors will determine change:
- Individual financial status.
- Family.
- Time .
For any change to be complete, one must incur certain expenses. In implementing a smoking cessation program, there are some cost factors to be considered. These cost factors are the determinants in the successes of the program. They provide funds to keep the program successful. In the smoking cessation program, individual financial status is one of the cost factors to be considered. Smoke cessation can be implemented by an individual or by the help of a doctor. The implementation process requires use of finances. It is up to the individual to ensure that he or she is able to acquire the requirements for the process to be successful. Poor individuals are likely to give up when they are unable to sponsor for their process. In addition, the family status of a client can determine the successes of a smoking cessation program. Rich families are likely to have successful programs compared to poor families. Last, time factor will determine the cost effectiveness of the program. A process that takes a long time is expensive.

Outcomes
Fully implemented program will be characterized by:
- Changed lifestyle.
- Reduction in health threats.
- Fully quit from tobacco use.
- Nurse would explore many opportunities.
The outcome of a smoke cessation program should indicate a positive change in the use of tobacco products. This implies that the user of tobacco should have successfully quitted smoking. Continued use of tobacco indicates negative results. First, the individual lifestyle should change from addiction to a normal life. The client should have the ability to avoid tobacco products. This case should apply even when the client is tempted. The client should demonstrate use by increased use of energy foods. The purpose of energy foods is to help the client maintain a healthy boy after quitting the use of tobacco.
The second outcome is that there should be a reduction in the health threats relating to use of tobacco. Use of tobacco is associated with a number of health threats. The most common is lung cancer. This threat normally reduce when people avoid smoking. Finally, a fully implemented smoking cessation program should be indicated by increase in opportunities to help people quit smoking. The purpose of this program is to implement smoking cessation in the daily nursing practice. Nursing environments, as explained earlier, have numerous opportunities to prevent smoking. The trust the nurses have and the information from the clients put them in a position to explore smoking opportunities (Registered Nurses Association of Ontario, 2007).

Outcome Measurement
- Rating response from family members.
- Provision of more links by the nurse.
- Interview.
- Observation.
Measuring outcomes is essential to understand the performance and effectiveness of the program. Through rating of the responses from the client, it will be easier to tell the successes of the program. Clients should rate the program highly for it to be considered successful. Negative responses will indicate that the program was ineffective and that there is need for improvement. Last, the clients response will be essential to identify areas that require improvement. Through interview, more information will be obtained to understand the effectiveness of the program. Las, observation as a tool will help generate opinion about the program.

Data Collection
Data will be collected by the implementation committee.
The purpose of data collection is to help analyze, and make predictions about the program. Proper data collection should provide the trend in the program. Data should be collected without biasness to help increase the relevance of the predictions. Data will be collected during the measurement of outcomes. Finally, data collected will be kept under tight supervision to enhance confidentiality of the clients personal information.

Summary
In summary:
- Smoking cessation combines a multiple strategies.
- Nurses have more opportunities to implement smoke cessation program.
- smoke cessation has both long and short term benefits.
- Smoke cessation is both nurse and client centered.
Smoking is normally addictive. Stopping an addictive habit is not an easy task. Use of one method to stop smoking is not easy. To stop smoking it is advisable for an expert to implement multiple strategies. For instance, using nicotine replacement method may not be successful because a person willing to stop smoking may not be able to consistently pay for nicotine replacement products. Such people should be provided with alternative methods that they can use when one method fails. This will help reduce the chance of re-smoking habit. Therefore, multiple smoking strategies reduces helps overcome the limitations in one strategy.
As nurses interact with patients on the daily basis they are exposed to an opportunity to meet more smoking people. This is because, in the United States, there is a large number of citizens that smoke. This people may not visit health centers to address there smoking habit, but in the process of seeking help on other habits, they can reveal there smoking behavior. Through nurse-patient relationships, a nurse may take the opportunity to encourage the patient to quit smoking. A nurse may advice the patient on the suitable methods to use. Finally, nurses have basic knowledge, which is required in the implementation of smoking cessation.
Smoking cessation benefits a smoker in different ways, both in long-term and short-term. In short-term, a patient will begin increasing wait, build good relationships, and reduce on cost on personal budget. In the long-run, the patient the country is likely to benefit from the reduction in the cost of preventing smoking. In addition, the country will witness a reduction in death emerging from smoking related diseases.
A suitable smoking cessation program should be nurse and patient centered. The method should give the smoker an opportunity to practically quit smoking. The client should be advised on what to do. In addition, the nurse should work with the patient for better follow-up program. A good client centered program can help the client quit smoking independently without nurse help.

Reflection
To this end, I have learned that evidence should come first before practice. Evidence is essential in drawing conclusions and making predictions. With evidence, a nurse will have confidence when implementing any program.
With the growing empirical world, use of evidence in nursing is also expanding. Empirical studies promote the use of evidence or logic reasoning before approaching a certain decision. Evidence-based practices are easy to justify before making certain decisions. In nursing, nurses are supposed to make decisions that they are sure of because nursing services touches an individuals life. With evidence, it is easy for a nurse to convince a patient. A nurse can explain the reason as to why a particular decision is being made. The predictions made from an evidence-based guideline are reliable and easy to follow. Guidelines provide necessary steps to adhere to when implementing a selected program. When a nurse carefully follows the selected guidelines, there is a reduction in human error and increase in performance. Therefore, evidence should be a first priority in implementing nursing decisions.

References
Baxter, S., Lindsay, B., Louise, B., Emma, E., & Julia, B. (2009). Systematic review of how to stop smoking in pregnancy and following childbirth. Review 1 (R1). Whichinterventions are effective and cost effective in encouraging the establishment of smoke free homes? Review 2 (R2). Factors aiding delivery of effective interventions.Review 3: The health consequences of -pregnant women cutting down as opposed to quitting (R3). Web.
Canadian Lung Association. (2008). How to quit. Web.
Centre for Addiction and Mental Health. (2007). STOP Study helps Ontario smokers “go weedless” – Nicotine replacement therapy dramatically improves quit rate. Web.
Jit, M., Barton, P., Chen, Y. F., Uthman, O., Aveyard, P., & Meads, C. (2009). Evidence review: School-based interventions to prevent the uptake of smoking among children and young people: cost-effectiveness model. West Midlands Health Technology Assessment Collaboration, University of Birmingham.
Pfizer Canada Inc. (2006). How hard is it to quit smoking? Smokers agree that quitting would be one of their greatest accomplishments in life. Web.
Registered Nurses’ Association of Ontario. (2007). Integrating smoking cessation into daily nursing practice (Rev. ed.). Toronto, Ontario, Canada: Author.
Tsoh, J.Y., McClure, J.B., Skaar, K. L., Wetter, D. W., Cinciripini, P.M., Prokhorov, A. V., Friedman, K., & Gritze, E. (1997). Smoking cessation 2: Components of effective intervention. Behavioral Medicine, 23(1), 15-27.