Abstract
The main objective of this report is to analyze the financial ratios of Dubai Islamic Bank to evaluate the performances over a period of six years (from 2012 to 2017). From the result of the liquidity, safety, debt management, profitability, operational efficiency ratios, and DuPont system analysis, this report will identify financial strengths and weakness of this bank and will address where the company is not performing well and areas for improvement. Furthermore, this project focuses on the comparative analysis of the financial statement using common size tools, such as, vertical and horizontal analysis of income statement and balance sheet to assess the financial trends, area of success, and response of this Bank. Here, different financial ratios of this bank will be presented by rearranging and simplifying the data from the financial statement of DIB group and the analysis will be done by creating relationship among the information of the balance sheet regarding the profit and loss account and by examining the viability, stability as well as the profitability of DIB group.
Background of Dubai Islamic Bank
As a pioneer of modern Islamic banking ‘Dubai Islamic Bank’ (DIB) was established in 1975, which is carried out a new approach in the conventional bank arena by upholding the strong business principles of Islamic Sharia pointed to the honest and fair deal at every step of trade and commerce. After four decades of operation, DIB is now an undisputed leader in the field of Islamic banking and its model of the financial institution has recognized globally; therefore, many foreign bankers are following its footprint of success for Sharia-compliant banking products those are the most popular religious mined Muslim countries (Dubai Islamic Bank, Annual Report 2017 18). UAE-based DIB further engaged the most giant Islamic banking professionals to generate new banking products and services such as Johara for women banking, Shaatir for children banking, Tamweel for housing and real estate, and Wajaha for wealth management and turned into the global leader of the global financial services industry (Dubai Islamic Bank, Annual Report 2015 14). Beside the banking sector, the DIB group also holds more than thirty subsidiaries in the automobile, brokerage, garments manufacturing, financial and legal advisory, and real estate development both in national and international market (Dubai Islamic Bank, Annual Report 2013 12).
Liquidity Ratios
The ‘Liquidity Ratios’ of the Dubai Islamic Bank is the indicator of DIB group to what extent it is capable of meeting up concurrent financial obligations as well as dues liability in the market from its present resources; thus, it is also termed as “Short-term Solvency Ratios” of that company. The short-range creditors as well as interim suppliers of the Dubai Islamic Bank are mostly concerned to know the liquidity ratios of that company, as they are highly interested to be paid as promptly as possible by comparing the current assets along with current liabilities.
Current Ratio
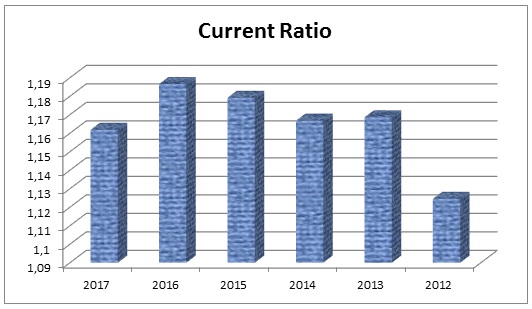
Table 1: Current ratio of Dubai Islamic Bank. Source: Self-generated.
It is important to calculate this ratio since it demonstrates a company’s capacity to reimburse the short along with long-term debts of a business; in addition, it measures whether the company will face any hindrance or not (Higgins 75). In table 1, it is indicated that the current ratio of DIB from 2012 to 2017 was 1.12, 1.17, 1.17, 1.18, 1.19, and 1.16 respectively. Companies working in the conventional manufacturing industries and trading those who need sufficient working capital investment they must have current ratios of 2 or more. However, for financial institutions current ratio measured smaller than 1 must be considered acceptable and firms capable to pay off short-term obligations easily. Figure 1 illustrates that the current ratio of DIB is in a sound and solvent position with enough liquid assets to meet up its short-term obligations.
