Introduction
As domestic markets mature and competitive activity intensifies, foreign business expansion is becoming an increasingly important component of most business enterprises across the world (Miller, 1998).
Future growth in international market activity is apparently expected to accelerate because of unprecedented opportunities that are presented by emerging markets. As observed by Miller (1998), emerging economies usually experience four distinct phases of demand development as shown in figure 1.
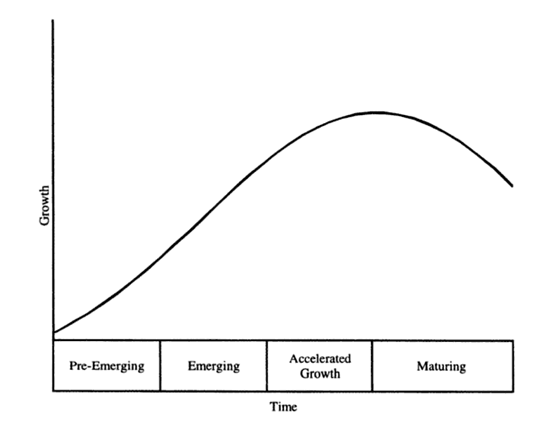
Figure 1: Phases of Demand Developments in Emerging Economies – adapted from Miller (1998)
One of the principal benefits of developing overseas markets is the opportunity to achieve increased sales. Managers around the globe are recognizing the increasing necessity for their companies to develop the skills, aptitudes and knowledge to compete effectively in international markets.
The emergence of a more open world economy, the globalization of consumer tastes and the unabated expansion of Internet access globally, all increase the interdependency and interconnections of national economies across the globe (Rugman & Collinson, 2009).
There are, however, challenges that are associated with entering a new market in a foreign country.
Because of geographical distances, and the complexities of operating in a number of disparate markets where risk and uncertainty are high, the need for knowledge and understanding is of paramount importance in international marketing (Doole & Lowe, 2008). Table 1 shows the differences between single country operations and international operations.
Table 1: Differences between Single Country Operations and International Operations
This paper presents an international marketing strategy to be used by a company to enter a new market in a foreign country. The paper is organized in three major sections: situation analysis, recommended marketing strategies, and economic evaluation.
Situation Analysis
Before a company can expand its market base to a foreign country, an in-depth preparation is very critical. The marketing department will need to plan the method by which the entry into the new country will be accomplished and how the stated objectives will be realized.
Usually, the objectives serve as the driving force for the ambition to move into the new ground (Clemente, 2002). A major responsibility on the part of the marketer is to determine the what, where, when, and how to complete the process. These are briefly explained in the following sub-sections.
What
Under ideal circumstances, all information could be made available to the market researcher and this can then be quickly sorted into what is relevant for the research. The reality, however, is that information is scattered and sometimes hidden and completely unavailable to the market researcher. Access to the information may be restricted by governmental, proprietary, budgetary and temporal constraints.
As suggested by Curry (2009), a company should divide its market research into two main sections. There will be cultural information and commercial information.
Where
To be successful, the company should conduct its cultural research inside the target nation. It is not advisable to depend on cultural information. Although reading tour guide books and national histories is useful, this should only be done as preparation for a research trip by the company’s marketing team and not a substitute for the real work that must be done in the target country.
Commercial research, on the other hand, may be partially conducted in the company’s domestic market in case the target nation has a history of economic openness. Despite the fact that the Internet and governmental databases may serve as good sources of statistical information, surveys and product testing must be conducted within the target market to get first-hand information (Doole & Lowe, 2008).
When
Although global business often moves quickly, research and access to information sources can be time consuming. It is important for a company considering entry to a foreign market to conduct its research as soon as possible within the shortest period considered prudent (Rossi, 2010). If the company takes too long to complete its research, the final report may contain information that is out of date.
How
The company may choose from a variety of different means available for conducting market research. One option is to gather its own information or use that was provided by government agencies or consulting companies. Face to face surveys among consumers or observing their behavior from a distance is another approach that the company can take in its research.
Other available options include the use of raw statistical data to build elaborate mathematical models of how a market will perform, and relying on empirical evidence as well as cultural history. According to Curry (2009), successful international market entries have been launched using all these models from large to small companies ll.
Components of the Strategic Marketing Plan
There are several different frameworks to think about and use while developing a strategic marketing plan. Some of these are explained in the following sub-sections.
