Executive Summary
Australian government’s economic growth has been inconsistent due to many factors, including changing economic cycles globally. This has acted as a call for the government to employ policies that will ensure economic growth while reducing inflation rates and unemployment.
By employing fiscal policies such as decreasing taxation and increasing government spending, the Australian government is in a position to foster savings and consumption in the population. In the end, inflation will be reduced. By increasing government spending on infrastructure, the Australian government will enhance employment opportunities and increase savings and investments in the economy.
The government is also encouraged to use the reserve bank to reduce bank rate percentage as a way of creating more employment opportunities as a lot of money will be available for disposal by the public. If these macroeconomic measures are strictly adhered to, the Australian government will weather global economic shake-ups effectively.
Introduction
Australian government’s economic growth has been inconsistent. The changing economic cycles in the global market are to blame for this. Global financial crisis posed a great risk to the economy. This has also acted as a wakeup call to the policy makers who are looking to apply macroeconomic policies to check this. Macroeconomic policies are essential if an economy is to realize economic growth and contain inflation (Hatch 2010).
The policies are necessary to monitor demand and ensure that the market is stable at any particular time. Policy makers use two types of policies to enhance growth and economic stability; these policies are monetary and fiscal policy. Fiscal policies are contained in the budget reports of government.
They help in checking inflation in the economy while stabilizing the demand side (Levitt & Dubner 2009). Monetary policies on the other hand are policies used by the reserve bank of Australia to monitor the flow of money in the economy. Moreover, the reserve bank of Australia uses this policy to influence the interest rates that will regulate the cost of obtaining money and its availability.
Economic growth and inflation policies
Australian economy has remarkably remained stable despite the teething effects of global financial crisis. The Australian policy makers’ initiative to use sound fiscal and monetary policies has led to a macroeconomic stability. The fiscal policies advanced are government spending, taxation and borrowing. The main reason for this is to balance budget deficit over the trade cycle. In addition, they help in containing inflation figures at 3%.
Australian government to foster economic growth and boost the savings of its entire population is using fiscal policies. Moreover, the policies aim is to eradicate poverty by improving economic growth. The policy has also nurtured and improved trade in the entire country. Disposable income is increased and individuals channel the same to the goods market for products. A part of disposable income is saved while another part is consumed.
Disposable income = Savings + Consumption
Yd = S + C. (Stonecash 2009)
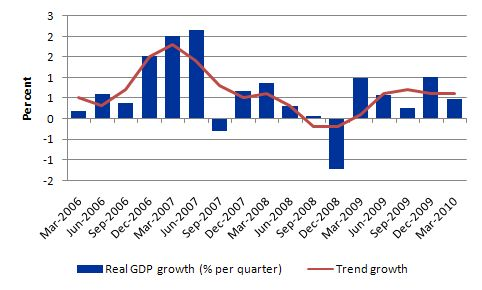
Monetary policy is another macroeconomic policy used to control the amount of money in circulation and improve the economic state of Australia. The policy helps regulate inflation and foster market stability. Inflation is the rapid rise in the prices of goods and services. This result from large amount of money in circulation (Jackson, McIver & McConnell 2008).
The Australian government has enhanced transparency in policy formulation; the initiative has increased investor confidence and level of participation in the macroeconomic environment. The reforms undertaken by the government have largely enhanced economic growth through the stabilization of exchange rates. In addition, structural reforms have enhanced the credibility of the federal bank hence enhancing its functions of containing inflation.
The Australian reserve bank uses monetary instruments to contain inflation figures and improve the state of the economy. The central bank sells treasury bills to mob up excess funds in circulation and stabilizes inflation figures. Market stability is paramount for an economy to be stable and grow.
Market confidence is realized when market prices are not fluctuating. Moreover, the recent improvement of the Australian dollar has fostered market confidence. The stability of the dollar has improved the balance of payment because imports are cheaper and exports fetch a fortune from the international market.
