Description of the Company
British Airways is a giant player in the global airlines industry connecting 20 million passengers through London, the world’s largest premium travel market; however, because of the hardest times of the history due to the global financial crisis, this business had to turn round its business in order to re-establish its position in the industry.
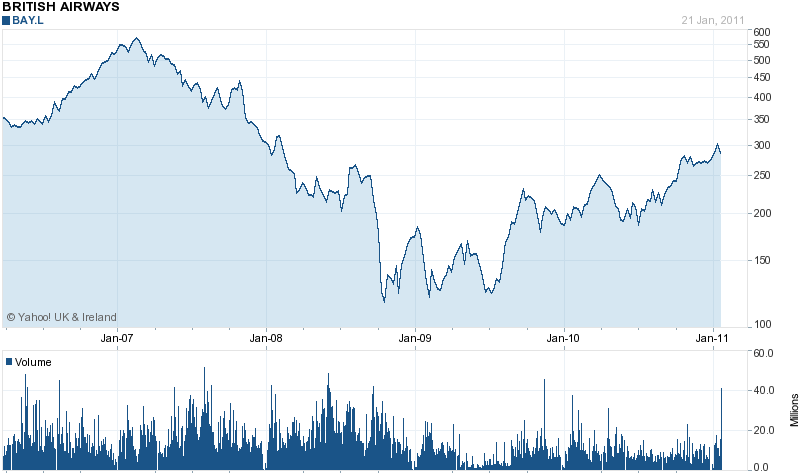
In 2008, tremendously raising of oil price and the shock of global credit crush has seriously injured the national flag carrier of Great Britain and now British Airways has shown success to overcome from the crisis; this has reflected in the basic chart of the company below which shows that it has started to recover from January 2011:
The Strategies of British Airways
According to the annual report 2010 of British Airways, the company has recently undertaken a range of strategies to overcome from the impact of global financial crisis and is hoping to perform better in good economic times through designing its long-term strategy to be the market leader as it has faced extremely harsh business environment during recession.
In addition, it has prepared its 3 years business plan and mentioned that its key goals were to develop Terminal 5’s strengths to improve the client experience, carry on to formulate the business more cost effectively, expand its businesses, and make CSR a important component of its business; however, it had to revise its plan considering recession (British Airways, 2010).
For formulating the current strategies, this airline company heavily relies on its business objectives based on which all the strategic directions has planned:
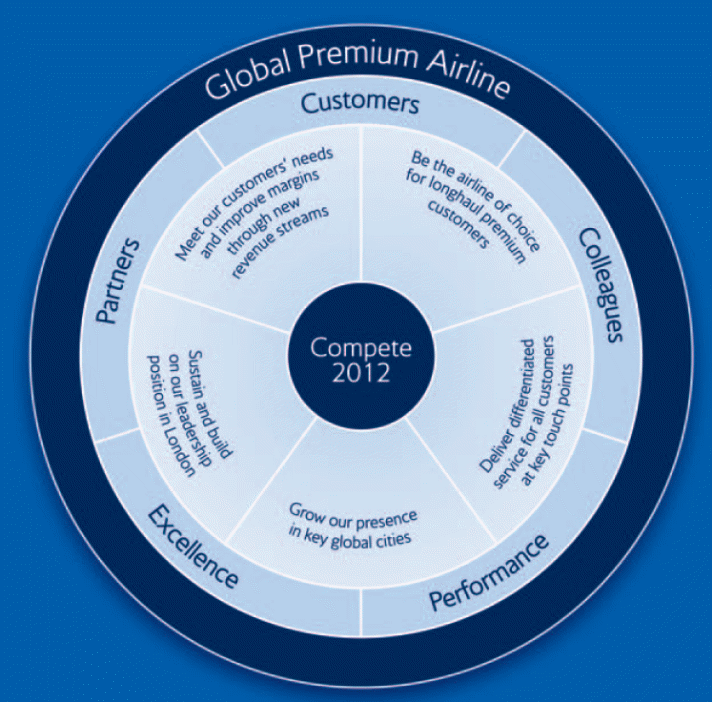
British Airways fixed its strategy considering the expansion of Heathrow Terminal 5 and it will complete BP 10 ‘Fit for 5’ programme to set the direction for the next 3 years and BP 11 contains a new theme of corporate-responsibility; in this context, summary of some of these strategies has been provided.