Strategy and Culture
The company’s culture is “made up of people, processes, experiences, ideas, and attitudes”. The strategy indicates where “the company is headed, what path it will take, and how it will get to its destination.” (Kim, Lee & Park, 2010). According to Boone and KurtzIt (2011), it is impossible to have strategy without culture and vice versa.
Internal and External Framework
A company will usually have an internal and external framework. The marketing strategy is external to an organization and contains information gathered from customers, competitors, industry, and the operational environment in order to “identify opportunities and threats.
Through employee surveys, board assessments, and financial statements, it is possible to identify the company’s strengths and weaknesses, which are internal” (Raymond, 2003).
The Balanced Scorecard Perspectives
This is a framework that is applied in order to develop objectives in four main directions. They include financial, customers, internal business processes, and people (Raymond, 2003). While financial, internal business processes, and people are internal the customer is external.
Market Focus
Growth always comes from the main focus being on customers and thus consequently delivering the best services to them. The market focus framework touches on making sure that customers are satisfied. It is very critical to the growth of the organization.
Preparing for Market Entry
Markets are never completely open or completely closed (Curry, 2009). Every market presents the aspiring entrants with an enormous number of possible doors through which to pass. Some of the doors are unlocked and as clear as glass, while others may be as solid as steel.
It is important for the company to understand that ease of entry does not directly imply that the company will realize good profits once it settles in the new country. Oftentimes, governments keep the most lucrative markets well secured mainly to protect its local businesses. Other times, doors are left open and unguarded in an attempt to lure unsuspecting investors or traders to a pitiable and profitless fate.
There are also possibilities of lucrative doors suddenly swinging wide open for a moment and then closing. In some instances, a company may only need to have the name of the right person associated with them to gain entry into a new country. In all these cases, a company’s ability to properly analyze the information available will determine which door to approach and what product or services to present when the door finally opens.
Regardless of the approaches that the company decides to take, devising a blueprint to guide the entire process of entry to a market in a foreign country is critical for success to be realized.
Carrying out an exhaustive research in the identified foreign market will enable the company to attain the original goal and avoid numerous distractions sound during the information gathering stage. A detailed marketing plan assures that everything is taken into account before the real investigative work can start.
Foundation for the Marketing Plan
A marketing plan is the “formalized roadmap that describes how the company will execute its chosen strategy” (Curry, 2009). The company’s international marketing plan will provide a strong foundation on which its entry into the new country will be based. It clearly outlines what the company intends to do so as to reach its intended goal.
An effective plan will help to focus the energy, resources, and time of everyone in the company towards the same direction. The plan will also make it possible for the company to build a competitive advantage, communicate its strategy to staff, prioritize its financial needs, and “provide focus and direction to move from plan to action” (Curry, 2009). It is the company’s plan of execution to ensure that everything goes well.
Elements of the Strategic Marketing Plan
Successful companies develop strategies for marketing their products. The strategic plan guides the marketing department as it makes decisions about the attributes of the product, its distribution, promotional activities and pricing (Pride & Ferrell, 2008). A clear understanding of the foundation of marketing is essential in formulating a strategy and in the development of a specific marketing plan.
The key elements of the strategic plan are vision, mission, goals and objectives, strategy, and execution and evaluation. Figure 2 shows some of the elements which are briefly explained in the subsequent sub-sections.
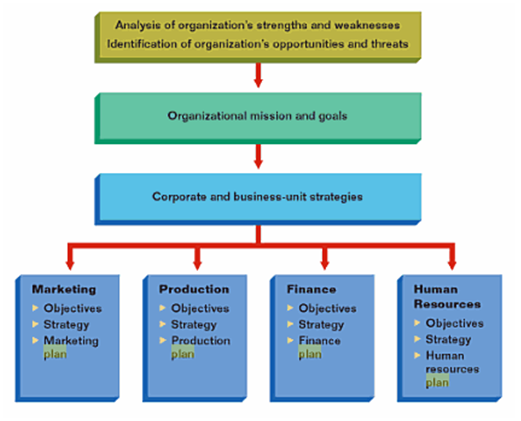
Figure 2: Elements of a Strategic Plan – adapted from Pride and Ferrell (2008)
Vision
Usually, one gets what he or she focuses on. The company must have a vision that will help to bring things to focus. Rather than paying attention to urgent problems, the company should instead focus on vital long term issues.
