- Introduction
- Failures and success of E-government
- Failure of E-Government Implementation
- Implementation of E-Government Capabilities
- Fighting Crime and Terrorism
- The Improvement in the Capability of U.S Representation in Court
- Ensuring Cost-Effective Regulatory Processes
- The Implementation of Information Management of E-Government in Kuwait
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
The definition of e-government has been given as government practices that take place through electronic communications in all government levels, citizens as well as business fraternity.
Such like practices include: acquisition along with the provision of services and products; placement and reception of orders; information provision and obtainment; and financial completion and transactions. In wider terms, “e-government is the application of information and communications technologies (ICTs) to enhance the performance of government functions and services.” (Adb.org, 2010).
Taking e-government as business as usual is wrong, but it needs to be considered as a focus on the usage of digital technologies in the transformation of government’s; structures, maneuvers, and most significantly the government culture. Its operation in most cases is value driven other that technology driven.
The advantages of e-government do not arise just because of information digitalization and online placement, in its place, they arise due to new ICT tools leveraging in the provision of good services to citizens, as well as making the government least responsive and effectives.
E-government need not to be taken as a single event, or even as a project that is short lived, rather as a long term project that can be applied in the transformation of the government concentration on the citizen services. As a result, it is much necessary to come up with a roadmap of high-level e-government. Such a roadmap, need to be bottom-up with a very detailed plan of implementation.
In case the design is top-down, the roadmap need to include strategic plans that are long-term, along with corresponding annual plans. On the other hand, the bottom-up strategic plan has to concentrate on the service delivery based on the citizens along with business needs. “It is necessary that the services are prioritized and included in the roadmap tasks,” (Adb.org, 2010) for instance, income tax payment, companies’ registration, personal document application like passports.
Failures and success of E-government
Though different studies have indicated that e-government usage results to greater impacts, but it needs a mass of citizens and business fraternity that are acquainted with e-communication knowledge. This will assist in the realization of sustainable effects which might be above internal efficiency and government transparency.
The failure or success of e-government implementation relays on the strength of demand a long with support from the population. First of all, demand strength will arise from the opportunity awareness that is offered through government online service delivery that is much efficient. In addition, there need to be motivation on the side of both citizens as well as the business fraternity on the e-government service usage via relevant, compelling and reachable digital content.
There have been many e-government initiative models that have been researched on and introduced globally, however, most of the studies have not included strategies as well as politics that have been implemented by the government already, along with those that ought to be implemented in future. The resistance to change is just as a result of inadequate education among government workers, in the information and technology usage.
Different studies have shown that, transition stage, is the most important one. This is based on the fact that, it comprises the major objective that has lead to the establishment of e-government. As an effect, most failures occur at this stage. The process of uncovering and challenges and problems at this stage, the organization change and innovation has been a complex phenomenon which needs to be identified for adoption and growth of e-government.
For the ICT implementation plan to succeed, it needs to be “the best method of achieving maximum advantages for the ICT implementation is to have all success factors without the occurrence of failure factors” (Al-Rashid, 2010). On the other hand, this can’t be the case in the real world.
Under such conditions, actions of increasing the success opportunities are much needed. It has been suggested that, e-government adoption and implementation might end up having some impacts by social network. As an effect, particularly in the Middle East, more studies need to be carried out.
There are different goals and degrees that the implementation of e-government in the public service transformation might imply. The barriers to e-government in most carries tend to be both technical as well as non-technical.
Research by Al-Rashid, has shown that, “successful e-government is at most 20 percent technology and at least 80% about people, process and organizations” (Al-Rashid, 2010). Among the numerous researches that have been done in the last few decades, only a few have addressed the barriers which have been affecting the implementation of e-government in the developing world.
Failure of E-Government Implementation
In the developing countries, it has been of much surprise to notice that, the failures of e-government project, is a problem that is real and much practical. The first reason that has led to this failure is the opportunity cost of the investment. This is so especially the outlay of scarce skilled labor and capital resources. Another reason has been due to the instances where the international funding institutions advocates for the information systems as being part of public sector reform plan.
