Project Objectives/Scope
Project description:
- Designing a new car with autopilot feature and an improved engine;
- Introducing the finished product into the global market.
Automotive industry in the 21st century:
- Toyota: innovative solutions, improved technical characteristics;
- Tesla: environmentally safe e-cars;
- Recent increase in the success of battery electric vehicles (BEVs) (“Global automotive executive survey 2017,” 2017).
The project is aimed at launching a new car into the global automotive market. The car is going to have a range of features including an improved engine and autopilot features. Therefore, despite the impressive competition from BEVs, it is bound to be a success.

Project Charter
Project objectives:
- Global car market exploration and trends identification;
- Brand image and branding strategy design;
- Creating a marketing approach and building a competitive advantage.
Project scope statement:
- Objective: introducing a new car into the global market;
- Deliverables: 0.1% of the market share or more;
- Milestones:
The project implies the design and the further promotion of a new car with autopilot functions and an improved engine in the global market. To complete the said objectives, one will have to research the target market, create the product, and brand it appropriately. The project is expected to be finished by August 31, 2017.
The product will come in three colors and 13 models. The project will require the financial backing of $100,000. The expected market share is 0.1%.

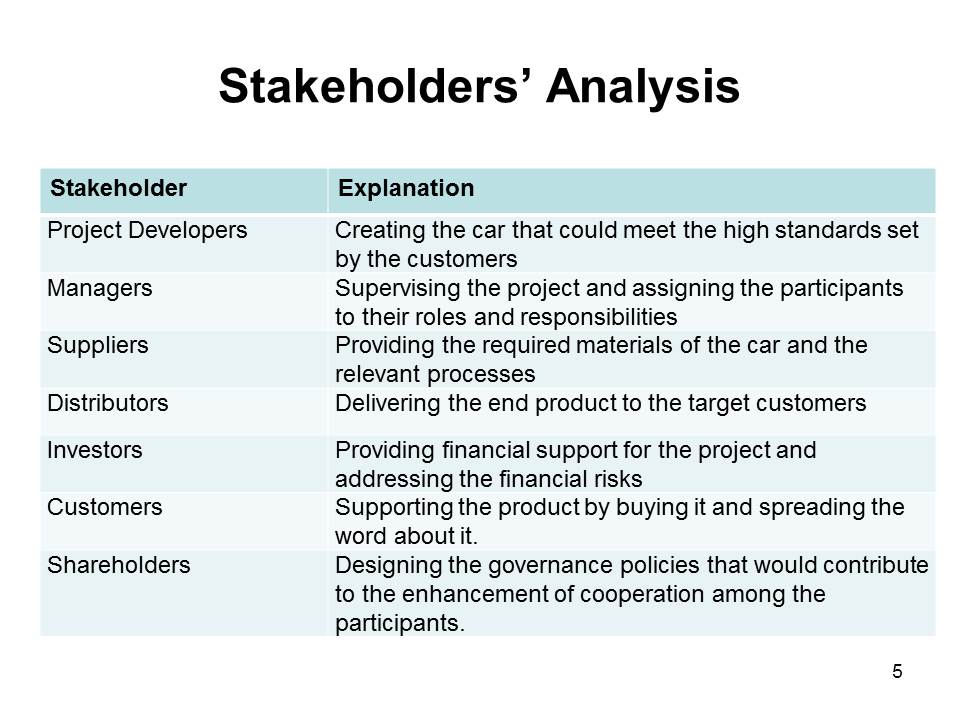
Stakeholders’ Analysis
Stakeholders of the project include Project Developers (creating the car). Managers (directing the project). Suppliers (providing raw materials), Distributors (delivering the product to the end customer), Investors (supporting the project financially), Customers (purchasing the cars), and Shareholders (governing the project).
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Project outline: determining the key steps;
- Leadership strategy creation: focusing on the transformational approach;
- Product design: defining the features of the car;
- Technology improvement: introducing the latest IT tools;
- Target market research: identifying the key competitors;
- Financial strategy development: introducing the principles of sustainability and lean management;
- Risk management strategy development: using the available resources;
- Exit strategy identification: a merger as a possibility;
- Communication strategy development: cooperation as the priority;
- Marketing campaign: incorporating the latest tools;
- Promotion campaign: a unique brand image;
- Product distribution: traditional distribution model.
It is crucial that the project should include the stages that involve the leadership strategy, as well as the focus on the product design. With a proper leadership framework, one will be able to keep the participants motivated. Furthermore, it will be necessary to focus on incorporating the latest technology and setting the quality standards high. The identified processes should be carried out along with the exploration of the target market. As soon as the crucial risks are identified, the marketing campaign should be carried out, with the following distribution of the product.

