Introduction
The railway is a significant means of transportation of both people and freight for such a growing country as Qatar. Although Qatar railway was established in 2011, it already implements some projects, which, after their completion, will constitute the railway network of the State of Qatar. Currently, there are three major projects such as the Doha Metro, the Lusail Tram, and the Long Distance Rail.
It is expected that the new network will unite all railway in Qatar and connect the country to the neighbouring states, thus contributing to the development of an integrated railway system in the region. However, in addition to comfort and reliability for passengers and businesses that will use the railway for transportation of goods, the major concern of Qatar Railway is safety on the whole and in emergency situations in particular. Thus, there is a need for the Railway Disaster Management Plan that will outline the algorithm of actions in case of emergency.
This Railway Disaster Management Plan has been created on behalf of all of the relevant responding agencies in Qatar. It has been written with the following risks in mind. Firstly, the railway system in Qatar is just developing. Consequently, the emergency services of the country do not have much experience in reacting to disasters on railroads. Secondly, a great part of Qatar railways is built underground and make a metro system. Despite the fact that this approach allows relieving roads due to the fact that many people prefer underground transport to avoid getting stuck in heavy traffic, underground stations and tunnels are the places of increased risk in case of emergency due to the lack of access to them. Thirdly, the risk of railway disasters in Qatar is mainly related to natural triggers.
Thus, the major hazards in Qatar are natural such as droughts, tsunamis and earthquakes. Cyclones and floods are rare, but in case of occurrence can also lead to an emergency situation on the railway. In fact, there are three major types of disasters that threaten railway safety. They are natural accidents (such as floods, earthquakes, cyclones, tsunami or landslides), those related to train accidents (for example, train marooned, collision, tunnel collapse, fire or explosion on the train, etc.), and man-made disasters, such as terrorist attacks or sabotage.
On the whole, emergency planning demands consideration of all factors such as the natural environment, societal factors, government and political factors, legal, technological as well as commercial factors. This approach allows evaluating the impact of hazards that can lead to emergency situations and are related to natural conditions (location of the country, its geography and weather), societal factors (including demographics, history, attitude to risk, and man-made environment), the impact of politics and government actions (national policies, priorities of local governments, activity of committees and agencies), and other issues.
Risks
- Lack of experience in managing railway disasters because the system itself is new
- Lack of training among emergency services
- Little awareness of the importance of the problem of railway disaster planning
- Diversity of projects that comprise the Qatar Railway system (metro, tram, and long-distance railway)
- The presence of tunnels in the railway network can become an obstacle for help delivery and rescue interventions in case of emergency.
- Natural risk factors of disasters that cannot always be foreseen and prevented
- Human factors, which frequently result in panic in case of a disaster
Problems
- The railway system in the stage of development, which does not allow the creation of a complete plan of action in case of emergency. However, the problem is likely to be eliminated after 2030 when the construction of the railway network is finished.
- Rail accidents are caused by a diversity of factors, and it is important to consider all of them because they can impact the algorithm of emergency actions. Thus, railway accidents are the result of drivers’ errors, signalmen’s errors, failure of rolling stock, failure of civil engineering, acts of other people, and natural factors.
- A certain part of Qatar railways is underground or in tunnels, which limits access to locations in case of a disaster. Therefore, rail infrastructure has to be planned in a way to provide enough access to every object and perform the necessary rescue measures.
Documents
The following documents have been consulted in the creation process of this plan:
- Towards Developing a National Disaster Risk Reduction and Recovery Plan for the State of Qatar. Draft Report. 7-10 March 2016.
- Railroad Emergency Preparedness Guide. Dangerous Goods Awareness Level.
- Disaster Management Plan Western Railway (ISO 9001-2008 Certified).
Aim Of the Plan
The aim of this plan is to develop steps that will serve as guidance for actions in case of emergency as a result of disaster on the railway. The clearly stated algorithm is expected to increase the efficiency of disaster management and reduce the risks related to the disaster. Moreover, a disaster management plan is aimed to help in mitigating the negative consequences of accidents on the railway.
Objectives of the Plan
The objectives of the plan are as follows:
- To identify the authorities responsible for plan activation
- To observe trigger points for plan activation
- To determine the roles and responsibilities of organisation involved in railway disaster management.
- To form management groups responsible for plan development and implementation.
- To identify control points.
