Introduction
360-degree feedback is an assessment evaluation tool that is focused on employee job performance from a multisource perspective. It is also referred as a multisource assessment or a multi-rater feedback since it relies on information from various actors. Ideally a 360 degree feedback assessment is done by evaluating an employee job performance through a comprehensive investigation of their working relationship, from both an internal and external perspective.
The idea is to generate an accurate assessment of an employee job skills, quality of work output and team work abilities that can be relied for employee assessment and job evaluation (Hazucha, Hezlett and Schneider, 1993). In this paper we are going to analyze the 360-degree feedback by discussing it process, pros and cons as well as investigate the effect of culture and ethnicity on it outcome.
360-degree Feedback Concept
The 360-degree framework of evaluation revolves around the employee on whom the assessment is being conducted plus four other key actors that complete the evaluation cycle; peers, customers, superiors and subordinates (Linman, 2006).
In some other instances, the 360-degree feedback evaluation is more comprehensive and incorporates a variety of other external factors besides the customer as is the case in the model shown below. A well implemented 360-degree feedback is very valuable both to the organization and to the employee since it is a valuable tool of determining an employee potential value which needs to be tapped.
While at the same time informs the employee on the areas that they need to improve on in order to advance their career (Linman, 2006).
Perhaps, the most important actor in the process of 360-degree evaluation is the feedback information obtained from peers who can accurately rate the employee work quality and habits since they are at the same work level (Vinson, 2010).
Superiors and subordinates are also important actors of 360-degree feedback evaluation since they determine the effectiveness of an employee from two other opposite perspectives. Finally, external actor’s such as customers are valuable as source of information only when they are reliable (Vinson, 2010). Indicated below is a theoretical and simplified 360 degree evaluation model.
360-degree feedback model
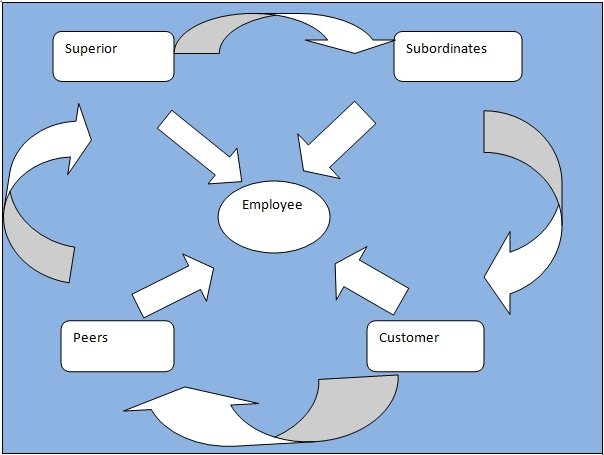
The importance of 360 degree feedback in organizations is one of valuable importance; the main objective is to generate reliable information that would enable employee to achieve self-development that would advance their career and in the process benefit the organization as well (Sullivan, 1998). As such 360 degree feedback tool is primarily used as a personal development tool rather than as an organizational evaluation tool.
360 degree feedback: Pros and Cons
The effectiveness of 360 degree feedback in any type of organization largely depends on the nature of working environment. While 360 degree feedback can be an accurate and reliable tool, it can also be abused to advance personal interest in work environments where office politics are very much polarized (Hazucha et al, 1993).
Hence, it is crucial for the management to assess and determine the suitability of using 360-degree feedback evaluation based on the unique circumstances of the organization by ensuring that it application cannot be sabotaged for personal gains.
More often and almost always the case, use of 360 degree feedback is seen to be ideal in organizations where employee support each other career growth within a productive work environment (Linman, 2006).
In such organizations employees do not take criticism negatively or personally, in addition the organization trains their personnel on proper method of giving feedback, enforces confidentiality code and customizes the 360 degree feedback approach to fit the particular organization goals (Linman, 2006). More importantly, the organization should not entirely rely or indeed peg this type of evaluation approach to employee promotion or as a basis of determining pay rise.
On the other hand 360-degree feedback evaluation process has been determined to be least effective in organizations that rely on it as a tool for employee promotions and pay rise (Linman, 2006). This is because under such conditions of employee evaluation the stakes are high enough to motivate malice that is intended to sabotage fellow employee career rise since the element of competition has now been created. In addition, lack of confidentiality on given feedback only serves to fuel the distrust and even heighten the office politics.
If the whole process is not customized to evaluate on the goals and objectives of the particular organization, and where no other evaluation approach is used to substantiate the 360-degree assessment, you can be sure that the whole process would be a big failure (Linman, 2006).
The effect of ethnicity and culture on 360 degree feedback evaluation can either have negative impact or no influence at all, again depending on organizational work environment (Heathfield, 2001). Most often, ethnicity breeds distrust in people when racial profiling is directed against particular communities, it is therefore obvious that peer review evaluation under such circumstances cannot be objective.
Conclusion
As such, it is important that a 360 degree feedback evaluation process be undertaken only in organizations where mutual trust exists among employee work relationships, and where work environment is generally respectful without the elements of competition. The aim of organizational leaders would therefore be to determine if the application of 360-degree feedback evaluation process would be suitable to their organization setup, and whether it would enable them to achieve an objective evaluation of their employees.
References
Hazucha, F., Hezlett, A. & Schneider, R., (1993). The Impact of 360-degree Feedback on Management Skills Development. Human Resource Management, 32(2): 325–351.
Heathfield, S., (2001). 360-degree Feedback: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly Defines and Examines Multirater Feedback. Web.
Linman, Terri. (2006). 360 Degree Feedback: Weighing the Pros and Cons. Web.
Sullivan, J. (1998). HR program Evaluation Template: 360-degree Feedback. Web.
Vinson, Mary. (2010). The Pros and Cons of 360 Degree Feedback: Making it Work. Web.