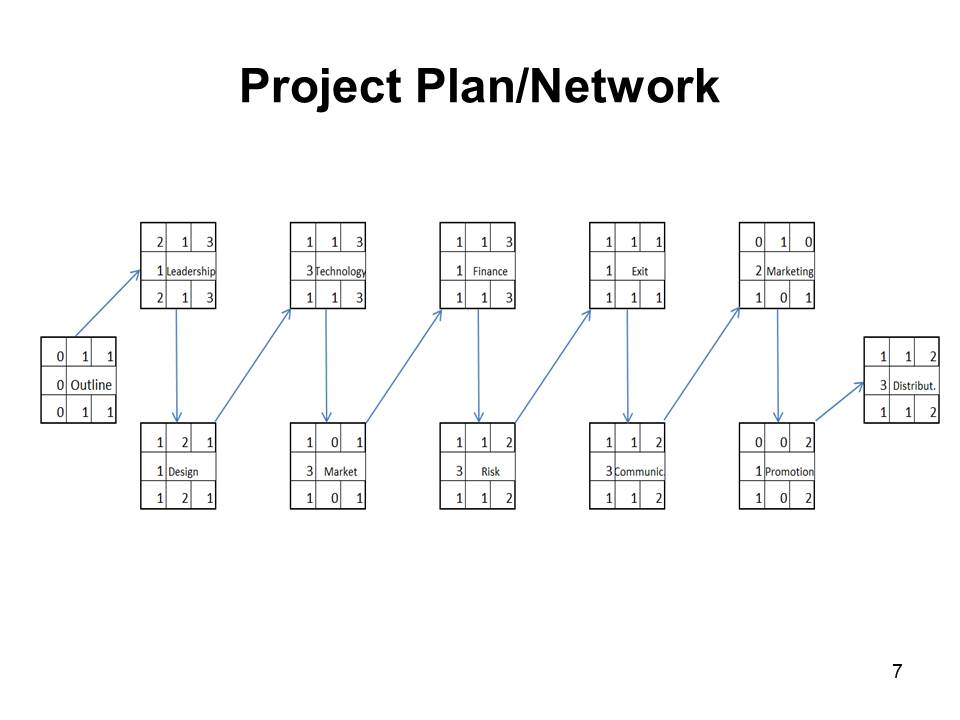
Project Plan/Network
The project network implies that the required steps will have to be accomplished in the following order:
- Product outline (car design, incorporation of innovative techniques, etc.);
- Leadership strategy design (preferably with the focus on the transformational leadership approach);
- Quality management (active use of the Six Sigma tools (particularly, DMAIC) and the Total Quality Management (TQM) framework) (Pyzdek & Keller, 2014);
- Procurement strategy design (with the emphasis on reducing time and costs during the delivery processes);
- Market analysis (a more detailed examination of the competitors, their advantages, and how they can be beaten in the context of the global market);
- Financial strategy design and risk management tools identification;
- Marketing and promotion, which are followed b product distribution (Larson & Gray, 2011).
Reducing Project Duration
- Increase of repeatability and reproducibility rates among the participants;
- Earned Duration Management as the essential tool;
- Enhancing information management among the key stakeholders (particularly, executives, managers, and suppliers).
The project incorporates all major tools for cutting the time taken to complete it.For instance, the emphasis on improving the repeatability and reproducibility of the production processes needs to be mentioned. The identified strategies serve as the means of bringing down the number of defects made during the production. Consequently, the project duration drops, whereas the quality of the product rises.
It is also noteworthy that the project includes the Earned Duration Management (EDM) framework as the device for reducing time significantly. EDM helps eliminate the financial data from the scheduling process, thus, making it less convoluted (Marquez & Lev, 2016). Finally, the focus on an improved data management needs to be listed among the key techniques.

