It is important to note that a proper strategic management analysis requires a comprehensive assessment of all critical components of a business entity, which enables a thorough application of strategic models and plans. The prime organization of interest is Microsoft Corporation, which is one of the largest multinational tech companies based in the United States. It mainly specializes in the production and selling of software programs, but its diverse set of products and services additionally include personal computers, consumer electronics, and other technology services, such as electronic market platforms. Microsoft has been a well-established and attributed company for the last decades, and the company has evolved over time, and changes have occurred to its strategies to keep afloat with the current market trends. It is consistently listed as one of the world’s top five companies to work for, and it is one of the big five American IT companies (Kelly, 2022). It is known to be a highly diversified company that produces different products and services for its consumers. Currently, the majority of the computer systems used in a multitude of organizations are mostly produced by the Microsoft Corporation.
Old Vision Statement
Microsoft’s current vision statement is “to help people and businesses throughout the world realize their full potential” (Gregory, 2022, para. 7).
Revised Vision Statement
The revised vision statement is “to be at the forefront of innovation to bring value to our customers, shareholders, and communities.”
Old Mission Statement
In order to comprehensively assess Microsoft’s relationships between its corporate, business, and operational strategies, it is critical to revisit its mission statement. The latter states that the company seeks to “empower every person and every organization on the planet to achieve more” (Microsoft, 2022, para. 1). The mission can be considered rather generic and nonspecific, which is why it would be more useful to tackle each strategic element separately followed by their interconnected dynamics.
Proposed Mission Statement
The proposed mission statement is “to provide innovative solutions to people and businesses.”
The core reasoning behind the proposed mission statement is rooted in the fact that the given industry is heavily focused on competitiveness through innovation. The process of the creation of sophisticated products, such as software and hardware, is highly dependent on human resources and talent. Therefore, innovation needs to be at the core of the vision and mission statement to reflect where and how the value is generated for both the customers and shareholders.
External Factor Evaluation Matrix
The External Factor Evaluation Matrix, or EFEM, is shown in Table 1 below. It reveals that the top priority issues involve talent and human resources since the company’s products and services are heavily centered around innovation. The current state of Microsoft is that it is static with minimal growth, mostly driven by the tight competition from other large competitors. The industry is fully occupied by few large corporate entities, which means there are no threats from new entrants, and even medium size companies are being bought by the giants (Lee, 2022). In such a tight market of technology and software, the leverage is obtained through new and better products and services since other rivals have the same buying and investing power.
Table 1: EFE Matrix
The Competitive
The Competitors
It is important to note that the market of Microsoft Corporation is oligopolistic by nature, and only a handful of big businesses dominate the market. The competition is tight, and each market share requires a significant amount of investment and risk management. There is no risk from new entrants since they are either quickly bought by substantially larger players or driven out of the market.
Although Microsoft offers and sells a highly wide range of products and services, it is stated that “the company’s largest revenue source is its cloud computing business, and it’s the fastest-growing segment of its business model” (Boyd, D. and Boyd, A. 2022, para. 12). The biggest competitors of Microsoft are Google, Apple, Amazon, IBM, and Salesforce (Hughes, 2022). Thus, firstly, the competitive rivalry in the market is intense and significant because the threat is coming from other large and powerful tech organizations with sufficient resources and capabilities to innovate and grow as well. Secondly, for the supplier power, there is no identifiable supplier for the cloud computing business besides microchips and hardware elements, such as China or Taiwan. In other words, the entire industry is impacted by such a force.
Thirdly, the buyer power is about massive primarily due to the presence of equally capable and resource-rich competitors, especially in the cloud computing business, such as Google and Amazon. The threat of substitution is high because innovation is equally valued across all tech giants, and they are constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible. However, the threat of new entry is minimal or non-existent because the industry is practically ‘ruled’ by a few large conglomerates, and new startups become bought before they can even rival Microsoft or its competitors.
Google/Alphabet
Alphabet, the parent company of Google and other companies, is a large multinational corporation. It was founded in 1998, and it is currently headquartered in California, US (Forbes, 2022a). The CEO is Sundar Pichai, and the company employs around 156500 people (Forbes, 2022a). It provides a wide range of IT services and software, among which the most prominent ones are the Google Search engine and G-mail integrated services (Forbes, 2022a). YouTube is another major business owned by Alphabet, which is considered to be the second most visited website after Google itself.