Quick Ratio
The concept of Quick Ration or Acid Test has pointed to the consideration that the DIB has sufficient liquid assets in-hand for every single penny of current liabilities and should be paid immediately (Higgins 75). In order to calculate this ratio, the liquid assets are identified by subtracting stock-in-trade, as it is not immediate convertible into cash (Higgins 76). It is also necessary to deducting prepaid expenditures from the total current asset; the standard assortment of quick ratio is 1:1; and it indicates the short-term financial statues of the company more efficiently than the current ratio;
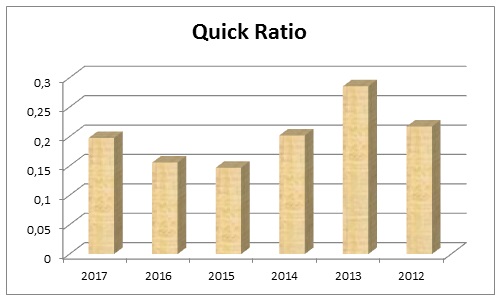
Table 2: Quick ratio of Dubai Islamic Bank. Source: Self-generated.
The Table-2 has presented the Quick Ratio or Acid Test of DIB and demonstrated that among the assessed years the Quick Ratio was higher in 2013 that scored at 0.285 and was lower in 2017 scaled at 0.197. Among the six years assessment the company failed to improve its Quick Ratio at least 0.5 and undoubtedly it is a poor indication. The quick ratio measured at lower than ‘one’ is alarming , but for financial industry it doesn’t indicate that Dubai Islamic Bank going into default or bankruptcy, rather it could indicate that the DIB is emphasizing seriously on the inventory or to paying other short term liabilities of the bank. Fig.2 shows the result of this ratio graphically –
Safety
Times Interest Earned
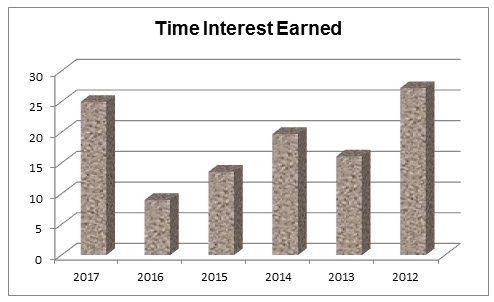
Time interest earned ratio (TIE) of the Dubai Islamic Bank has presented in the Table-3 bellow in order to identifying how efficiently DIB is capable to cover its interest payments before tax, in 2012 the EBIT of the DIB was AED1,144,654 and interest charged was AED 42,082 thousands; thus the TIE stands 27.20. It indicates that in 2012, Dubai Islamic Bank earned 27.20 times of its interest charged during that period. The TIE of DIB was 16.08 in 2013, 19.73 in 2014, 13.50 in 2015, 8.98 in 2016, and 24.96 in 2017. In figure-3 the time interest earned ratio (TIE) of the Dubai Islamic Bank for six years has plotted and illustrated that earning of the bank is significantly higher than its interest and it is enough sound to solvent to cover interest payments as well as some principal repayments.
Table 3: Times interest earned of Dubai Islamic Bank. Source: Self-generated.
Debt to Equity Ratio
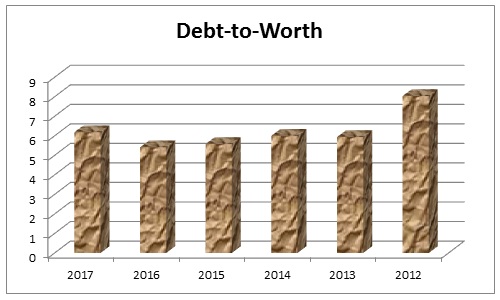
Table-4 illustrated that, during the year 2012, the total debt of DIB was AED 84,804,844, its total equity was AED 10,559,855.00, and its debt equity ration stands 8.031, in the next five years up to 2017, the debt equity ratio of the DIB was 5.932, 5.997, 5.576, and 5.576. The six years debt equity ratio of the DIB has plotted in the figure-4 and indicates that a relatively higher while the industry average is 2.2 for commercial banking and 3 for investment banking; thus, DIB is adopting aggressive growth strategy with the prospect of increasing profit along with associated risk of loss.
