In this laboratory work, the correlation between salt concentration in water and boiling point was studied. Thus, for the experiment, the temperature of water brought to boiling was measured beforehand, and then 12 g of sodium chloride was added into the glass one by one. In the end, we obtained a solution of 36 g of salt in 100 ml of water. At each stage of the experiment, the temperatures of the solution were measured with the help of a thermometer.
Table 1. Corresponding amount of salt in water and boiling point of solution.
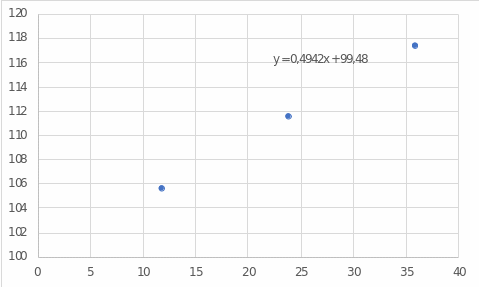
The difference between pure water and water mixed with salt is noticeable. If one pays attention to Figure 1, one can see that with an increasing salt concentration in the water boiling temperature increases almost linearly. This effect is caused by the presence of ions of sodium and chlorine in water, which form a salt, which itself has a higher boiling point than water: 1413 °C versus 100 °C (Helmenstine, 2020). Therefore, by continuing to add salt to the water, one can achieve an increase in temperature.
On the contrary, if one had increased the amount of water instead of doubling the amount of sodium chloride, one would possibly be able to lower the boiling point. This effect is related to the sodium chloride’s concentration. Adding more water is the same as reducing the total salt concentration, which means reducing the boiling point.
The linear regression model and figure 1 were used for these calculations.
It can hardly be said that adding salt will raise the boiling point infinitely. Salt cannot dissolve endlessly in water since there is a limit in the form of saturation: after a certain number of grams, the substance stops dissolving even in hot water, so the salt ceases to affect the boiling point. In this case, the graph will appear on a plateau and will not change significantly anymore.
References
Helmenstine, A. M. (2020). Why adding salt to water increases the boiling point?ThoughCo. Web.