Apple
Apple is the largest tech company in the world, which provides both hardware and software products as well as services. It was founded in 1976 by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne, and it is currently headquartered in California, US (Forbes, 2022b). The CEO of Apple Inc. is Tim Cook, who manages approximately 154000 employees worldwide (Forbes, 2022b). Key competitive products with Microsoft include iOS, phones, market platforms, and computers.
Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM)
Table 2: Competitive Profile Matrix for Microsoft Corporation, Alphabet Inc., and Apple Inc.
Primary Implications from CPM
The CPM can be accessed in Table 2 above, where the analysis reveals that Microsoft holds a strong market position with minor weaknesses and strengths compared to its competitors. For the most part, the performance is equivalent among all three companies as expected since they are resourceful, large, and dominant in what they focus on in the market. Therefore, it provides more justification for increasing innovation.
The Financial Statement
The income statement and balance sheet can be accessed in Tables 3 and 4 below, respectively. Microsoft’s both profitability and asset size have been increasing since 2019, which shows that the company is performing well despite the pandemic. However, the latter can be attributed to the tech industry in general, which was minimally impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic disruptions. In other words, the online nature of the business was a key strength for Microsoft during lockdowns.
Income Statement
Table 3: Income Statement for Microsoft Corporation
Balance Sheet
Table 4: Balance Sheet for Microsoft Corporation
Historical Ratios
The historical ratios for Microsoft Corporation can be accessed in Table 5 below.
Table 5: Historical Ratios: Microsoft Corporation
Internal Factor Evaluation Matrix (IFE Matrix, IFEM)
Table 6: Internal Factor Evaluation Matrix for Microsoft Corporation
The Internal Factor Evaluation Matrix (IFEM) for Microsoft Corporation is shown in Table 6 above.
Strategy Analysis
Strengths-Weaknesses-Opportunities-Threats Matrix (SWOT)
Table 7 below shows the SWOT analysis for Microsoft Corporation.
Table 7: SWOT Analysis for Microsoft Corporation
Boston Consulting Group Matrix (BCG)

Internal-External Matrix (IE)
Internal-External Matrix by product
Table 8: Internal-External Matrix by product for Microsoft Corporation
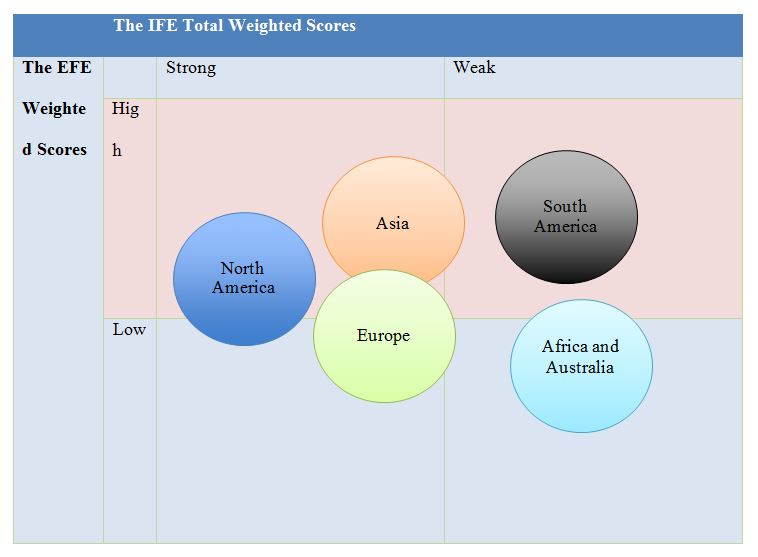
Internal-External Matrix by region
Table 9: Internal-External Matrix by region for Microsoft Corporation
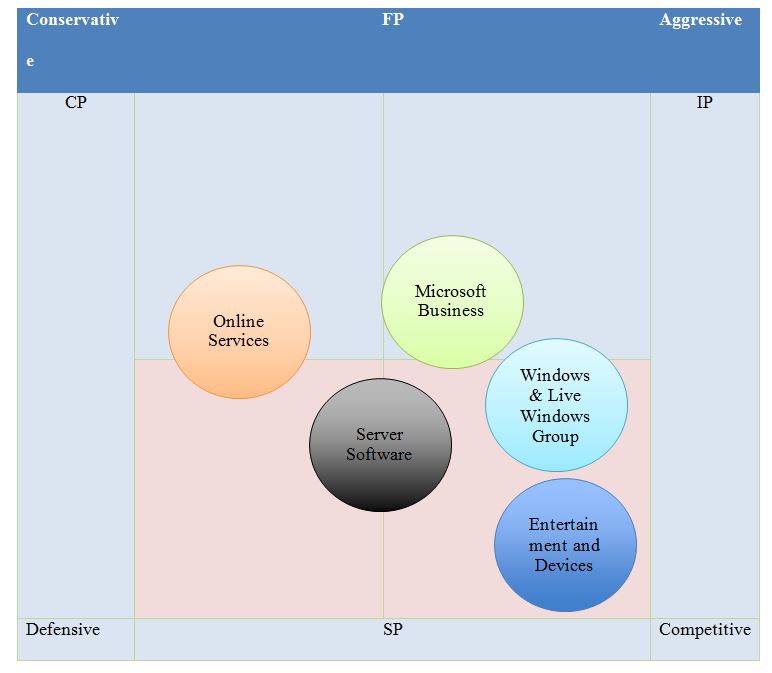