Table 4: Debt to equity ratio of Dubai Islamic Bank. Source: Self-generated.
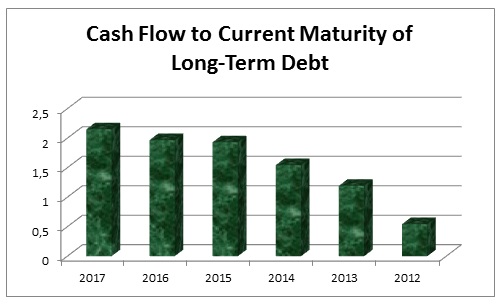
Cash Flow to Current Maturity of Long-Term Debt
Table-5 presented that in 2012, the Dubai Islamic Bank had repaid AED 2,434,918 from its long-term obligations or liabilities while the net profit along with non-cash expenses were AED 1,322,701 and the ‘Cash flow to current maturity of long-term debt’ was calculated 0.543. Current portion of long-term debt (CPLTD) of DIB was 1,553,515 in 2013, 1,906,799 in 2014, AED 2,069,046 in 2015, AED 2,139,471 in 2016, and AED 2,170,468 in 2017 while the bet profit along with non-cash expenses were 1,853,091, 2,941,186, 3,993,446, 4,207,886, and 4,668,754 in the respective years. The analysis illustrates that the ‘Cash flow to current maturity of long-term debt’ was 2.151 in 2017, 1.97 in 2016, 1.93 in 2015, 1.54 in 2014, and 1.19 in 2013 which are demonstrated in Figure-5 that this ratio of DIB has increased in the corresponding years.
Table 5: Cash flow to current maturity of long-term debt of Dubai Islamic Bank. Source: Self-generated.
Profitability
Gross Profit Margin
The Table-6 illustrated that the gross profit of Dubai Islamic Bank was AED 3,710,119 in 2012 and the respective total sales was AED 5,026,324, and the ‘Gross profit Margin’ has calculated 0.73813765 or 0.74. Meanwhile the gross profit margin was 0.80 in 2013, 0.87 in 2014, 0.86 in 2015, 0.78 in 2016, and 0.75 in 2017 and presented in Figure-6 that illustrated that DIB has been conducting its business efficiently with a higher but steady gross profit margin and relevant to the industry average DIB is capable to generate reasonable profit on its sales.
Table 6: Gross profit margin of Dubai Islamic Bank. Source: Self generated.
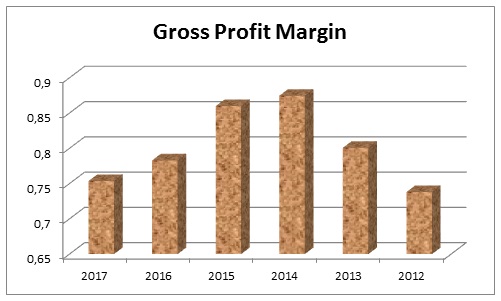
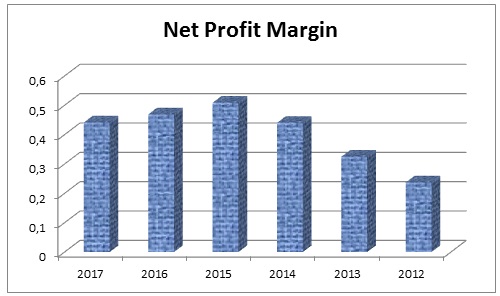
Fig. 6: Gross Profit Margin of Dubai Islamic Bank (Self-Generated).The net profit margin of Dubai Islamic Bank indicates net income that the bank generates in relation to its product and service sold, DIB generated net profit of AED 1,192,154 for total sales of AED 5,026,324 in 2012 and the net profit margin stands 0.237. Table-7 also demonstrated that the net profit margin of DIB was 0.325 in 2013, 0.440 in 2014, 0.509 in 2015, 0.468 in 2016, and 0.442 in 2017; the six years data of net profit margin has plotted in the Figure-7 and demonstrating what amount of profit DIB makes for each dollar of its profit on each dollar sales. For banking sector industry, it is a sustainable profit margin while the DIB management could draw further attention to the present net profit margin in order to redesign its pricing strategy.
