Executive Summary
This report is an outcome-based evaluation plan for a public health program designed to help drugs and substance abuse patients to recover from chemical addictions. The John Muir Health Facility designed and implemented the program, which is domiciled within the hospital’s Addiction Medicine Recovery department. The aim of this evaluation plan is to establish the effectiveness of the program in addressing patients’ behavioral and attitudinal issues affecting their commitment to sobriety.
Using a mixed method framework that integrates qualitative and quantitative aspects of the evaluation, interview findings and secondary research data will be the main sources of information. Data obtained will be useful in improving the efficacy of public health interventions aimed at helping victims of drugs and substance abuse to maintain their commitment to sobriety. Consequently, policymakers who have a duty to create a conducive environment for the implementation of public health programs will find such information to be useful in their decision-making processes.
Introduction
This project evaluation plan is based on the addiction medicine recovery services at John Muir Health. The plan is in five key sections: stakeholder engagement, description of the program, evaluation design, processes of gathering evidence, use and dissemination of lessons learned, reflections on standards of good evaluation and justification of conclusions.
Engagement of Stakeholders
Stakeholder engagement is an important attribute of community health planning because it allows coordinators to gain a holistic understanding of all issues involved in a health program. Patients, community health volunteers, government health agencies and the host community are key stakeholders involved in the John Muir Health program. Public health volunteers/workers and government health agencies are directly involved in the program because of their involvement in service delivery, while patients and the host community are direct benefactors. Government agencies and public health workers are primary users of the evaluation findings because they can use it to make better and more effective health promotion plans.
Subject to the aforementioned issues, there is a need to respect all human actors involved in stakeholder management. To this end, permission to interview participants will be sought from the Institutional Review Board. Additional approval will be obtained from the John Muir Health Institutional Review Board to interrogate their program data. No conflict of interest emerges in this evaluation plan because the process is based on an independent analysis of all factors affecting the outcomes of the John Muir Health program. Cultural competency issues will be addressed by including local community members in the evaluation design and implementation phases. Their input will be instrumental in ensuring that all activities align with community norms and customs.
Description of the Program
Statement of Need
Drugs and substance abuse is a public health concern in California and the US. State data from California show that, in 2017 alone, more than 19 million Americans battled some form of drug abuse (Thomas, 2020). Alcohol abuse is one of the most common forms of substance abuse in the US because approximately 74% of people who reported to have suffered from substance abuse also suffered from alcohol disorder. In the state of California, about 11.32% of adults suffer from drugs and substance abuse. The John Muir Health program aims to reduce the incidence of drugs and substance abuse by providing social support services to people who need psychiatric help and mental health assistance to overcome their addictions.
Unlike national statistics, which suggest that alcohol abuse is one of the most common forms of disorders, marijuana use is one of the most common forms of substance use in California. Reports further suggest that this form of substance abuse is most common among people who are aged between 18 and 25 years (Rehab LLC, 2020). In Contra Costa County where the John Muir Health program is domiciled, it was reported that 71,314 individuals above 12 years were suffering from substance abuse (Thomas, 2020). Out of this number, the largest proportion of victims were abusing marijuana.
Alcohol abuse was the second most common cause for rehabilitation admission programs in the county. Binge drinking was also linked to about 18.8% of all adults in the county, while individuals who were aged between 18 and 25 years had the highest incidence of substance abuse. These populations eventually strain rehabilitation services in the county and cause social disharmony because, if left untreated, their substance abuse issues permeate into their adult years.
Expectations
The John Muir Health – Behavioral Health Center is a rehabilitation facility located in Concord, California. Founded more than 85 years ago by local physicians and residents, the facility has grown from an organization of a few hundred employees to having more than 1,000 primary care and specialist physicians (Rehab LLC, 2020). Today, the non-profit health-based institution is part of an integrated system of doctors, healthcare facilities and third-party players offering support services to substance abuse patients. The health facility is also committed to provide its patients with the highest form of healthcare quality through the contribution of healthcare workers and all that support their activities.
Activities
John Muir Health offers in-patient and outpatient treatment through individual counseling sessions and holistic therapies. The program is based on the medical model of treatment, which views drug and substance abuse as a mental health disorder that progressively affects its victims (JMH, 2020). It is intended to help people who suffer from multiple forms of drug abuse, such as alcohol dependence, prescription drug medications, and designer drugs, such as ecstasy, to overcome their addictions. Detoxification and in-patient services are mainly offered to local community members. The programs also include after-care programs offered to substance abuse victims and their families. The sessions are classified into two, with one of them being for patients aged between 18 and 30 years, while the latter caters for those who are older than 30 years.