Project Communication Plan
Internal Communication
- Reports;
- Weekly meetings;
- Intranet;
- E-mail;
- Organizational support
External Communication
- E-mails;
- Blogs;
- Vlogs;
- Online surveys;
- Hotlines;
- Online chats.
In order to maintain consistent communication between the managers and the employees, one should consider active use of reports and e-mail. Furthermore, to make sure that the staff’s requests are heard and taken into account, the project should have an intranet for corporate communication Weekly meetings will help communicate the key roles and responsibilities to the staff.
External communication (i.e., the conversation with customers) will be supported with the help of e-mails, blogs/vlogs, and online surveys. The latter are especially important as the means of gathering feedback from the target population. In addition, a hotline and online chats will be used to respond to the clients’ requests immediately (Laasch & Conaway, 2014).

Assumptions, Exclusions, Dependencies, and Other Major Issues
Assumptions, Exclusions, and Dependencies
- It is assumed that the members of the project will deliver the performance of the required quality;
- It has been calculated that the project budget will be enough for completing the objectives;
- The time frame should be viewed as the key constraint;
- The Start-to-Finish framework will be deployed.
How They Have Been Handled
- Transformational leadership was used to enhance motivation and performance levels among the participants;
- An efficient strategy for addressing the financial risks based on the principles of sustainability was utilized;
- An elaborate schedule was designed.
It is believed that the performance of the people involved in the project will meet the required standards due to the usage of the transformational Leadership framework. The budget of $100,000 is also considered to be enough to complete the said goals. The time issue will have to be addressed appropriately so that the project should meet the deadlines. With the help of the Start-to-Finish framework, one will be able to carry out the necessary steps properly (Chatfield & Johnson, 2013).

Scope, Time and Cost Constraints
Scope
- Introducing a new car into the global market;
- Gaining new customers.
Time
- Several months for project development;
- Significant time constraints may lead to quality issues.
Cost
- The budget does not allow for numerous expenses to be taken;
- The principles of lean production and sustainability may help address the cost issues.
The scope can be deemed as an important constraint since it the objectives revolve primarily around gaining new audience as opposed to keeping them invested.
As stressed above, the project is restricted significantly as far as the time is concerned. Particularly, it is necessary to deliver the product to the target customers before the competitors come up with a similar concept (i.e., within the next few months). Furthermore, the a number of expenses that the participants can afford is rather limited, which means that the support of investors may be required.

Project Lessons Learned
- Flexible leadership strategy;
- Efficient conflict management approach;
- Using compromise-based negotiation strategies;
- Focusing on innovation;
- Enhancing communication as the key to success;
- Encouraging the participants to acquire new knowledge and skills.
The project has shown that it is crucial to be a good leader that convinces the staff members to use conflicts as the source of sensible solutions to the problems. Furthermore, the significance of innovation as the basis for success needs to be mentioned. Finally, the quality of communication defines the efficacy of the participants’ performance, as the project shows.