Table 7: Net profit margin of Dubai Islamic Bank. Source: Self-generated.
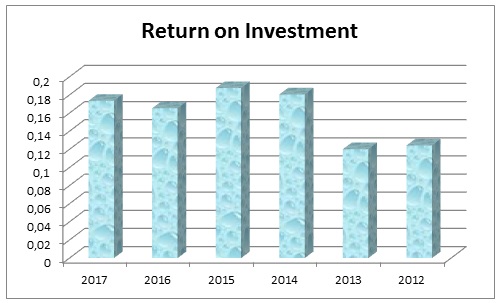
Return on Investment (ROI)
Table 8 illustrated that the Return on investment (ROI) of DIB was 0.124 in 2012, 0.120 in 2013, 0.181 in 2014, 0.187 in 2015, 0.165 in 2016, and 0.174 in 2017; as significant tool for performance measurement, it involves to analyze the investment efficiency by counting the volume of return in relation to the timeframe. Calculating ROI is a most commonly used financial ratio, the management as well as the stakeholders of DIB could use ROI for their investment and business decision-making to funding new projects of DIB or invest on its share. Figure-8 demonstrated six years ROI where the ROI gained gradually gained higher with affordable investment costs.
Table 8: Return on investment of Dubai Islamic Bank. Source: Self-generated.
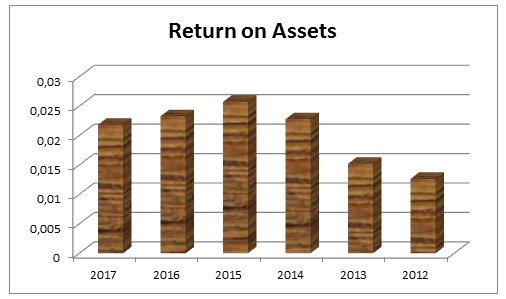
Return on Assets (ROA)
It is essential to note that higher percentage of ROA illustrates that the firm is profitable, and is getting stronger with time; however, it is difficult for financial institutions to achieve a greater percentage of the ratio. Table 9 shows the calculation of ROA and from this data, it can be said that Dubai Islamic Bank had comparatively strong ROA in 2015; however, this bank had failed to perform up to the mark. Fig. 9 shows the result of this ratio graphically –
Table 9: Return on assets of Dubai Islamic Bank. Source: (Self-generated).
Operational Efficiency
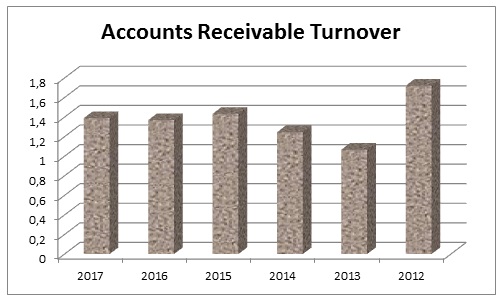
Accounts Receivable Turnover
Table 10: Accounts receivable turnover of Dubai Islamic Bank. Source: Self-generated.