Resources
Like other public health programs, the John Muir Health program requires different types of resources, but the most important one being the family unit. This unique attribute makes it one of the most progressive rehabilitation centers in California. The main philosophy informing the family-oriented therapy design is the belief that drugs and substance abuse are inherently family-oriented problems and solutions have to be found within the same social unit.
Based on this philosophy, the family unit gets as much attention as a patient does during recovery. Therefore, it is a core requirement that patients have a member of the family who is close to them to be part of the program. The family-based therapies last for 6.5 hours and involve a psychiatrist, patient and a family member (Rehab LLC, 2020). The main areas of discussion dominating these sessions include the importance of having effective communication, minimizing the risk of relapse, and the management of withdrawal symptoms.
Non-addictive medications are also offered to participants who take part in the program to reduce complications that may emanate from having aggressive withdrawal symptoms. The nursing staff of 140 personnel also help patients to experience maximum levels of comfort and care they can receive in the course of their treatment process (Thomas, 2020). Each of the nursing staff has a responsibility to ensure that the recovery plan suits a patient’s individual needs. The healthcare staff are also responsible for educating employees about how to stay committed to their sobriety with the core emphasis being avoiding triggers.
Some of these educational programs are implemented in support groups where patients can share their experiences with one another or with those who have experienced similar events. Overall, employee tasks are split into two categories: leadership and orientation. Three nursing personnel who are two chiefs of staff and one vice president head the leadership team, while the orientation department has 1,600 volunteers (Rehab LLC, 2020). Together, they form the care coordination team.
Program’s Stage of Development
The John Muir Health program has three stages of development: planning, implementation and effects/outcomes. In the planning stage, all stakeholders are involved in developing the program’s structures with the help of experts who give advice regarding the program’s structure and implementation matrix. Based on their metrics of planning, the program is currently being implemented as a one-day or two-day rehabilitation exercise for both in-patient and outpatient groups. A patient’s level of need is determined by the intensity or type of therapy administered. The implementation phase involves two groups of people.
The first one consists of women and morning process groups, while the second one is comprised of skill-based groups. The latter category is involved in different types of rehabilitation activities, including sharing strategies for avoiding relapses, developing groups that help patients avoid negative consequences of relapsing and nurturing the creative talent of patients engaged in expressive art forms, such as Yoga.
In the first stage of development, patients receive individual therapy once a week (Thomas, 2020). Family therapy and daily homework assignments are also used as tools for assessing the effects or outcomes of the program. In their adoptive frameworks, cognitive behavioral therapy tools are employed to promote the development of healthy coping skills. Additionally, the 12-step program associated with Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) is employed at this stage of development and patients are encouraged to get a sponsor and acquire additional resources to help them in their sobriety.
Program’s Context
As highlighted in this report, the John Muir Health program is domiciled in Concord, California. The metropolis is the largest city in Contra Costa County. Situated North of Francisco, the place is mainly agricultural with the early history of its inhabitants being in the trade. Most public health programs offered in Concord have failed to address the growing public health problem of substance and drug abuse. Instead, most of them have primarily focused on addressing female reproductive challenges, sexual health issues and supporting immunization programs (Contra Costa Health Services, 2020). The current health program fills this gap and is administered in a private setting with individually- tailored therapies designed to provide a custom treatment approach for each patient. Patients are also provided with an ambient environment characterized by music, art activities and recreation.
Logic Model
A sequence of events have to be followed to realize John Muir Health program’s goals. As highlighted in figure 1 below, patients have to experience a three-stage process of information flow to get medical services. In the first one, a patient is supposed to schedule an appointment and speak to a representative of the organization. At this stage of engagement, he or she is supposed to give information regarding their family history and medications. At this stage of engagement, the main goal of the plan is to make an educated assessment of the patient’s medical background. In the next stage of engagement, the respondents are supposed to find a location that suits them and speak to a doctor. Its goal is to give patients an opportunity to get professional advice from qualified medical personnel.
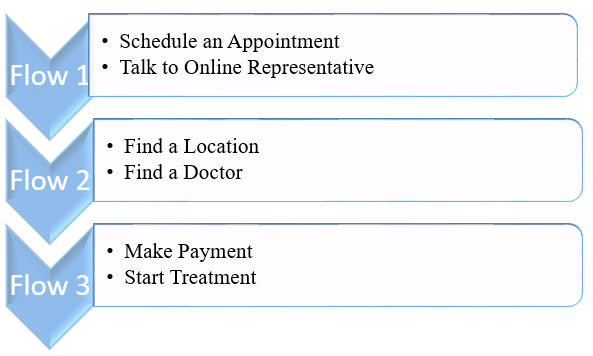
In the last stage of evaluation, a patient is supposed to make payments and start treatment. At this phase of development, they need to be furnished with a list of requirements needed at the facility, including their insurance card, money, and identification documents. Alternatively, at this stage of engagement, they are informed of items that will be disallowed at the facility, such as electronics and mobile phones. The treatment commences when the individual requirements are fulfilled.