Due to this, either total failure or partial failure in one way or the other affects the entire plan, due to the negative impacts on the picture of the government implementing the project. “There accreditation rate with the international financing institutions might be affected adversely, along with their reputations for good governance might diminish.” (Al-Rashid, 2010) As a result, it is much significant to look at the failure reasons as well as e-government success initiatives in developing states.
Discussions of failure reasons for e-government implementation have just been placed as a theme in the literature of the information system. The major reason that has been placed on the failure of such projects concentrates more on the “interplay between people and technology” (Stanforth, 2011). Other than just concentrating on messy issues, this emphasis concentrates social technical issues affecting the implementation of information management in e-governments, especially in developing nations.
For instance, the discussion has been based on the interplay between technology and individuals, through e-government definitions. Though e-government has been given several definitions, they all provide the insights “into the limited sense in which the public sector reform objectives of E-government are conceived by several stakeholders” (Stanforth, 2011).
Due to summary database that has been provided, this kind of reiteration on public sector reforms and its connection to the ICTs for good governance got lost in the process. Such matters have been sidelined in most of the conferences. This is due to the fact that, conference delegates have been concentrating more on lengthy discussions that concerns technology in put, as well as the e-government program output.
At these times, the program is being regarded by the parties involved in the e-government program enactment like the concerned ministries, as technological attainment other than the function and application. Currently, “they are only development planners as well as the theorists who are voicing their concern that, the concentration should be based more on the public value along with returns that are provided by these technological investments” (Stanforth, 2011).
This idea has supported the fact that, some socio-technological point of views has been much appropriate for the analysis of information management implementation in e-government in developing nations. On the other hand, there are these which have been of great help in knowing the exact interplay that exist between social and technical factors and how it takes place. In addition to this, they also show what ought to be implemented practically when designing and implementing e-government processes to ensure failure factors are reduced.
Implementation of E-Government Capabilities
Different departments have implemented the information management in e-government capabilities across their core functional areas, with the aim of improving the department’s capability in the fulfillment of its missions. Some of these departments include the Department of Justice in the United States. This department has implemented the e-government program in the following ways;
Fighting Crime and Terrorism
The department has implemented e-government abilities in different ways upon which it helps fighting terrorism and other criminal practices. The cornerstone of this form of transformation is “the Law Enforcement Information Sharing programs, (LEISP)” (justice.gov, 2011). This has been the strategy of justice department to share information routinely, with all degrees of law enforcement fraternity. It has also used this strategy to guide the resource investment in the systems of information that will further the previous objective.
Some of the examples that have been incorporated in LEISP include; the system of tracking bomb and arsons, that was launched 2004, by the Tobacco, Alcohol, firearms and the explosive Bureau. This program is an internet accessible system that gives room to local, states, as well as the federal Law enforcing agencies to share all kinds of information concerning bombs and arson incidences and cases.
This bureau has been charged with the responsibility of all explosive incidences and cases information maintenance. It has been used as a library local, states and federal; law enforcing agencies can use and manage information.
The FBI has also developed a “robust intelligence production and sharing processes that is enabled by technologies and operated by the criminal justice information systems, (CJIS) Division” (justice.gov, 2011). For instance, the FBI intelligence web page came into being with the objective of making security information accessed by the FBI partners who have been given their own class referred to as the unclassified category, at different levels of law enforcing organs.
Around 30, 000 law enforcing personnel have participated in law enforcement online. On the other hand, the system is been accessed over 670,000 times every year. On top of all this, the FBI department has a plan of starting the collection of criminal investigation tips, or any other suspicious practices over the internet.
The implementation of the Joint Automated Book Keeping System has also strengthened the homeland securities and law enforcement practices. The move has automated the processes of booking and provision of rapid and positive mechanism of individual identification, by the use of fingerprint submission to the “FBI’s Integrated Automated Fingerprint Identification System” (justice.gov, 2011).