Unless the company can get staff to focus on a common vision, chances are that it will not go anywhere (Monye, 2000). A clear vision will ensure that the energy of all key players is directed towards the common goal of developing the foreign market. It will therefore pay for the company to have a vision that will allow it to marshal the efforts of its team.
Mission, Goals, and Objectives
The mission statement, goals, and objectives exist in a strategic plan to empower employees to be more effective. They provide the framework to be used by the company to make independent decisions that will make it possible for the company to be successful in the execution of its marketing plan.
The company must have its mission statement, goals, and objectives for the entry into the new country clearly stated and in a way that can be easily articulated by all the concerned parties.
Strategy
Once the mission, goals, and objectives of the entry into the foreign market are made clear, the company will then proceed to establish how they will be achieved. The strategy will show how the company will achieve what it wants with the resources at its disposal.
With a good strategy, the company will be able to out-perform its competition, achieve a sustainable competitive advantage, grow its revenue, maintain or shrink its expenses, satisfy its customers in the new market, and respond to the changing international market conditions.
Execution and Evaluation
All the best missions and strategies in the world are a waste of time if they are not implemented. With a clear marketing plan in place, the company should not hesitate to move into the action stage. The success of the planning process is usually about keeping the plan active. To ensure that the company does not go off target, execution should be subjected to periodic evaluation.
Major Planning Pitfalls
The company should be aware of the fact that the planning process may yield less than desirable results due to the presence of numerous challenges that may be encountered in the process. First of all, a plan is only as good as the information on which it is built (Moutinho & Chien, 2008).
The company should avoid depending on untested assumptions which are always risky to follow and lead to erecting the marketing plan on an unsteady foundation. The company should also not ignore any information discovered during the planning process that may require the company to take a different direction.
Before embarking on a serious plan to enter the foreign market, it will be helpful for the company to clean up any internal messes which may later interfere with the entire process. It is important for the company to be in good shape before moving forward.
Finally, the company should not fall into the trap of copying the best practices of another company involved in a similar business. Even though employing best practices from your industry is important, experiences of other organizations may not be relevant. It is important for the company to find its own path rather following that of others.
Tips for Better Planning
There are a number of useful tips to ensure that a company succeeds in its supposed entry into the new country. The first thing is for the company to put together a diverse but appropriate group of people to constitute the planning team (McEwan, 2001). A better marketing plan will result from diversity.
For effectiveness, the company should bring together a small core team of leaders and managers who represent every area of the company. Another useful thing to do will be to allow enough time for strategic thinking. It does no help to try and squeeze strategic planning discussions in between putting out fires (Sen & Bhattacharaya, 2001).
The company should do whatever is necessary to create time for big picture thinking. This may include taking the team off site. It is also important to get full commitment from key people in the organization. If the team does not receive support from key stakeholders, it may result in a disaster eventually. There should be an allowance for open and free discussions regardless of each person’s position within the company.
If necessary, the company should hire an outside facilitator. Since good strategic plans are flexible, the company’s marketing plan should not be made rigid or unbending. It must be reviewed periodically to make sure that everything is on course.
Assessing the Company’s Readiness
As part of the situation analysis, it will be wise for the company to assess if it is ready to take the challenge of entering a foreign country. Successful planning and implementation will require a keen understanding of how well the company can adapt to fit into the foreign market. Introducing a concept at the right time is critical to guaranteeing a successful implementation.
This is the point in the entire planning process where it is important to be brutally honest. Any company that jumps into planning by assuming it is ready is likely to fail somewhere along the way and the whole process can easily get derailed.
As part of evaluating itself, the company should look at where it is presently, where it wants to go, and how it will get there. These are briefly explained as follows.
Where the Company is currently
This can be easily determined by looking at the foundational elements to ensure there has not been a change. It is important to look at what is happening internally as well as externally to determine how the company needs to shift or change.
These foundational elements are the mission statement, values or guiding principles, and Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats (SWOT) analysis. These elements are crucial in assessing the company’s strategic position. While the company can build on its strengths, it can make attempts to minimize weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and recognize the threats.
Where the Company is heading
This helps in imagining how the organization will look like in the future. The elements that help to determine the future of the company include sustainable competitive advantage and vision statement. Sustainable competitive advantage explains what the company is best at compared to its competitors. Vision statement on the other hand helps to formulate a future picture of the company.