Evaluation Design
- Purpose: The general intent of the evaluation is to improve the efficacy of drugs and substance abuse programs aimed at reducing the incidence of relapse in the community.
- Users: The main groups of people that will receive the evaluation findings include health practitioners and policy experts.
- Uses: Policy makers may find the evaluation findings to be insightful in developing policy decisions relating to public health interventions. Comparatively, public health professionals would gain additional insights from the same information to develop more impactful health programs.
- Methods: The case study research design will be employed to gain insight into the project evaluation process. Particularly, the case study will be domiciled at the John Muir Health – Behavioral Health Center, which runs the family-based drug addiction program aimed at rehabilitating drug addicts.
- Agreements: The evaluation process will be finalized after liaising with the educational institution of the evaluator. Permission will be sought to pursue the project in fulfillment of the evaluator’s academic requirements. Overall, the evaluation plan will involve a team of three people. The first one will be the academic supervisor who will guide the evaluator in designing and implementing the evaluation plan. The second one will be a colleague who will assist the evaluator to contact respondents who are willing to share data and experiences about the public health program. The researcher will also receive help from a family member who will introduce other respondents to the study. The evaluation activities will be implemented by assessing hospital records and data relating to the John Muir Health program. This information will be compared against projected or forecasted milestones to identify areas of consistency or departure from the original objectives.
- Addresses Evaluation Impact: The impact of the evaluation process will be measured against the national and statewide statistics on substance and drug abuse. Therefore, it would be possible to determine whether the county findings were subpar or optimal compared to generally available data on relapses and hospital admissions.
Gathering Evidence
- Indicators: The effectiveness of the John Muir Health program will be evaluated by assessing patients’ behavioral and attitudinal issues affecting their commitment to be sober. The goal is to reduce the incidence of drugs and substance abuse by providing social support services to people who need psychiatric help and mental health assistance to overcome their addictions. The dependent variable in the evaluation plan will be individual therapies and the dependent variables will be commitment level, relapse rate, membership numbers and emergency hospitalizations emanating from drug overdoses and substance abuse. Data will be gathered as outlined below and compared with similar statistics involving related health programs in California.
- Sources of Evidence: Data will be gathered from healthcare participants who are involved in the project implementation phase as well as secondary data from published reports about public health programs of a similar nature. The secondary data will be soured from credible sources of information, such as government websites, state-prepared healthcare reports and healthcare publications. Interviews will be arranged to gather the views of five members of the project team who have executive powers. They will be selected to participate in the study using the snowball sampling method as the researcher has developed a rapport with one of them.
- Quality: The information gathered and assessed will be assessed using the member check technique whereby data is cross-referenced with the participants’ views before publication. The goal will be to give the informants an opportunity to examine the contents of the report before publication to verify that the information presented reflects their true views.
- Quantity: The use of two sources of information to obtain data complements the integrity of the evaluation findings because more than one source of information will be used to come up with the findings. This dual data collection method ensures that the weaknesses of one technique are counter-checked with the strengths of another.
- Logistics: Due to the difficulty of undertaking face-to-face communications, interviews will be conducted online, using Skype. This platform gives researchers and respondents the flexibility needed to schedule an interview at a time that is appropriate for both of them. Based on the organization of the interview schedule, the data collected will capture the program’s effectiveness at one point in time. However, the secondary data, which will be integrated in the findings, will provide an expanded period of assessment because current data will be compared with the effectiveness of other programs, which have been launched in the past five years. The main limitation associated with the online interviewing technique is the difficulty in making a good first impression on a virtual platform.
- Addresses Information Scope and Selection: The scope of the information gathered for the assessment will only cover data relating to relapses and successful treatment of addition cases. These pieces information will be used as a measure for the effectiveness of the program because a higher rate of relapse will be associated with poor efficacy, while a lower rate of relapse will be related with a higher rate of efficacy. The data obtained will also only be relevant to the period in which the program has been implemented.