These, for example, includes promoting consumer satisfaction by means of the preface of text and cell phone services for business class clienteles, renovating airplane task force and presenting new services, supervising cost base, augmenting company accountability by ecological performance and affiliation; moreover, the organization have some other plans to boost revenues as well.
Terminal 5 has created based on the concept of bespoke contract to enhance its operational activities and customer services with intention to upgrade reliability and baggage targets.
Its first target is to develop customer service by the attractive product, such as, both Boeing-747 and Boeing-777 aircraft offered some additional facilitates, which are extremely gorgeous and it had also arranged fantastic reception in both terminal 3 and 5 for customer satisfaction; however, its other key strategies comprise the following outlined in the table:
Figure 3: – Some key strategies and Explanations of the directions
As the global financial crisis and recessionary economy has seriously influenced the growth of British Airways, it has strongly stood on its Global Premium Airline strategy to attain its objectives of industry leadership by cooperative strategy and cost reducing policy.
Following this global strategy BA has aimed to take the challenges of being official carrier of London Olympic 2012 and overcome the major shocks of financial downturn; the cooperative strategy has driven BA to work together with its competitors in the international operation while its cost driven strategy already contributed BA to drop £597 million fuel cost (British Airways, 2010).
BA addressed the British business community to collaborate with US business to triumph over the recessionary impact and announced a £15 million free travel packages for the business community aimed to economic improvement.
Moreover BA has determined another premium leisure strategy that driven BA to start on five new flights in 2010 routes to the Dominican Republic, Maldives, Las Vegas, and Caribbean region with almost forty percent increased capabilities both for passengers and cargo flights.
International cooperative strategy of BA inspired it to merger with Iberia, joint collaborated flight operation with American Airlines has facilitated British Airways to encounter with the flourishing mergers in the Airlines Industry that most of the competitors in the market already merged their major operations (BBC News, 2010).
The concurrent market trend of the airlines industry has driven its players to commence a large number of mergers and acquisitions all over the world; thus, the mentioned collaborations of BA with Iberia and American Airlines are an appropriate initiative of BA to gain competitive advantage to open new routes in the international operation and to grow revenues.
In addition, BA has planned a strategy to maintain a strong supply chain management with an expense of £5.2 billion per annum to procure goods and services from its tested suppliers where BA looks to the quality, cost, and resolute to establish trustworthy dealings with the supplying partners emphasising on its procurement process.
For instance, the supply of jet fuel at Heathrow is a crucial event due to the dispatch of bio-fuel and jet- fuel goes through the same pipeline while the contamination can carryout any major damage, but partnering with Solena, BA has mitigated such risk up to 2014. Conversely, this airline giant has planned some other initiatives for sustainable development.
For example, Wynn (2010) pointed out that in order to overcome this recessionary impact, BA has signed an agreement with two companies to buy sustainable jet fuel and this fuel will be produced from waste.
Here it is essential to mention that BA has already reduced the emission of CO2 up to 28% since 1990 and its present target to reducing the emission of CO2 by a further 25% within 2025 and 50% with 2050 and BA has contracted with IATA to protect the environment from pollution and to save the world from global warming.
However, Wynn (2010) also added that this project would reduce cost for fuel purpose because this plant will produce more than 16.0 million gallons green jet fuel by processing and converting 500,000.0 tonnes of waste and BA intended to get 10% of all its jet fuel from this sector by 2050.
Human Resource Management Plan of British Airways
In 2010, BA reported that its human resource consists of 34,911 UK local staffing while the numbers of overseas employees are 4,990; board of directors of BA point out the necessity of recruiting its human resources in the required fields to meet the organisational strategic objectives by reviewing management performance complying with the values and standards to bring highest outcomes.
The company has already integrated IT facilities to receive online application and selection process for its HR for international and domestic recruitments; it believes that proper HR management depends on building efficient human resources through adequate training program along with satisfactory financial reserve are two principal factors accomplishing vision 2012 as well as lead to the global airways market successfully.