- To provide maps or site plans of railway network objects that are already functioning or are being constructed.
- To develop action checklists
- To include aide-memoires for further guidance
- To present interventions for training and testing
- To plan to audit, review, and monitoring of railway disaster management
Scope of the Plan
The scope of the plan is as follows. The plan is focused on railway disaster management and its peculiarities. At the same time, it does not specify actions depending on the type of disaster. Still, the plan does not include other disasters that are not related to the railway in Qatar.
Authority to Activate the Plan
The activation of the Railway Disaster Management Plan involves certain authorities.
The person(s) with authority to activate this plan is as follows
The major authority responsible for activating Railway Disaster Management Plan is the Safety Directorate of Qatar Rail. The Directorate prepares the plan and makes the necessary changes during its discussion and implementation.
The persons with whom they must consult before activating the plan are
It is important to consult with the Board of Directors of Qatar Rail to discuss both financial and safety issues of the plan.
The persons with whom they may consult before activating the plan are
It is also possible to consult or involve in plan development such directorates as civil engineering, finance, electrical and security, and others. This complex multi-team approach will allow developing a functional plan that is likely to be effective for managing disasters in conditions of the Qatar railway network. People involved in plan discussion are the advisor safety board, general manager, chief safety officer, and safety officers of divisions responsible for every project of Qatar rail.
Trigger Points
The trigger points for activating this plan are:
- There is a risk of disaster according to forecasts (for example, flood is expected because of heavy rains in the area)
- Emergency service agencies issue an emergency warning
- Warning about a disaster in the area near the railway
- Accident on railway
Notification of Plan Activation
Notification of plan activation should be issued timely but not earlier than the plan is ready to be implemented. It should be preceded by plan discussions and evaluation of the possible risks as well as ways of their mitigation. Notification of plan activation should be distributed among all of the stakeholders, starting from the Board of Directors to workers on construction objects. Also, it is possible to place this notification on the Qatar Rail website or involve other media such as radio and television.
Roles and Responsibilities
A disaster management plan involves certain organizations, each of which has distinct roles and responsibilities. The effective cooperation of these organizations contributes to the more successful management of disasters on the railway. For Railway Disaster Management Plan, the following organizations are important.
Organization 1
General Directorate of Civil Defence, which is the new name of the Civil Defence Department, is one of the authorities responsible for internal security.
The Directorate develops and implements the rules of civil defence that should be used as guidance by other departments and organizations. Also, it follows the necessary procedures in case of a disaster occurs. Among other significant functions, the General Directorate of Civil Defence carries out the training of civil defence members.
Organisation 2
Land Transport Planning Department is responsible for general planning and design as well as planning the construction of railway transport network. The plans should follow the existing safety requirements and be precise. It is important to consider peculiarities of land and the existing infrastructure during the planning of railway construction to provide adequate access to all the objects in case of emergency (Ministry of Transport and Communication 2018, 5).
Organisation 3
Land Transport Licensing Department is involved in legislation and regulations related to transport on the whole and railway transport in particular. It is also responsible for the development of rules for railway transport services and providers. The department is expected to check and control transport compliance with the existing specifications, which is likely to decrease the incidence of accidents on the railway.
Organisation 4
The responsibility of the Land Transport Quality Performance Department is to set and develop technical performance standards and monitor their performance (Ministry of Transport and Communications 2018, 7). Also, the Department is expected to check quality standards and ensure the safety of transportation. Interventions of this department are aimed at reduction of transport disasters related to the quality of technical equipment of railway transport and safety of the provided services.
Organisation 5
Qatar Rail is the organization that provides railway service in the country. Its responsibility is to deliver rail transportation service to population and organizations throughout the country and follow its development plan on the extension of the railway network. One of the primary roles of this organization is the delivery of service safe for both customers and the environment.
Organisation 6
Qatar Meteorology Department is responsible for weather monitoring to predict natural events such as weather changes that can lead to a disaster on the railway. Also, this department provides seismic observation, thus assessing the risk of an earthquake, which allows developing safety measures when disaster is inevitable.
Organisation 7
Fire Protection Department is responsible for quick reaction to disasters that involve fires. It is expected to provide the necessary measures to reduce the negative impact of fire on individuals, equipment, constructions, and the environment.
Management Groups
Management groups involved in Railway Disaster Management Plan development and activation are as follows.