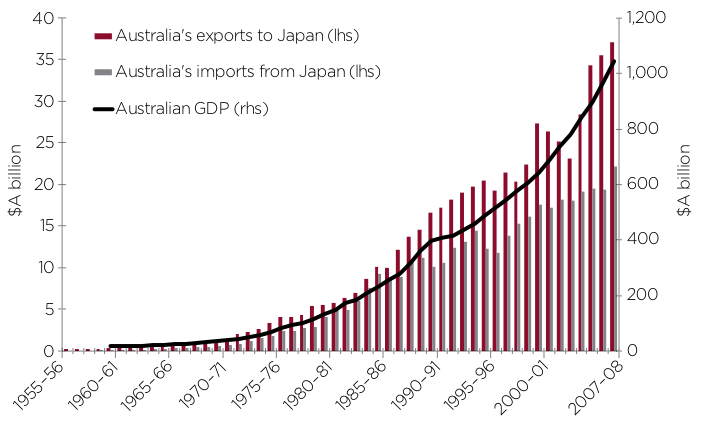
Unemployment polices
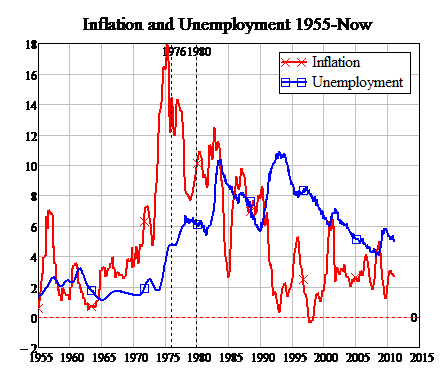
The global economic crisis led to many layoffs in the world, Australia too was largely affected. Unemployment is a situation where individuals who are able and willing to work are locked out of the market because of fewer opportunities. Together with the global crisis, an aging working population is another problem facing Australia government and policy markers.
Most of the elderly individuals have stale ideas and are unable to cope with the rapidly changing world. The recent crisis forced the policy makers go back to the drawing board to devise policies of addressing the issue.
Employment is an ultimate way of taming poverty and the government of Australia has for long used government spending to increase the disposable income of the citizens. The spending by the government has always been on infrastructure. The government has advanced several projects including the broadband network infrastructure lay off to open avenues for employment (Taylor & Moosa 2008).
The primary objective of the Australian government is to implement sound employment policies with a sole aim of achieving full employment. Some monetary policies have been advanced to stimulate the market. When policy makers want to increase employment and amount of funds in circulation, bank rate is used to this effect (Reserve Bank of Australia 2011).
Bank rate is the percentage that a commercial bank earns by depositing with Australia reserve bank. Given the need to create employment opportunities, the reserve bank will reduce the bank rate percentage. This incentive will encourage increased lending by the commercial banks therefore increasing funds required for startups.
In addition, the Australian government has formulated policies to improve the quality of labor and make it competitive. The policies adopted include; better State Strategy and Skills Strategy for South Australia’s Future and better skills, better work. This has produced a clique of employees who are well versed with the global requirements and able to compete globally.
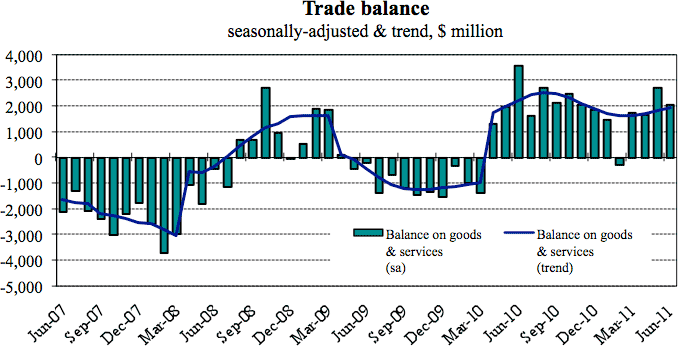
Trade policies
The economic growth and development of Australia largely depends on trade. Australia trade policies have enabled her enhance investment and improve her international standing in terms of trading. The balance of payment has been favorable and this is attributable to increased amount of exports in relation to imports.