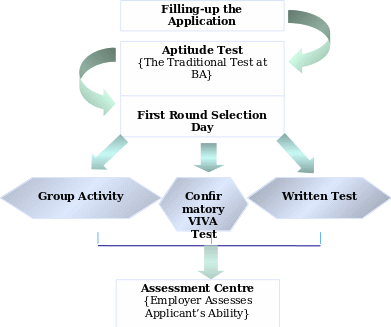
Figure 4: – Human Resource Management at British Airways
It is notable to address that the HR department of BA follows the recruitment and selection process given below to appoint new workers in the company:
Proposed Changes in Programmes of British Airways
- As the competition among airlines industry is too high, British Airways should concentrate on its fundamental service delivery to re-establish its competitive advantage
- In this context, it should consider consumers’ demand first and pay attention in market segmentation that should reflect on both income level and age limit that means it should set up the price of air ticket considering the oil price and global economy
- It is important to recommend technological advancement strategy as an effective solution for future development of BA; moreover, for long-term market expansion, it should survey the market to assess the customer demands as well as competitors’ strategies
- The business should focus more to identify potential risks and started working to minimise those risks; most importantly, it should reduce operating expanses to overcome the company from the global financial crisis
- It should increase the budget for promotion and it should build public awareness about environmental issues by advertising that low cost fuel increase CO2 emission;
- It should continue to take advantages from technology, for example, adding a scientific calculator to prove that the price of its service also competitive comparing other low cost airways; in addition, it must follow the decision of directors and non-executive directors
- It should also increase advertisement cost to convey the message to its customer that low cost offerings does not mean low quality but low cost service provider use lower quality fuel, which extremely harmful for our environment concerns; lastly, it must consider the present stock performance with a continuous monitoring.
Implementation Plan
The CEO of the company seems that implementation of the strategies and human resource management plan is one of the most important factors to overcome from adverse impact of global financial crisis as this company experienced more than £1 billion in 2010 whereas low cost airways expanded their business with profits.
Therefore, he concentrates more on the implementation of the plans and he identified that the company should restructure its human resource plan and change few strategies in order to sustain as a market leader in long-haul routes.
To implement strategies, it should require to focusing on organisational structure of BA, role and responsibilities of the directors, review corporate governance system along with corporate social responsibility, independence of the non-executives directors and so on.
However, British Airways is the pioneer of global airlines industry connecting 20 million passengers through London and it has business operation in more than 155 long-haul routes; therefore, this company has to follow complicated organizational charts, which specially includes responsibilities of the executives, and employees.
In addition, this company has more than 39900 employees and many executives to organize several sectors; therefore, it is difficult to coordinate tasks though organizational structure describes the tasks of top-management. However, the following figure demonstrates organisational chart of British Airways –
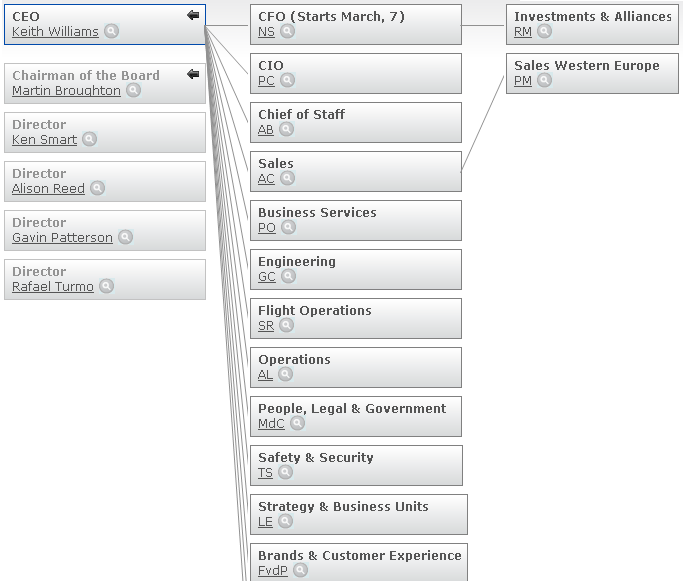
According to the annual report 2010 of BA, the Board of directors comprised Chairman, Deputy Chairman, Chief Executive Officer, CFO, and nine non-executive directors who are responsible to take major decisions and publish reports to develop corporate governance practice.
However, the board takes major decision but they need to follow the guidelines of the company, investment, and divestment strategies, Companies Act 2006; in addition, the board is accountable to its shareholders and stockholders for their activities.