This ratio illustrates how many times account receivables are paid and regenerated throughout the fiscal year; here, it is notable from the above calculations that accounts receivable were quite lucrative in 2012, 2015, and 2017 for this bank (table 10); however, it has opportunity to improve this ratio to increase cash on hand. Fig. 10 shows the result of this ratio graphically –
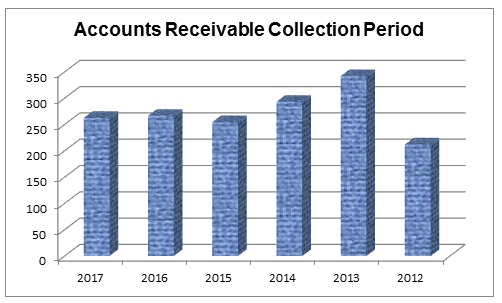
Accounts Receivable Collection Period
Table 11: Accounts receivable collection period of Dubai Islamic Bank. Source: Self-generated.
This ratio explains a number of times it requires to collect all accounts receivable; here, it is notable from the above calculations that Dubai Islamic Bank had taken the highest time in 2013 in comparison to 2012; however, table.11 demonstrates that this bank failed to collect accounts more speedily. Fig. 11 shows the result of this ratio graphically –
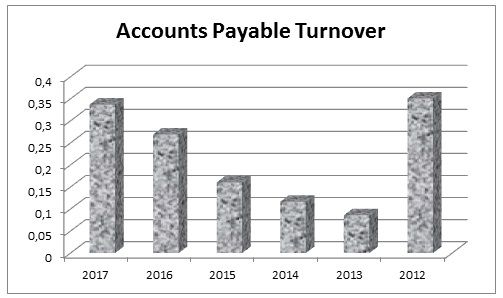
Accounts Payable Turnover
This ratio indicates how many times in a fiscal period the firm turns over its accounts payable to creditors; from the calculations, it can be said that it has limited difficulty to repay its creditor (table 12); at the same time, Dubai Islamic Bank has the opportunity to hold the fund for a long-time to invest for business. Fig. 12 shows the result of this ratio graphically –
Table 12: Accounts payable turnover of Dubai Islamic Bank. Source: (Dubai Islamic Bank, Annual Report 2013 5).
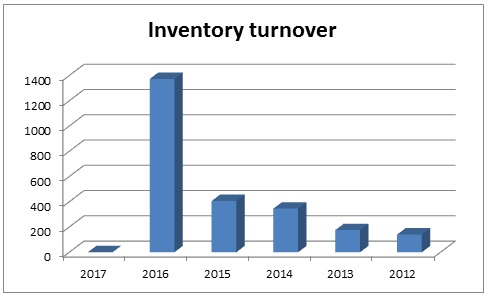
Inventory Turnover
It is essential to note that the inventory turnover ratio specifies whether a company is able to effectively handle the inventories or not; moreover, a larger ratio illustrates that robust sale; in this situation, Dubai Islamic Bank has successfully improved this ratio from 2012 to 2017 (table 13). However, fig.13 shows inventory turnover ratio graphically –
Table 13: Inventory turnover of Dubai Islamic Bank. Source: (Dubai Islamic Bank, Annual Report 2012 78).
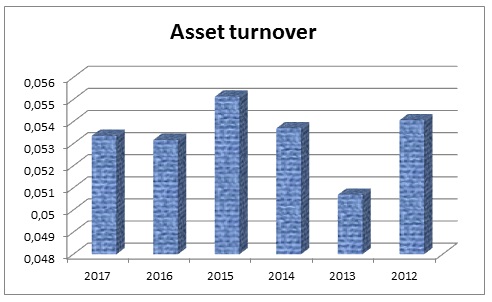
Asset Turnover
Lower total asset turnover indicates vulnerable corporate financial condition; in present case, Dubai Islamic Bank has failed to perform up to the mark; however, this situation also indicates that this bank faced external and internal challenges to carry on financial activities (Table 14). However, fig.14 shows asset turnover ratio graphically –
Table 14: Asset turnover of Dubai Islamic Bank. Source: (Dubai Islamic Bank, Annual Report 2014 54).