Strategic Position and Action Evaluation Matrix (SPACE)
Table 10: Strategic Position and Action Evaluation Matrix (SPACE) for Microsoft Corporation
Grand Strategy Matrix (GRAND)
Table 11: Grand Strategy Matrix (GRAND) for Microsoft Corporation
Quantitative Strategic Planning Matrix (QSPM)
Table 12: Quantitative Strategic Planning Matrix (QSPM) for Microsoft Corporation
Strategy Conclusion
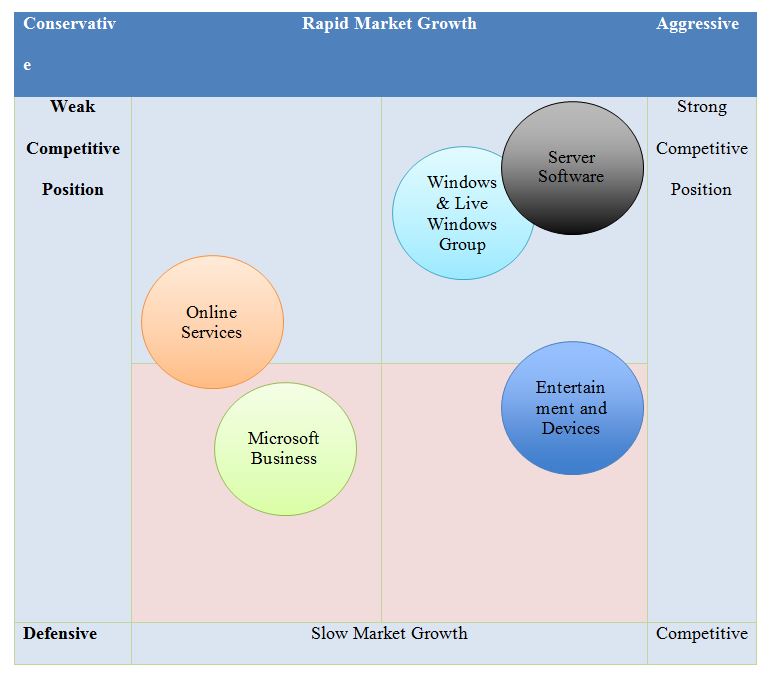
Firstly, the company’s corporate strategy is highly centered around the divisional organization, which is about having five independent divisions. These include “Windows & Live Windows Group, Server Software, Online Services, Microsoft Business, and Entertainment and Devices” (Stony Brook University, 2022, para. 1). In addition, each division has its own sales professionals, research and development, and customer service staff, which means that all employees of a division are located in one area for efficiency, convenience, and cohesion.
Secondly, the business-level strategy of Microsoft is focused on market excellence through expansion driven by innovation. It is stated that “the company’s business strategy is currently focused on three elements – ‘cloud-first, mobile-first, growth through mergers and acquisitions and exploring business opportunities related to AR/VR (Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality)” (Analytics Insight, 2019, para. 11). In other words, it is evident that the corporation is extensively trying to innovate and grow through the latter.
Thirdly, one should be aware that the current operational strategy is about productivity above everything else. The company wants to perfect and improve ten key areas, such as maintenance, scheduling, inventory, supply chain, HR and job design, layout design and strategy, location, capacity and process, quality, and design of goods/services (Smithson, 2017). From the information above, all three level strategies are cohesively interconnected. For example, it can be stated that each department works independently from the other and the department heads. The operations managers are able to make strategic decisions due to the expansion of the company’s products and services. The diversification of the business allows the managers to make broader decisions in lieu of its future growth and to maintain efficiency. Creating products of proper quality is at the forefront of the company’s values since before an item is introduced into the market, it undergoes rigorous testing by trying to acquire feedback from the existing customers. The given principles are deeply reflected and based upon Microsoft’s mission and vision statement.