However, the program has not been limited to the justice department clients alone, but is much open to homeland securities, health, defense department, as well as the human services. The implementation of this program resulted to a reasonable government savings.
The Improvement in the Capability of U.S Representation in Court
The justice department has also been transforming on how to litigate through two initiative participation. One of them is through the electronic case filling. This has involved “electronic exchange of the litigation and is based on the implementation of the administration documents with the federal courts, and is based on the implementation of administrative office of the U.S courts (AOUSC) case management system, or the system of electronic case filling” (justice.gov, 2011)
The records of attorneys in the systems of federal courts, has been using this two way systems of web based communication for electronic formation, filling as well as the exchange and access of litigation papers. “There are 57 district courts that have implemented case management and electronic case filling; others include 79 bankruptcies, international trade courts as well as the courts of federal claims” (justice.gov, 2011). In addition, there are over sixteen million cases that are either in case management or electronic case filling systems.
As if that is not enough, around 13,000 attorneys have filled papers over the net. The departmental elements that have been affected by this implementation include the; U.S attorneys, the Trustee Program of the U.S, and the litigation sub-divisions. “The business processes and reengineering studies are planning to absorb the dramatic alterations at the justice department in an effective manner” (justice.gov, 2011)
Another application has found its way in the case management line of business, (CMLB), under the department leadership. The implementation objective include; the development of common solutions architecture, that has enabled the case management information be efficiently shared both within and without the agencies.
The second goal is the improvement of effective and efficient law enforcing, investigating, as well as the civil and criminal litigation case management in business processes. The third goal is the identification of common case management processes across all elements and agencies that have been driving the system and function consolidation.
The fourth aim is addressing both immediate and long-term case management requirements in the federal case management fraternity. The last but not least objective “is the provision of guidance for future CM investments across the federal agencies” (justice.gov, 2011). By the year 2005, the target architectures were developed to litigate the administrative and investigative business functions.
Ensuring Cost-Effective Regulatory Processes
The justice department has also used the e-government information management system for the transformation of the performance of our regulatory duties as follows; this has been achieved through the firearms integrated technology (FIT) initiative. The target of integrated regulatory and enforcing strategy is the provision of electronic filling abilities 600,000 “members of ATF industries, agencies of law enforcements, as well as the public in general.” (justice.gov, 2011)
The FIT objective is the elimination of standalone, as well as the isolation of applications to ensure that, all systems of firearms and arson interface and effectively communicate with other systems of AFT. FIT has been consolidating systems that have been considered as being stand-alone, that provides support to the tracing of guns; information analysis; information storage, like the on-line lead. For instance in 2004, “the system of new e-trace, dealt with over 14,000 enquiries from around 800 law enforcing personnel.” (justice.gov, 2011)
On the other hand, Drug Enforcing Administration, (DEA), has been developing two main systems; one of them being the “electronic prescription for controlled substances (EPCS), along with the controlled substance ordering system (CSOS).” (justice.gov, 2011)
This kind of initiative in one way develops the framework that allows electronic transfer of prescribed data to the pharmacy from the prescriber, while on the other hand; it involves the framework development that allows the electronic style of “DEA 222 order form industrial handling supply chain of substances that are controlled.” (justice.gov, 2011)
As an effect, in future, DEA has to standards of performances via its regulations. In addition, it has to build a public key infrastructure that will be in a position of issuing digital certificates that allows such like organizations as well as vendors serving them to transform their way of from paper transmission. Under this project, around one million medical personnel will take part.
Another application has found its way in “National Instant Criminal Background Check System.” (justice.gov, 2011)This system has been utilized by Federal Firearms Licensees when carrying out background checks on purchases termed as potential, or even those under possession of firearms. The descriptive information that is tabled by the purchasers and possessors is always searched and verification done against NCIC contained records.