- Planning group.
- Risk assessment group.
- Plan activation group.
- Emergency management group.
- Coordination group.
- Recovery group.
- Assessment and audit group.
Control Points
Control should be provided at every step of disaster management. The key control points are those during the response, recovery, and mitigation of disastrous consequences. During the response stage, it is important to control the identified risks and react in case one or more of them are likely to influence the current situation. In case of disaster threat, the control should be provided over activation of Disaster Management Plan.
During the recovery stage, it is necessary to control the coverage of recovery interventions to provide adequate assistance to human victims and technical support to restore the functions of the equipment. Also, it is vital to control the recovery of the environment in the area of disaster in case it was affected. As for the mitigation stage, control points include short-term, medium-term, and long-term consequences that should be mitigated. Finally, the control points are the evaluation of plan effectiveness and its audit with the following alterations if inefficiencies are identified.
Resources
To provide effective management of disaster, it is important to identify the available resources that can be used during the implementation of the management plan. The resources necessary for successful plan implementation include equipment, personnel who operates this equipment or have special training to respond in case of emergency, and environment officers, who will be responsible for environmental regulations. Resources will differ depending on the type of disaster. Thus, in case of flood, boats will be necessary to evacuate the people while in case of an accident on the railway in mountains helicopters will be needed. In case it was identified that there are not enough resources to implement a disaster management plan, there is a need to find the necessary amount or volume to provide effective work.
Maps and Site Plans
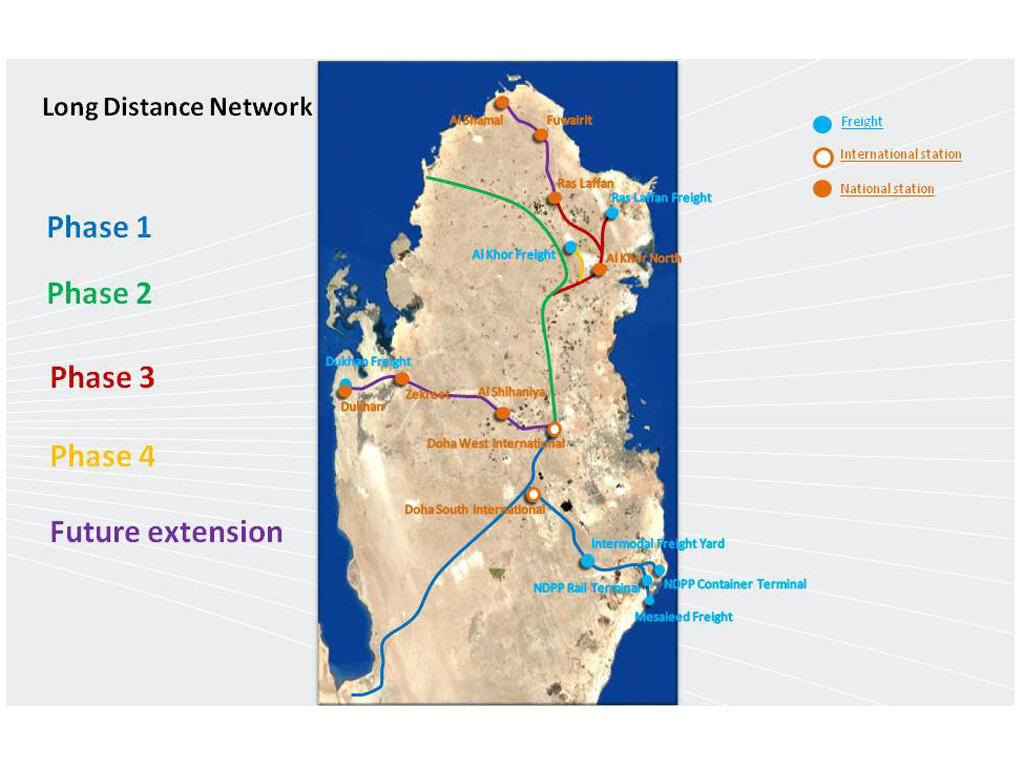
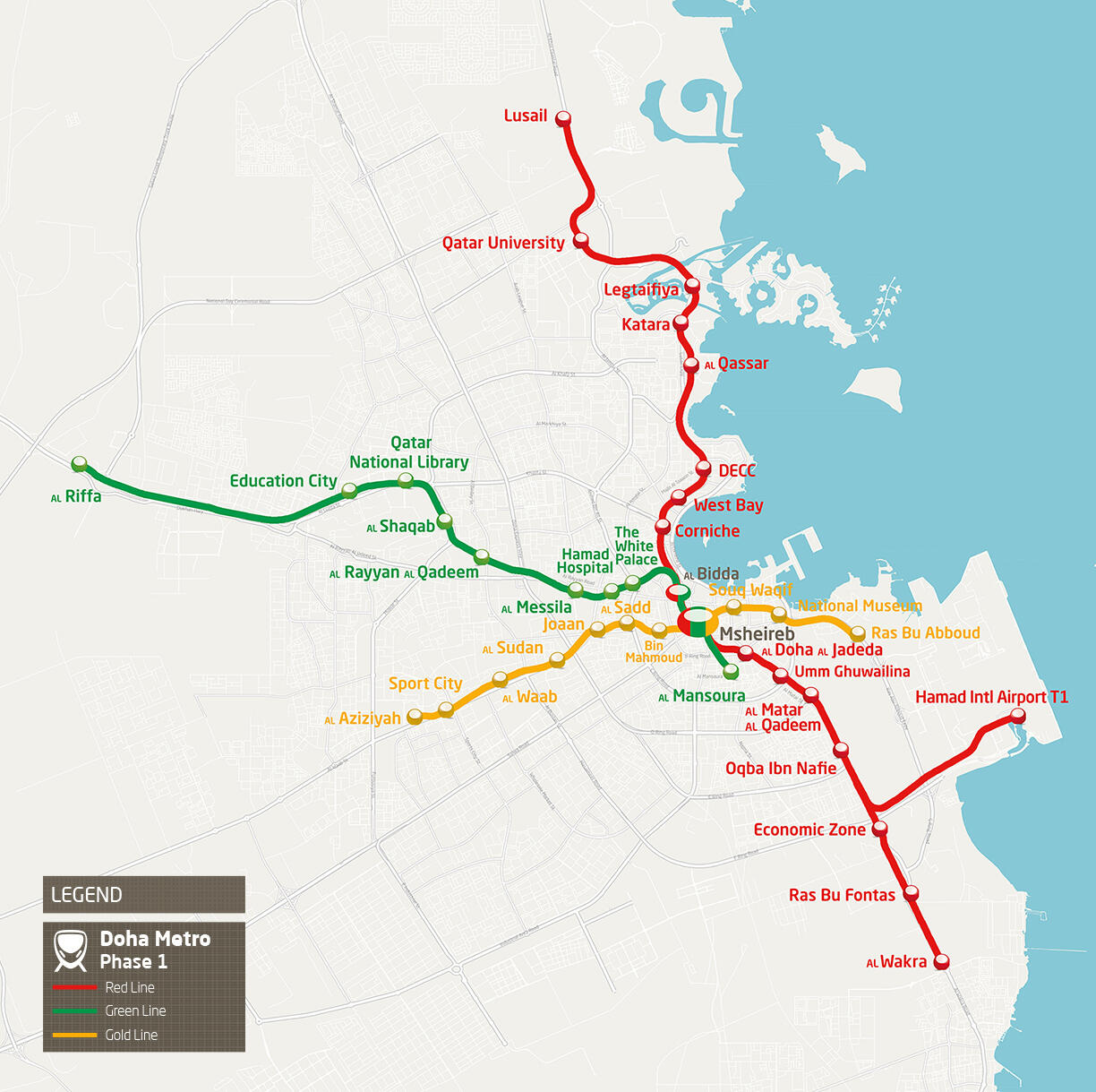


Action Checklists
- Plan initiation checklist:
- Notification of senior management about disaster or its possibility;
- Setting up a disaster recovery team;
- The division into working groups;
- Determination of responsibilities;
- Determination of disaster degree;
- Contact all stakeholders.
- Follow-up checklist:
- Check teams and their specific tasks;
- Implementation of recovery plan;
- Progress monitoring;
- Transportation organization;
- Creation of personnel lists with contact details;
- Organization of effective communication among teams;
- Establishment of the necessary supplies;
- Equipment delivery to the disaster location;
- Involvement of environment services;
- Notification of insurance companies;
- Audit the plan implementation;
- Evaluation of plan effectiveness.