How the Company will get there
This is like the core of the marketing plan but also the most time consuming. It takes long mainly because there will be a number of routes from the current position to where the company desires to be.
Recommended Marketing Strategies
One entry mode that may be used by the company is Foreign Direct Investment (FDI). This approach involves the transfer of financial, capital, technology, and other skills that are considered necessary (Moosa, 2002). It gives rise to costs and benefits for the countries involved. Both the investing country and the host country are affected in the process (Agarwal & Ramaswamy, 1992).
Other useful strategies to use are joint ventures and strategic alliances. The company may enter into joint venture agreements to provide services jointly with companies based in the host country. Strategic alliances will be useful where the company intends to work in the host country through local partners without fully establishing itself in there (Plante & Nordhill, 2011).
Of the three entry modes discussed above, joint ventures and strategic alliances are cheaper and commonly used by most companies. The company may therefore make use of the two options.
Another strategy that may also be used by the company to penetrate the market in the new country is branding (Zou, Kim & Cavusgil, 2009). According to Jain and Griffith (2012), developing a global branding strategy is increasingly becoming an important priority for many firms.
It will certainly be very useful for the company to brand its products as part of the strategy to enter into the new country (Welch, Benito & Petersen, 2007). The impact of global brands has further been enhanced by the movement of people, goods and ideas across national and regional boundaries (Jain & Griffith, 2012).
Other marketing strategies that will be helpful include segmentation, targeting, differentiation, positioning, and working on having healthy public relations.
Segmentation
This is the procedure whereby marketers determine how large or how small a group to approach with their products is. It is about dividing a mass market into identifiable and distinct groups or segments (Habiyaremye, 2011). Opportunities for segmentation in international marketing may seem endless.
The world can be treated as a single marketplace, or it may be seen as composed of billions of single member marketers in the form of individual human beings.
The degree of segmentation is determined by the appeal of a product to a general market and by the ease with which that product can be adapted to increasingly specific markets. For this reason, most companies start off with as broad an appeal as possible and then sharpen their focus as more insights are gained.
Initially, targeting an entire country can be risky, especially when the geography is expansive and the population diverse.
Marketers must determine how consumers in any particular group respond to the marketing mix of the product, its price, promotional efforts, and the means of distribution. Information gathered during research will be used to make this initial determination, which over time will be increasingly defined.
Given that the company may not have all the resources required to meet the demands of all people who may be scattered all over, market segmentation can be used to enable it to use what it has effectively. This will also enable it to ensure that the marketing mix elements namely; product, price, place and promotion are designed to target the selected customers (Habiyaremye, 2011).
Market Targeting
Market targeting is a company’s decision on which market segments to pursue. It commences once the company segments its market.
It is based on the evaluation of the market potential of each individual segment as determined by such factors as market size, growth, competitor activity, and the company’s own resources and corporate objectives. Based on its strength, the company should focus on delivering goods and services to a selected market segment. When this is properly done, the company will be more effective in its delivery.
Differentiation
Differentiation is the conscious effort by a company to distinguish itself from its competition. Even when a segment has been selected, it must be understood that a competitor has already made the same selection or will shortly.
This is where differentiation comes into play as a means of reaching the consumer (Lennick & Kiel, 2005). Every consumer has a reason for buying a particular product. Starting from the macro-level of marketing, marketers will have only a general understanding of such motivations upon entering a new national market. Time and familiarity will bring about micro-level marketing approaches such as consumer buying patterns.
Positioning
This is the means by which a marketer establishes the product as a distinct image or brand in the customer’s mind. Simply put, it is the management of perception and it goes beyond the consumers’ general belief about a product. Products are seen as part of a larger category, but a marketer seeks to hold a separate and singular position in the consumer’s mind (Hollensen, 2007).
There are six main steps that one can use to prepare a positioning strategy. They include segmenting the market, listing competitors, determining how competitors are positioned, identifying open positions, determining how consumers make decisions, and differentiating a company’s products.
Public Relations
This is where a company does activities to maintain or improve its image and change the consumers’ attitude towards its products and personnel. Positioning is part of this image maintenance (Czinkota & Ronkainen, 2007).
Marketers realize that a company’s image can be changed in the consumer’s mind but that too much change or too drastic a change may result in damage. Oftentimes, the image of a company isn’t entirely under its own control. The media can be a very powerful tool both for building an image and destroying it.