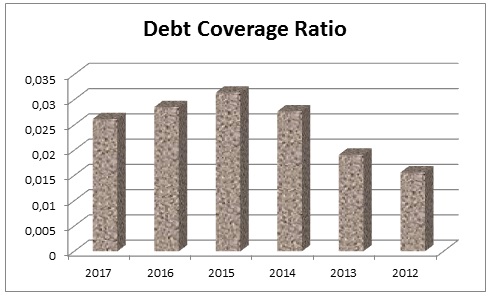
Debt Management
Debt Coverage Ratio
This ratio illustrates the organization’s capability to assure its debt requirement, and its ability to undertake extra debt without impairing its continued existence; however, the result of this ratio demonstrates that the position of Dubai Islamic Bank was in a volatile situation (table 15). Fig.15 shows debt coverage ratio graphically-
Table 15: Debt coverage ratio of Dubai Islamic Bank. Source: Self-generated.
Performance of the Company and Areas for Improvement
This paper presented different financial ratios for the year 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016, and 2017 by using financial statements of Dubai Islamic Bank; however, the result of the report demonstrates that the management disclosed financial information fairly and the international standard of reporting, which is appreciable to the investors. Thus, this report has prepared maintaining the ethical responsibilities those have sufficient basis to believe appropriate; however, this report identified that this bank failed to manage liquidity risks; so, the management should focus more on the financial credit risks.
Asset turnover ratio, debt coverage ratio and safety ratio illustrated that the performance of this bank was not in satisfactory level; however, it should increase efficiency level by monitoring financial risks and controlling expenses; furthermore, the management of this bank should concentrate on the diversified funding sources in order to minimize financial risks (Dubai Islamic Bank, Annual Report 2012 110).
The investors of this bank may lose their confidence to invest more for the further development due to continuous fall of net income and increase of operating expenses; therefore, a number of sectors require improvement for performing with a suitable economic environment and present in the financial market strongly.
The financial statements of the Dubai Islamic Bank along with its balance sheet had presented in the annual report of corresponding years, but unfortunately, it had not delivered the exact profitability as well as financial status of the bank; so, there were many facts, which were difficult for the shareholders to make sense regarding the business health of this bank. Meanwhile the ratio analyses presented in this paper are the most significant tool that assists the stakeholders to understand with an easygoing process; in addition, presentation of every numeric terms and figures would provide depth insight to the stakeholders about the liquidity, profitability, as well as solvency of this banking group.
Furthermore, these accounting ratios are simplified and concise an extensive collection of accounting data those are presented in the annual report of DIB while the presentation of six years data by graphs and figures simultaneously would generate relationship and means of comparative study with one year to another.
From the ratio analysis of DIB, it can be said that the estimations presented in its annual report has various uncertainties connecting to the Islamic financing and financial derivatives those are necessarily demand step-by-step evaluation, assessment and gradual development rather than portfolio-based-approach. Otherwise, the investors would be thrown in serious threat of bench marking loss rates; therefore, the management of DIB needed to reschedule and re-engineering the model of Islamic financing.
It is important to mention that the management of this bank had already addressed some financial risks and conducted credit assessments; however, the board members has to ensure its stakeholders that this bank would be truly profitable for the further investment (Dubai Islamic Bank, Annual Report 2016 5). However, the Chairman of this bank stated that the external business environment has changes due to increase of oil price; therefore, the credit growth estimated to above twice compared to the previous fiscal year (Dubai Islamic Bank, Annual Report 2017 3).
Comparative Analysis of the Financial Statement Using Common Size Tools
Common sized income statement sheet – vertical analysis with sales demonstrated that net come of Dubai Islamic Bank had increased from 44.2% in 2012 to 46.9% in 2013, but it had dropped significantly from 32.5% in 2016 to 21.3% in 2017; at the same time, the percentage of expense had boosted from 31.9% in 2016 to 51% in 2017. Table-16 also represented that gross profit margin had decreased slightly from 80.1% in 2016 to 73.8% in 2017, but this bank failed to control administrative and other operating costs; therefore, it should control expenses though this bank is running business with profits.
Table 16: Common sized income statement sheet – vertical analysis with sales. Source: Self-generated.