Aide-Memoires
Pre-implementation considerations
- The plan is carefully developed and includes all the necessary parts.
- Major stakeholders are involved.
- The plan is ready to be implemented.
Team roles and staffing
- Teams are identified.
- Basic roles are determined.
- Teams include professional and specially-trained staff.
Implementation considerations
- Plan corresponds to the needs of a disaster management situation.
- The plan allows responding then major stages of disaster management.
Documentation
- Documentation is created according to the existing accepted forms.
Communication
- Communication is organized and effective.
Post-implementation considerations
- The plan addresses disaster consequences.
- Plan audit is conducted to assess its effectiveness.
Stand Down and Debrief Arrangements
Stand down and debrief arrangements should be followed to provide effective functioning of personnel and avoid burnout. Thus, shift debriefing is not suitable for disaster situations and post-incident or post-response debrief should be applied. It means that debriefing will be conducted after the emergency response is over. Still, in case the management of disaster on railway takes time longer than personnel shift, debriefing is provided when it is necessary to guarantee effective teamwork. Drawbacks in stand down and debrief organisation can lead to lower efficiency of disaster management interventions due to the high intensity of work.
Recovery
Recovery is the stage that follows a disastrous event. Recovery is vital for the further functioning of the railway and the safety of the territory where the disaster happened. Consequently, it has to be coordinated with response actions and other planning. Recovery involves both that of individuals who suffered in the accident and the environment of the disaster location. Disaster recovery can be conducted according to the crisis management plan, which is a part of the Railway Disaster Management Plan. Successful recovery can be provided in some phases. Phase I includes defining the victims and evaluating the degree of damage to people, constructions, equipment, and the environment.
Phase II is aimed at the restoration of the basic functions of all the objects involved in the disaster. It means that people should be hospitalized for further examination and treatment, constructions should be secured to avoid further destruction, equipment should be transported to service stations, and actions should be taken to secure the environment if it was also affected. Phase III presupposes restoration of railway functioning with further monitoring of possible delayed consequences of the disaster.
Training & Testing
Training and testing are vital in disaster management planning because it is likely to increase awareness of the involved individuals with the importance of timely and planned interventions that can limit the negative consequences of disasters on the railway. Training is usually organized with the use of drills and exercise that are aimed at the formation of a definite algorithm of actions to be applied in case of emergency. Testing is necessary to check the effectiveness of training and evaluate the readiness of individuals to act appropriately in conditions of disaster.
Training interventions can be general and specialized for every department involved in Disaster Management Plan implementation. Thus, general training prepares to respond to diverse railway accidents, including derailments, spills, or incidents involving hazardous materials. This type of training can be provided in communities around railway centres to prepare citizens to act in case of emergency and provide them with knowledge about self-protection as well as mitigation of negative consequences of disaster for the community.
Specialized training is aimed at preparing professionals working in diverse divisions and departments to respond to an emergency situation on the railway. Training can be provided in classrooms where the theoretical background is taught and in real-life conditions with the use of training trailers, training tank car, or simulations.
Auditing, Reviewing & Monitoring
Auditing as well as reviewing and monitoring of Plan implementation are vital because they allow revealing the existing drawbacks of the plan and, as a result, their elimination, which contributes to planning effectiveness. The major goal of Disaster Management Plan auditing is to identify if it addresses the preparedness in handling a disaster. The audit can be provided through examination of Qatar Rail Board records that contain data about action in case of disasters. Audit can be conducted within the whole railway or one of its divisions. Also, it can be provided by a multi-disciplinary team from an outside organization or a team formed from representatives of company divisions.
If auditing reveals the lack of preparedness to face disasters, there is a need for reviewing the plan. After auditing defines the drawbacks of the plan, changes in these areas are suggested, and the plan is changed. After that, the implementation continues under careful monitoring. Monitoring is necessary to provide data for future auditing to increase the effectiveness of the Railway Disaster Management Plan for the State of Qatar.
Appendices
Appendix A
Qatar Rail Long Distance Passenger & Freight Rail network.
References
Doha Metro 2018. Web.
Ministry of Transport and Communications 2018, Organizational structure. Web.
Qatar Rail restarts civil works tendering 2015. Web.
Profiles. Qatar rail 2016. Web.