Justification of Conclusions
- Standards: The values that stakeholders hold dear to the evaluation plan will be used to inspire all aspects of the evaluation plan. To this end, the evaluation process will be used to help people who are struggling with drugs and substance abuse to start their lifetime journey of recovery. Therefore, the values held by the stakeholders are premised on empowering patients with the resources needed to make a full recovery.
- Analysis and Synthesis: The thematic and coding method will be used to analyze all data gathered from the evaluation. The process is synonymously associated with the analysis of qualitative data emanating from interviews, which will be one of the primary modes of data collection in the evaluation plan. The thematic and coding process will consist of six steps, which include familiarization of data, coding, generation of themes, reviewing the themes, defining and naming the themes, and writing up the final report.
- Interpretation: The process of interpreting data will be premised on the interaction between qualitative and quantitative data emanating from interview and secondary data, which will be the main sources of information in the evaluation. In other words, the primary research findings will be interpreted in the study by comparing the effectiveness of the present health program with its intended goals as well as the effectiveness of other similar programs.
- Judgements: The findings of the proposed evaluation process will be compared against standards provided by the World Health Organization regarding the provision of quality health services (WHO, 2020). These standards are designed to focus on the provision of quality services as the core of public health management programs.
- Recommendations: The findings of the evaluation program will be analyzed and disseminated within the context they were developed. In this regard, they may only be indicative of the challenges or issues affecting the implementation of public health programs in the state of California. Therefore, they should be used cautiously especially when applying them in a different context from the case study.
- Addresses identification of Values: The overall report findings should reflect data obtained from qualitative and quantitative sources – interviews and secondary research. Its efficacy should also be measured based on the efficacy of older health programs and the project’s goals. The overall framework of analysis will be based on the main value held by stakeholders, which is to empower patients suffering from drug and substance abuse to make a full recovery.
Use and Dissemination of Lessons Learned
- Design: Questions that will be posed to the interviewees will be open-ended but focused on understanding the main influences of the program’s features on patients’ attitudes and commitment to staying sober.
- Preparation: The findings of the evaluation report will be openly published online to expand the body of knowledge on the development of public health interventions on substance abuse. Policymakers will also be included in the planning phase to improve the probability of getting their buy-in.
- Feedback: All stakeholders involved in the evaluation plan will be enrolled in a WhatsApp group where ideas will be shared and feedback received. Group meetings will also be held twice a month to enhance team synergy.
- Follow-up: The contacts of the evaluators will be provided after developing the final report to give users an opportunity to make follow-ups regarding any aspect of the data published.
- Dissemination: The findings of the evaluation will be published online to allow users to get timely access to the information published.
Reflections on Standards for Good Evaluation
The standards used for evaluation will be borrowed from four key criteria that include utility, feasibility, proprietary and accuracy standards as described below.
- Utility Standards: Utility standards are mainly preoccupied with the use of the evaluation findings. To this end, there will be a keen focus on identifying people involved in the project, evaluate their credibility and examine the scope of the information that will be shared with them for review. Their values will be evaluated to ensure they are consistent with the overall objective of the report and timelines for completing different stages of the implementation process shared. To maintain high levels of utility, the report will also have clear and achievable goals to understand the systems, processes and procedures that underlie the health program.
- Feasibility Standards: The evaluation process will be undertaken as an independent process, thereby avoiding the possibility of interrupting everyday operations at the health facility. The political viability of the plans will be safeguarded by making sure that all interested parties are involved at the project design phase. Additionally, the cost of the evaluation process will be consistently monitored to ensure that the findings are valuable and do not undermine the organization’s bottom-line.
- Proprietary Standards: By involving all stakeholders in the project-planning phase, the evaluation process will serve the needs of all participants. All stakeholders will sign a formal agreement detailing their participation requirements and expectations from the report. The rights of all participants will be respected and conflicts of interest declared. At the same time, fiscal responsibility will be maintained throughout the entire evaluation process to reflect sound accountability procedures that are synonymous with the John Muir Health facility.
- Accuracy Standards: All evaluation processes will be documented and a context analysis done to understand all factors that influence project success. The quality of information contained in the documents will also be evaluated to ensure they have high integrity and are reliable. Overall, a meta-evaluation will be done at the end of the process to compare the evaluation findings with state and national data on similar substance abuse health programs.
References
Contra Costa Health Services. (2020). Public health clinic services. Web.
JMH. (2020). Addiction medicine recovery services. Web.
Rehab LLC. (2020). John Muir Health – Behavioral Health Center: Addiction treatment. Web.
Thomas, S. (2020). Alcohol and drug abuse statistics. Web.
WHO. (2020). Global standards for quality health care services for adolescents. Web.