Recommendations
For such a large company operating in a strong oligopoly market, growth can only be achieved through innovation. The main reason is that there is no financial or resource-based leverage for Microsoft since all of its competitors are as equally rich and capable as the company. The growth is saturated and maximized by all competitors, which is why the expansion is about new and better offerings. In other words, the goal is to defeat the rivals by taking their market shares with better products or services. The first option for Microsoft is to invest in the acquisition of new startups on a massive scale, which will drive innovation and provide a ready-to-use product. The evaluation of this path shows that it will be costly and expensive because other competitors want to buy new startups as well, driving the price higher. The second option for the company is to focus on its talent and human resource management to cultivate innovation within instead of buying it externally. The given alternative is more reliable and not-easy-to-replicate.
The evaluation of options reveals that the second option of driving innovation within is a better recommendation. The accompanying business objective of cultivation of internal innovation and its justification comes from the expensiveness of the first option and support from research. It is stated that innovation is mainly driven by the cultivation of innovative traits among employees of an organization (Poirier et al., 2017). Research shows that “knowledge acquisition positively affects innovation performance and that HRM moderates the relationship between knowledge acquisition and innovation performance” (Papa et al., 2018, p. 589). In other words, the business objective of attracting the best talent in the labor market, accompanied by superior innovation-focus human resource management, can improve innovation. In addition, Microsoft does not need to implement these changes radically because they are just as effective when integrated incrementally (Agostini et al., 2017). Thus, Microsoft’s business goal is growth through innovation, which should be done internally through the cultivation of innovative improvements.
Organizational Structure
Old Organizational Structure
Improved Organizational Structure

The proposed plan is a strategic and organizational one, which is why the key change agents include the top leadership, management, and HRM. The suitable structure for the implementation of the plan is a top-down approach because innovation needs to be encouraged by high-level managers. Since the role of HRM is significant during this organizational shift, the bottom-up framework might not be most suitable due to HR being most influenced by the top management, not employees. In addition, key motivation factors and improvement of hygiene factors can only take place if the management decides to order HRM to do so. Lastly, the framework is plausible because the existing structure requires some restructuring by adding more cohesiveness among divisions to integrate innovation cultivation universally across the entirety of the company.
The implementation plan needs to occur in three phases in accordance with Kurt Lewin’s model of organizational change. It states that change occurs in three stages, which include unfreezing, change, and freezing (Whatfix, 2022). Microsoft needs to address its current talent before proceeding to new talent, which needs to be followed by improvements in organizational cohesiveness (O’Donovan, 2022). Firstly, the company needs to slowly unfreeze its existing frameworks, during which the management can shift its focus from startup acquisitions to internal cultivation of innovation. Secondly, the second half of the unfreeze stage needs to improve hygiene factors relevant to employees and enhance motivators. Thirdly, during the change stage, the company needs to ensure the restructuring of its organization to become more cohesive and uniform to ensure that changes are integrated properly throughout the entire company (David & David, 2017). Fourthly, the most important part is solidifying the changes in the freezing stage, which requires top management’s constant enforcement of the measures until they become the new norm.
The dependency of the plan on top management and their authority over HRM makes the top-down approach essential. It is stated that the key advantages of such a structure are faster implementation, clearer communication, and widespread familiarity with what is taking place (Asana, 2021). In the case of the plan implementation, Microsoft’s leadership needs to show proactivity and reciprocity about the proposed organizational change. It is clear that culture and leadership play a significant role in facilitating implementation at the company (Bovée & Thill, 2007). In other words, the top-down approach is to be utilized to ensure the effectiveness and efficiency of the plan.
Moreover, when it comes to informing and prompting the leaders to undertake such an endeavor, the strategy might include these elements since they need to be properly adjusted and positively tuned for change. Since the latter statements mean that if the leaders and managers are supportive of the proposed measures for improvements, the culture can be sufficiently primed for the continuous increase in innovation. Any form of implementation and integration plan needs to be properly designed in accordance with organizational needs and specificities. The implementation design for the proposed strategic plan is to be calculated, precise, and quantitative (Norton & Wiburg, 1998). The underlying reason is that the comparison mandates precise measurements, and then these can be conducted through innovation to increase values and talent productivity.