International companies have enormous public relations concerns as they must contend with a wide variety of overseas media cultures as well as with their own domestic news outlets (Lymbersky, 2008). Abroad, virtually everything a foreign company does both prior to and after entering a new country will be scrutinized.
Economic Evaluation
Economically, it will be necessary for the company to do a thorough evaluation to determine the possibility of carrying on with the plan to move into a foreign market. This evaluation includes undertaking a cost benefit analysis.
The company may use the Net Present Value (NPV) technique to determine whether it makes sense to carry on with the project. Other approaches include Return on Investments (ROI) and Internal Rate of Return (IRR).
Conclusion
From the discussion presented in this paper, it is quite obvious that the process of entering a new market in a foreign country is quite an elaborate one. This paper, however, presents a useful guide that may be used by a company to successfully penetrate a foreign market. If followed properly, it will lead to impressive results in the end.
References
Agarwal, S. & Ramaswamy, S. N. (1992). Choice of Foreign Market Entry Mode: Impact of Ownership, Location and Internationalization Factors. Journal of International Business Studies, 23 (1): 1 – 27.
Boone, L. E. & Kurtz, D. L. (2011).Contemporary Business. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
Clemente, M. N. (2002).The Marketing Glossary: Key Terms, Concepts and Applications. Glen Rock, New Jersey: Clemente Communications Group.
Curry, J. E. (2009). A Short Course in International Marketing: Approaching and Penetrating the Global Marketplace. Petaluma, California: World Trade Press.
Czinkota, M. R. & Ronkainen, A. (2007). International Marketing. Mason: ThompsonSouth-Western.
Doole, I. & Lowe, R. (2008). International Marketing Strategy: Analysis, Development and Implementation. Boston, MA: Cengage Learning EMEA.
Habiyaremye, J. (2011).Market Segmentation and 4 Ps. Norderstedt, Germany: GRIN Verlag.
Hollensen, S. (2007). Global Marketing: Decision-oriented Approach. Harlow: Pearson Education.
Jain, S. C. & Griffith, D. A. (2012). Handbook of Research in International Marketing. Massachusetts, USA: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Kim, G. S., Lee, L. Y. & Park, K. (2010). A Cross National Investigation on how Ethical Consumers Build Loyalty toward Fair Trade Brands. Journal of Business Ethics, 96 (4): 589 – 602.
Lennick, D. & Kiel, F. (2005). Moral Intelligence: Enhancing Business Performance and Leadership Success. London: Pearson Higher Education.
Lymbersky, C. (2008). Market Entry Strategies: Text, Cases and Readings in Market Entry Management. Germany: Christoph Lymbersky.
McEwan, T. (2001). Managing Values and Beliefs in Organizations. London: Financial Time Press.
Miller, R. R. (1998). Selling to Newly Emerging Markets. Westport, CT: Greenwood Publishing Group.
Monye, S. O. (2000). The handbook of International Marketing Communications. Oxford: Blackwell Publishers, Inc.
Moosa, I. A. (2002). Foreign Direct Investment: Theory, Evidence and Practice. New York, NY: Palgrave Macmillan.
Moutinho, L. & Chien, C. (2008). Problems in Marketing: Applying Key Concepts and Techniques. Los Angeles: sage Publications.
Pride, W. M. & Ferrell, O. C. (2008). Marketing. Boston, MA: Cengage Learning.
Plante, J. & Nordhill, K. (2011). Beyond the Choice of Entry Mode – A case study of Micropower. Norderstedt, Germany; GRIN Verlag
Raymond, M. (2003). Tomorrow People: Future Consumers and how to Read them. New York: Financial Times Press.
Rossi, C. L. (2010). Compliance: An Over-looked Business Strategy. International Journal of Social Economics, 37 (10): 816 – 836.
Rugman, A. M. & Collinson, S. (2009). International Business. New York: Financial Times.
Sen, S. & Bhattacharaya, C. B. (2001). Does Doing Good Always Lead to Doing Better? Consumer Reaction to Corporate Social Responsibility. Journal of Marketing Research, 38: 255 – 243.
Welch, L. S. Benito, G. R. G. & Petersen, B. (2007). Foreign Operation Methods: Theory, Analysis, Strategy. Massachusetts, USA: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Zou, S., Kim, D. & Cavusgil, S. T. (2009). Export Marketing Strategy: Tacit and Skills that Work. New York: Business Expert Press.