Use of Lessons Learned for the Future
- Promoting change and improvement as the basis for the project development and implementation;
- Detailing the significance of communication and cooperation to the people involved in the project;
- Creating an efficient strategy for improving the team members’ competencies.
The implications of the project indicate that the organizational behavior of the team members and the choice of the leadership strategy play a significant part in the overall outcome. Therefore, it is essential to make sure that the proper leadership approach is used to reinforce the communication process and encourage the participants to share the available information. Moreover, the team members must feel inclined to acquire new skills and knowledge and use them to advance the project. Thus, an impressive success can be expected, and the foundation for the further accomplishments will be set.

Project Documentation
- Using intranet as the means of transferring and collecting the relevant information;
- Recording the crucial events with the help of the electronic tools;
- Making the staff members submit reports detailing the actions taken in the course of the project on a daily basis.
All important steps of the project must be documented properly. Corporate databases will be used to store the crucial data, whereas the organization’s intranet will be utilized to transfer and collect it. Finally, reports submitted by the staff members on a daily basis will serve as the source of crucial information.

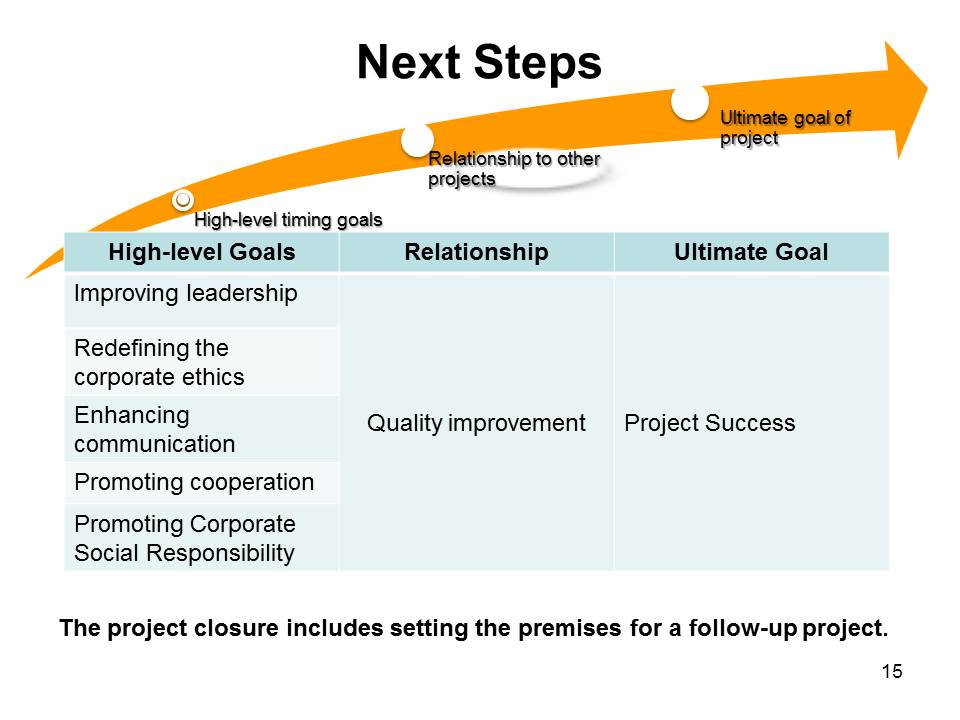
Next Steps
- High-level timing goals;
- Relationship to other projects;
- Ultimate goal of project.
The project closure includes setting the premises for a follow-up project.
References
Chatfield, C., & Johnson, T. (2013). Microsoft Project 2013 step by step. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education.
Global automotive executive survey 2017. Web.
Laasch, O., & Conaway, R. N. (2014). Principles of responsible management: Global sustainability, responsibility, and ethics. Thousand Oaks, CA: Cengage Learning.
Larson, E. W., & Gray, G. E. (2011). Project management (5th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Professional.
Marquez, P. F. G., & Lev, B. (2016). Big Data management. New York, NY: Springer.
Pyzdek, T., & Keller, P. (2014). The Six Sigma handbook (4th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Professional.