Introduction
Modern technologies are making it easier for business organizations to achieve their potential. Business leaders should be aware of emerging innovations and utilize them effectively to meet their customers’ needs. This paper examines the relevance of technology in fast food industry.
New Technology
The field of technology is diverse and it encompasses a wide range of areas, such as computers, smartphones, social media networks, and advanced cooking systems. Domino’s is one of the American franchises operating in the United Kingdom. This franchise has acquired and implemented emerging technologies that can streamline operations. The identified one is that of robotics. Domino’s is presently using artificial intelligence to provide virtual robots that can communicate with customers (Thornhill, 2019). This technology is founded on the concepts of voice recognition and machine learning. This innovation continues to entertain customers while at the same time tracking the nature of service delivery. The use of drones is also ensuring that more customers receive their orders in a timely manner.
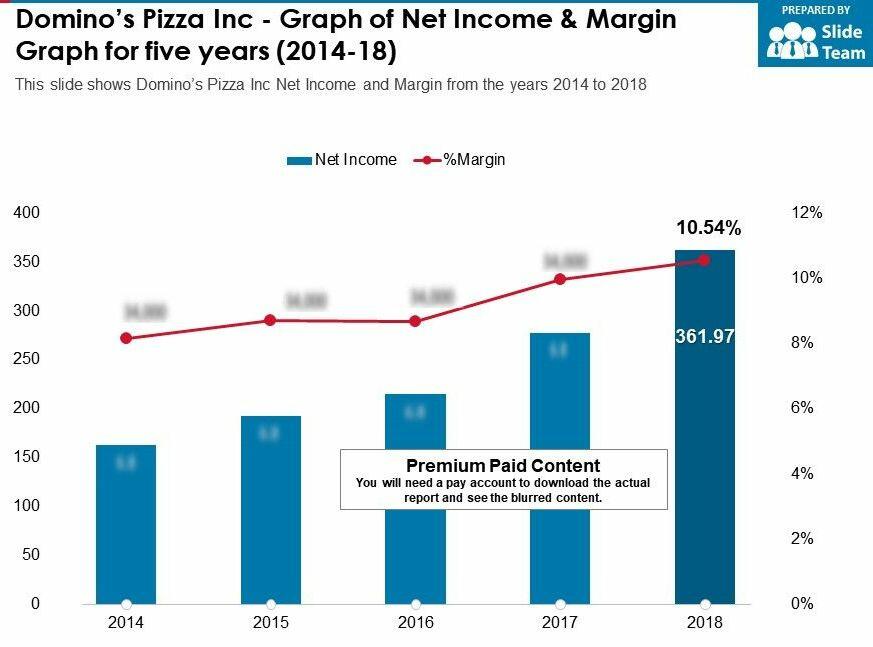
The adoption of this innovation has reduced this company’s operational cost. It has streamlined the acquisition of various supplies while at the same time serving more customers (Walker, 2019). Consequently, it has managed to reduce the prices for its products (see Figure 1). This is a clear indication that the adoption of this kind of technology is influencing this company’s performance positively. It has made timely production, service improvement, and cost decisions. Such attributes will continue to make it more profitable in the UK market.
Smartphone Apps
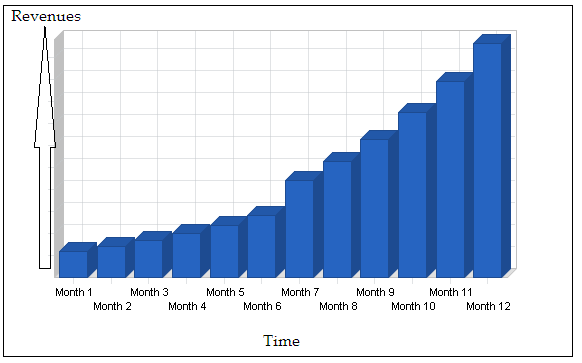
Firms and franchises operating in the fast food industry can use apps to improve performance and meet their customers’ demands. The use of this innovation is capable of allowing individuals or users to place orders before they can arrive at the store (Begg & Ward, 2016). A good example is geo-fencing location technology whereby individuals will ensure that their products are ready before they can arrive at the outlet (Avant, 2017). Any franchise firm that embraces this technological app will attract more clients, meet their needs, and record increased revenues. The level of customer satisfaction will increase and eventually maximize performance (see Figure 2).