In addition, the trading cycle has opened many job opportunities in the economy, relatively bringing down the unemployment rates. Australia policy makers have advanced policies aimed at opening both regional and international markets. The economy is engaging with other countries in regional economic blocs in agitating free markets.
The establishment of foreign affiliates by Australian firms to provide international services to the word has fostered the trade cycle. The profits that increased relatively to stand at $6.5 billion at the end of 2010 boost the economy greatly. These Australian affiliates have been on the rise since 2003.
Trade barriers are major impediments to international trade. The World Trade Organization has been at the forefront in establishing a liberal market for world economies. Australia has been a huge supporter of this initiative and in extension agitating for trade talks with other nations. Agricultural trade has been experiencing fluctuations in the international market, negatively affecting the economic stability of Australia.
The government has marshaled other nations and established a body to focus on how positive results can be obtained in the agricultural sector. The name of the body is Cairns Group. Through Cairns Group, the nations have achieved breakthrough in the agricultural sector. Removal of barriers and increased subsidies are some of the breakthroughs Exports market has improved largely since the establishment of the group, favoring the Australian balance of payment.
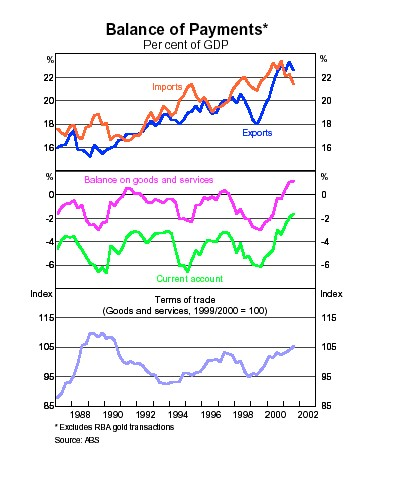
Australia imports have over the years increased the proportion of expenditure spent on them. Most of the imported commodities are luxury goods. The amount has increased from 11 % in 1960 to the recent 17%.This has largely affected economic growth as it is overstretching the funds obtained from exports.
Conclusion and recommendations
Macroeconomic policies are paramount in attracting foreign investors to the economy. They help stabilize not only the market but also the inflation state of the country. It is therefore the responsibility of the government to employ macroeconomic policies to try curb unemployment and soaring inflation rates while fostering economic growth. Use of taxation, by the government, is an effectual measure in the control of the amount of money in circulation.
As such, the Australian government can utilize taxation to increase money in circulation, or reduce taxes to increase money in circulation. The end effect is lowered inflation rates as the overall push and pull factors of demand and supply will lead to a reduction in prices. The Australian government, by using fiscal policies, can enhance employment and thus foster economic growth by spending on infrastructure.
The current efforts on infrastructural development need to be fostered. This would lead to direct and indirect employment and an increase in savings and consumption. By employing monetary policy, the Australian government can foster market stability and monitor inflation effectively. The government should continue offering treasury bills for sale and the reserve bank adopt reduction of the bank rate percentage to increase savings and demand.
Reference List
Edgmand, M. R., Moomaw, R. L. & Olsen, K. W. 2007, Economics and contemporary issues. 7th edn, Thomson, South-Western.
Gittins, R. 2007, Gittonomics. Allen & Unwin, Crows Nest.
Hatch, J. V. 2010, Reading between the lines. Pearson, Frenchs Forest, NSW.
Jackson, J., McIver, R. & McConnell, C. 2008, Economic principles. 2nd edn, McGraw-Hill, Sydney.
Levitt, S. D. & Dubner, S. J. 2006, Freakonomics. Penguin.
Levitt, S. D. & Dubner, S. J. 2009, Super freakonomics. Penguin.
McTaggart, D., Findlay, C. & Parkin, M. 2010, Economics. 6th edn. Pearson, Sydney.
Reserve Bank of Australia. 2011, Monetary policy. Web.
Stonecash, R., Gans, J., King, S. & Mankiw, N. G. 2009, Principles of economics. 4th edn. Thomson.
Taylor, J. B. & Moosa, I. 2008, Economics, 4th edn. John Wiley, Brisbane.