The Implementation of Information Management of E-Government in Kuwait
Kuwait and Singapore signed a memorandum of understanding on undertaking co-operation e-government in 2004. The intention of this MOU was the identification of different ways of accelerating the implementation of e-government in Kuwait. In 2005, Kuwait signed another MOU with the Microsoft Corporation.
The main objective of this agreement was the expansion of information and communication technology usage and the provision its support in the state of Kuwait. As a result, Kuwait has become the highly ranked ICT knowledge based society in the Arabic nations as indicated in table 1 bellow.
Table 1, e-government ranking for the GCC countries
From: www.iseing.org/emcis/EMCIS2010/Proceedings/…/C65.pdf
Conclusion
The issues concerning technology are neither technical or means to an end, however, it needs to be considered that, the technology essence is to reveal the challenges that are facing the world, by its ordering along with the creation of concrete infrastructures. This framework can be applied well when discussing the information management in e-government implementation in developing nations. This is based on the fact that, the technology ordering concentrates relation between the admin and the citizens.
This is so particularly “in setting the boundary between the state and the market, along with ensuring greater transparency and accountability” (Danish, 2006). This has been stated as the as the as the main reason for developing nations to implement e-government plans. They do believe that, with such a project in place, it is enough to equate good governance along with increased development models. As an effect, it ends up affecting levels of international aids that they do receive from donor countries.
It has been stated that, the main reasons that contributes to the failure of e-government in most countries is “the mismatch between present realities and the future e-government system design” (Al-Rashid, 2010) the probability of failure increases, as the gap grows. The figure 1 in the appendix section has been used in the explanation of condition.
The problem that has been arising with most nations in the implementation of e-government is that, there are several mismatches between the present systems and the future systems. As an effect, there exist a lager gap between “the physical, economical well as several other contexts, between the software designers and the location in which the system is implemented” (Al-Rashid, 2010)
On the other hand, there are nations which have already implemented the information management in their e-government systems. For instance, the United State has implemented this system in the Justice department very well. Also Kuwait has signed different MOUs to ensure the success of this project.
References
Adb.org. (2010). The e-Government Applications. Retrieved from www.adb.org/Documents/Papers/E-Government/egov-techgov.pdf
Al-Rashid, H. (2010). Examining Internal Challenges to E-Government Implementation from System Perspective. Retrieved from www.iseing.org/emcis/EMCIS2010/Proceedings/…/C65.pdf
Danish, D. (2006). “The Failure of E-Government in Developing Countries: A Literature Review”. EJISDC. 26(7), 1-10. Retrieved from www.ejisdc.org/ojs2/index.php/ejisdc/article/view/277/176
Justice. gov. (2011). The Department Of Justice E–Government Act Implementation Update Budget Data Request No. 05-08. Retrieved from www.justice.gov/jmd/ocio/egovactreport2004.pdf
Stanforth, C. (2011). Using Actor-Network Theory to Analyze E-Government Implementation in Developing Countries .Retrieved from itidjournal.org/itid/article/viewFile/229/99
Appendix 1
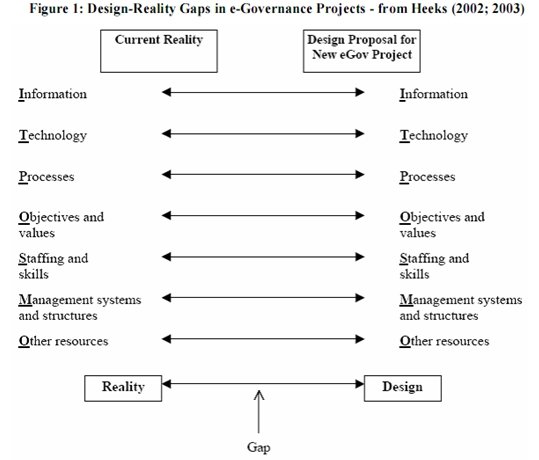
Figure from: www.ejisdc.org/ojs2/index.php/ejisdc/article/view/277/176