The high research and development (R&D) rate is an external technological element that signifies a rapid technological improvement in the mass media and entertainment sectors. In the context of the tech environment, the technological development represents a danger that intensifies competitiveness. Nonetheless, the same distant or macro-environmental aspect presents a chance for Microsoft to expand by deliberately boosting its R&D pace to meet or surpass that of competitors. Additionally, the growing popularity of augmented reality presents a potential for the firm to improve its performance.
Perceptual Map
Table 13: Perceptual Map for Microsoft Corporation
EPS/EBIT Analysis
Table 14: EPS/EBIT Analysis for Microsoft Corporation
Company Valuation
Table 15: Company Valuation for Microsoft Corporation
The Projected Financial Statements
Projected Income Statement
Table 16: Projected Income Statement for Microsoft Corporation
Projected Balance Sheet
Table 17: Projected Balance Sheet for Microsoft Corporation
Executive Summary
In conclusion, Microsoft’s competitive advantage in its saturated oligopoly market depends on innovation. The latter can be bought externally, such as startups, or cultivated internally. Buying new startups is expensive because competitors have the resources to drive the prices up. Cultivating innovation from within is more sustainable and hard to replicate, but it requires changes in hygiene factors, motivator factors, and organizational cohesiveness. The plan needs to be implemented in a top-down approach in three of Kurt Lewin’s stages across a two-year period. The majority of internal and external factors indicate the prevalence of opportunities for developing a larger customer base. The development in these areas will allow the company to increase all of its product lines. On the basis of the analysis provided above, the company’s strategic options include the following:
- Microsoft should revise its human resource management in accordance with its core objectives by attracting talent with less political agenda.
- Microsoft should work on its employee retention methods since the existing workforce is not stable or loyal.
- Microsoft should gradually proceed with its differentiation strategy by ensuring that each new product is launched and sustained to maximize its long-term performance.
- Microsoft should continue using its industry leadership to penetrate the markets of its competitors to capture some of its market shares.
References
Agostini, L., Nosella, A., & Filippini, R. (2017). Does intellectual capital allow improving innovation performance? A quantitative analysis in the SME context.Journal of Intellectual Capital, 18(2), 400-418. Web.
Analytics Insight. (2019). Unveiling business strategy: Microsoft. Web.
Asana, T. (2021). Top-down approach vs. bottom-up approach: what’s the difference? Web.
Bovée, C., & Thill, J. (2007). Business communication essentials (4th ed.). Pearson Prentice Hall.
Boyd, D., & Boyd, A. (2022). How does Microsoft make money? Finty. Web.
David, F. R., & David, F. R. (2017). Strategic management concepts and cases (16th ed.). Pearson Prentice Hall.
Forbes. (2022a). Alphabet. Web.
Forbes. (2022b). Apple. Web.
Gregory, L. (2022). Microsoft’s mission statement & vision statement.Panmore Institute. Web.
Hughes, J. (2022). Microsoft competitors analysis: top 5 competitors.Business Chronicler. Web.
Kelly, J. (2022). Massive Microsoft survey of 31,000 people to vibe check the workplace shows a mismatch between managers and employees. Forbes. Web.
Lee, J. (2022). U.K. warns Activision merger gives Microsoft ‘unparalleled advantage’. The Washington Post. Web.
Microsoft Corporation. (2022). Annual Report 2021. Web.
Microsoft. (2022). Our mission. Web.
Norton, P., & Wiburg, K. M. (1998). Teaching with technology. Harcourt Brace College Publishers.
O’Donovan, C. (2022). Microsoft tries collaborating with unions to avoid ‘public disputes’. The Washington Post. Web.
Papa, A., Dezi, L., Gregori, G. L., Mueller, J., & Miglietta, N. (2018). Improving innovation performance through knowledge acquisition: The moderating role of employee retention and human resource management practices.Journal of Knowledge Management, 24(3), 589-605. Web.
Poirier, V., Schwartz, L. H., Eddy, D., Berman, R., Chacour, S., Wynne, J. J., Cavanaugh, W., Martin, D. F., Byrne, R., & Sanberg, P. R. (2017). Thoughts on improving innovation: What are the characteristics of innovation and how do we cultivate them?Technology & Innovation, 18(4), 319-330. Web.
Smithson, N. (2017). Microsoft Corporation’s operations management, 10 decisions, productivity.Panmore Institute. Web.
Stony Brook University. (2022). Corporate and business level strategy. Web.
Whatfix. (2022). Lewin’s 3-stage model of change theory: Overview. Web.