Common sized balance sheet (vertical analysis with sales) shows that the percentage of cash had increased from 192.9% in 2016 to 273.4% in 2017; at the same time, the ratio of accounts receivable had boosted from 58.1% in 2012 to 93.7% in 2013.
Table 17: Common sized balance sheet – vertical analysis with sales. Source: Self-generated.
According to the result of common sized income statement sheet (horizontal analysis) the percentage of sales had escalated from 14.4% in 2015 to 18.1% in 2016, which was positive sign for this bank; consequently, the gross profit ratio had increased from 4.2% in 2015 to 13.7% in 2016. At the same time, the percentage of net income had risen from 5.5% in 2016 to 11.2% in 2017; however, it is important to mention that the ratio of net income was 60.3%, which indicated the performance of this bank has dropped over time and increased the chance of liquidity risks.
Table 18: Common sized income statement sheet -horizontal analysis. Source: Self-generated.
According to the result of common sized balance sheet (horizontal analysis), the percentage of cash had escalated from 24.2% in 2015 to 67.4% in 2016; in addition the ratio of accrued expenses had boosted from 16.6% in 2015 to 21.7% in 2016; total liabilities and equity had also increased over time.
Table 19: Common sized balance sheet -horizontal analysis. Source: Self-generated.
From the analysis and review of the common sized balance sheet (vertical analysis with assets), that the percentage of cash was in lowest position in 2015 it has increased from 9.5% in 2016 to 13.4% in 2017; on the other hand the ratio of total equity has dropped from 15.6% in 2016 to 13.9% in 2017.
Table 20: Common sized balance sheet – vertical analysis with assets. Source: Self-generated.
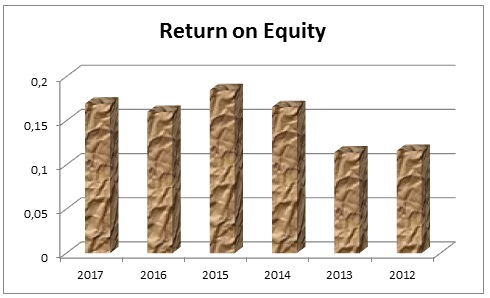
DuPont System Analysis Company’s Strengths and Rooms for Improvement
This is one of the most effective tools to measure financial strength of the company and ROE of Dubai Islamic Bank was the lowest in 2013; here, fig.16 shows that its financial leverage was strongest in 2012 and it was in satisfactory level; however, it should advance its asset turnover. Fig.16 shows the calculation of ROE graphically –
Table 21: DuPont analysis. Source: Self-generated.
Conclusion
From above discussion, it can be said that the ratio analysis will assist the top management of Dubai Islamic Bank for further decision regarding their business expansion, investment, new product development, dividend distribution and future business planning while this analysis also assist the investors, suppliers and all other stakeholders could decide whether they invest in this company or not.
The result of ratio analysis and financial statement demonstrates that Dubai Islamic Bank performed quite well in 2013 and 2014, but botched to uphold the consistency; as a result, it can be concluded that the financial strength of this bank is not in stable position though it is one of the largest Islamic bank in the world.
Common sized income statement sheet (horizontal and vertical analysis with sales and assets) demonstrated that the percentage of net income has declined and total cost has increased from the last two years, which indicates the management Dubai Islamic Bank should concentrate on the cost reduction mechanism and proper corporate governance system.
Works Cited
Dubai Islamic Bank. Annual Report 2012., Web.
Dubai Islamic Bank. Annual Report 2013. 2014? Web.
Dubai Islamic Bank. Annual Report 2014. 2015, Web.
Dubai Islamic Bank. Annual Report 2015., 2016. Web.
Dubai Islamic Bank. Annual Report 2016. 2017. Web.
Dubai Islamic Bank. Annual Report 2017. 2018. Web.
Higgins, Robert. Analysis for Financial Management. 11th ed., McGraw-Hill Education, 2015.