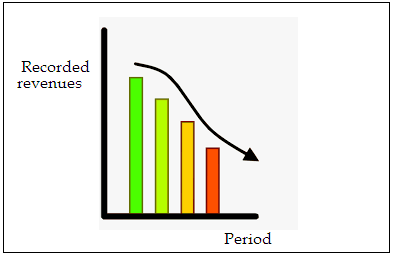
Similarly, a local or individually owned shop that fails to embrace the power of this technology will record a negative growth pattern. Chances are high that emerging firms in the fast food sector that focus on such innovations will attract more customers (Walker, 2019). This is the case since many people prefer business models that provide convenience, timely support, improved service delivery, maximized user experience. The use of smartphone apps will deliver these key opportunities. A locally-owned shop that ignores the power of emerging technologies will record reduced revenues (See Figure 3).
Benefits of Smartphone Apps
The use of modern smartphones and apps is an emerging trend that will continue to dictate the performance of business organizations. Thornhill (2019) reveals that such innovations can guide firms to acquire and keep timely data. By monitoring the collected information, managers can monitor the purchasing behaviors of the targeted customers and introduce new approaches to improve their experiences. They can also monitor emerging trends or demographics to support business performance. Organizational leaders can focus on the acquired data to learn more about the spending habits.
This knowledge can inform a superior model for transforming performance and service delivery (Ferguson, 2002). The issue of price discrimination has emerged as a critical concern for both customers and businesspeople. With the acquired data, it can be possible to get a clear picture of consumer behaviors and ensure that standardized prices are applied (Sloman & Jones, 2017). Additionally, businesses can consider the data acquired through such apps to offer additional products or items to specific customers who appreciate them or are willing to spend more money. These initiatives will eventually improve the level of business profitability.
Implications
Technology remains one of the facilitators for improved business performance. The above descriptions support the adoption and implementation of emerging innovations in different sectors, including the fast food industry. These changes revolving around the use of smartphone-based apps will support the creation and establishment of more locally, individually-owned shops in the future. Such an approach is a new opportunity for attracting more customers, delivering high-quality services, and improving performance continuously (Bounds, 2018).
More small firms operating in this sector will be able to compete with giant ones by focusing on their customers’ emerging needs and addressing them using evidence-based initiatives. They will level the playing ground by providing superior fast foods products and delivering them to the targeted clients using drones. They will also utilize social media platforms and other emerging technologies to transform their marketing approaches.
Conclusion
The above discussion has supported the adoption of emerging technologies to improve service delivery in the fast food industry. Companies that consider these developments will become more competitive while those ignore such innovations will have higher chances of becoming obsolete. The future will be bright for small enterprises since they will acquire such innovations and compete successfully with established ones.
References
Avant, M. (2017). 5 technology trends to know. QSR Magazine. Web.
Begg, D., & Ward, D. (2016). Economics for business (5th ed.). Maidenhead, UK: McGraw-Hill Education.
Bounds, A. (2018). UK digital technology sector outpacing wider economy. Financial Times. Web.
Dominos Pizza Inc graph of net income and margin graph for five years 2014-18. (n.d.). Slide Team. Web.
Ferguson, K. (2002). Essentials of economics. New York, NY: Palgrave.
Sloman, J., & Jones, E. (2017). Essential economics for business (5th ed.). London, UK: Pearson Education Ltd.
Thornhill, J. (2019). The food industry is due another revolution. Financial Times. Web.
Walker, J. (2019). Fast food robots, kiosks, and AI use cases from 6 restaurant chain giants. Emerj. Web.