According to the ethical code of conduct, the company is committed to follow the listed rules and recommendation of the reports, for example, Greenbury report to set remuneration of the executives, Higgs report, and Turnbull report to internal control, and all the provisions of Companies Act 2006 to control the company.
The CEO of BA observed that many large organizations have been collapsed for not to follow the measures designed for expense of remuneration paid to the directors’ guided in the Companies Act; as a result, BA would concentrate more on s.1 of the Combined Code, Listing Rules of the London Stock Exchange to restructure remuneration policy and human resource management.
The leadership style
The CEO of the British Airways would like to consider three major leadership approaches in order to govern the company as the success of the company depends on the implementation of the strategies of the directors.
However, he strongly train the managers to avoid autocratic leadership approach as managers enjoy ultimate power in case of implementation of strategies, act in more self-centred ways, take decisions more unilaterally under this approach and the employees are bound to follow the instruction of the higher authority.
At the same time, the aim of the CEO of British Airways is to maximise profits by ethical means; therefore, the management of this company will not impose over burden on the employees and provide liberal workplace environment. However, the CEO suggests following leadership style –
Participative Leadership Style
This approach is more consistent with the democratic style of leadership where the leaders consider open-minded attitude to deal with employees. In the era of 1980s, the leaders of BA strictly controlled the employees to govern the company and they took major decision without taking account the opinion of others, which was one of the main barriers of the company to become market leader in the aviation industry.
However, the people who are involved in decision-making process exert more effort to implement the decision than those not involved in decision-making process; therefore, the aim of participated leadership approach is that leader always makes the decision based on the participation of others.
Situational Leadership Style
According to the view of Robbins & Judge (2008), Situational leadership style does not follow any specific style of leadership rather leaders attitude differ time-to-time considering external and internal factors, motivation of subordinates, the ability of the organizational members, leader-subordinate relationship, how leader perceive the situation, the level of stress, and so on.
At present, BA is committed to control the company by maintaining under strong corporate governance system and it has Board of directors, Leadership team, and independent auditors in order to manage the company and take major decisions in accordance with the Companies Act 2006 and ethical code of conduct.
The current CEO of BA would conduct a survey to know the view of the workforce of BA on their desire leadership style and what is their expectation from the leaders in case of decision making.
However, the CEO would recommend leadership style considering the outcomes of the survey report and he would scrutinise directors’ report, Audit Committee, the Nominations Committee and Independent auditor’s report in order to ensure quality service for the customer by changing environment.
Hitt, Ireland & Hoskisson (2001) argued that there are primarily six influential aspects to the style of leadership such as efforts of the employees and subordinates, outside coordination, structure of company, support and resource, group cohesiveness and collaboration, capability of subordinates and finally clarity of the job responsibility.
On the other hand, Weihrich & Koontz (2005) pointed out another three other influential issues that affect the behaviour of the leaders and these factors are – the subordinate’s forces, the situational forces and leader’s forces; therefore, the CEO of BA would consider all the influential aspects along with survey reports to set situational leadership style.
Transformational Leadership Style
Robbins & Judge (2008) stated that leaders should inspire the subordinates to perform the required task, which motivate the team members to work with highest satisfactions; however, the CEO of BA believes, the leader always tries to build a vision in the mind of the subordinates to achieve the trust from them.
Actually, transformational leader knows well how to exert the potentials from the subordinates, and through it, he or she can achieve the objectives; however, the CEO of BA would not support this style if leaders do not follow any convention and code of conduct of BA in performing the task.
Reference List
BBC News (2010) British Airways and Iberia sign merger agreement. Web.
British Airways (2010) Annual Report 2010. Web.
British Airways (2010) Our strategy and objectives. Web.
British Airways (2011) Explore Our Working World. Web.
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., & Hoskisson, R. E. (2001) Strategic Management. 4th ed. South-Western Thomson Learning.
Robbins, P. S. & Judge, A. T. (2008) Essentials of Organizational Behavior. 8th ed. London: Pearson Prentice Hall.
The Official Board (2011) Organisational Structure of British Airways. Web.
Weihrich, H. & Koontz H. (2005) Management a Global Perspective. New Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill.
Wynn, G. (2010) British Airways to buy jet fuel from city waste. Web.
Yahoo Finance (2011) Basic Chart for British Airways (LSE). Web.