Abstract
VMware server and desktop virtualization solution is used to reduce Total Cost of Ownership for the hardware and software used in an Information Technology organization. VMware virtualization infrastructure solution provides high availability with Disaster Recovery, Consolidated Backup and VMotion to migrate Virtual Machines. This report describes how the three main components of a computer, the CPU, input/output and the memory are virtualized in VMware virtualization solution. The report describes the fault tolerance and security features in VMware infrastructure.
Enterprise desktop is one of the important advantages of VMware that not only eliminates the CPU unit from a desktop but also enables easy configuration and control of desktops in an enterprise. The consolidation of servers on one virtual server and enterprise desktop together provide a test and development environment with optimized hardware resources and centralized management via VMware VirtualCenter.
Server containment is an additional advantage of consolidation: once a virtual server is configured new VMs can be configured on the server for new applications instead of adding new boxes. The report also includes two case studies on how VMware server and desktop virtualization solution solved seemingly unrelated problems. Reduction of carbon footprint and rapid desktop deployment problems are solved for WWF-UK and Bell Canada respectively with VMware solution.
Introduction
“The term virtualization broadly describes the separation of a resource or request for a service from the underlying physical delivery of that service” (Virtualization Overview, 2006).
Virtualization is a hardware and software solution for the allocation and configuration of computing resources for optimum utilization and to reduce the operational and maintenance costs for higher Return On Investment in a business. The virtualization method is useful in computing intensive businesses such as data centre where virtualization can be used to consolidate multiple server functionality on a single physical server.
Ignorance about virtualization technology and the cost afford-ability of computer servers leads to simple deployment for reduction of software conflict probability. Due to easy availability of computer servers administrators may configure fewer applications on one server. However the increased number of computer resources leads to higher maintenance cost and wasted processing power. In order to increase resource utilization and to reduce the operational and maintenance cost of computer servers powerful processors are used in the computer servers and multiple applications are installed on a single server. (Enhanced Virtualization on Intel Architecture-based Servers, 2006).
Thesis – Virtualization Overview
- Virtual Machine has Single OS &
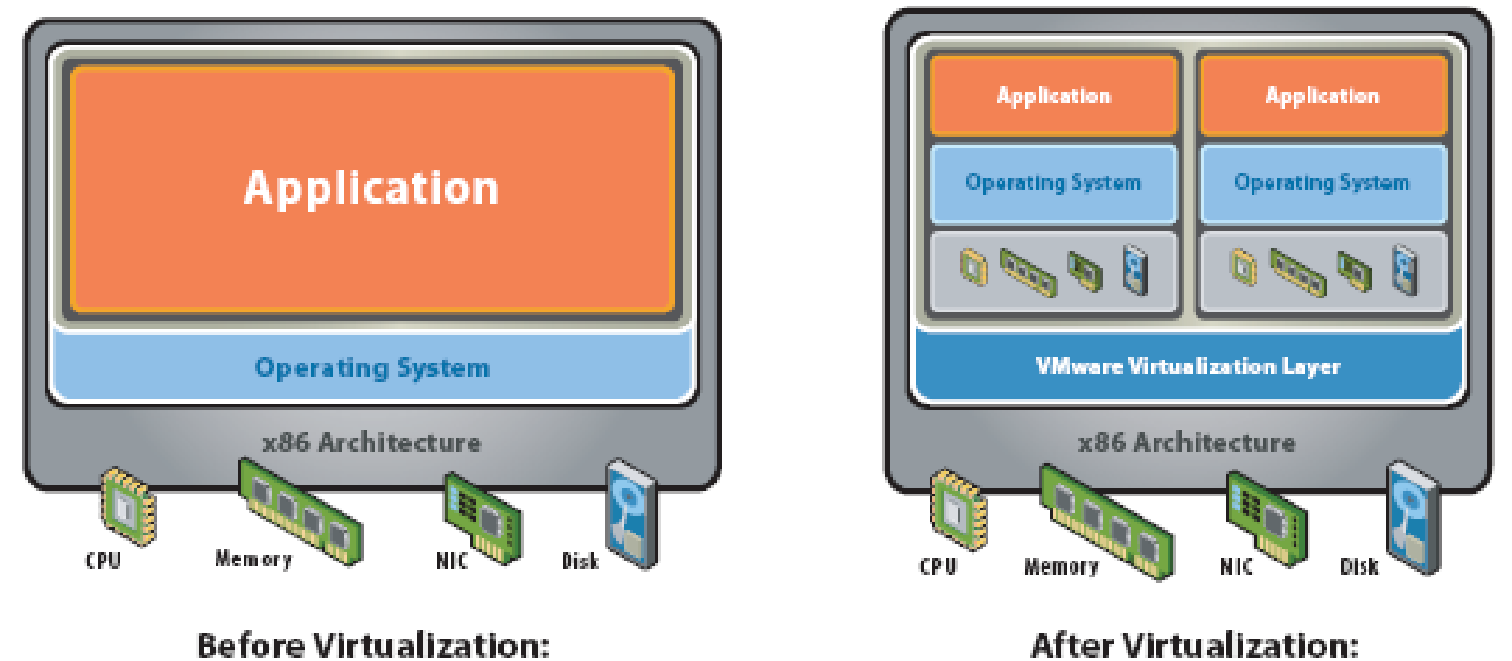
A layer is created between the hardware and the Operating System (OS) that manages the Virtual Machines (VM) created on top of the OS. This layer enables these VMs to access the underlying hardware resources. This layer is generally called Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM) or Virtualization Layer and manages the control of VMs that are abstractions of the hardware resources on a single server. The VMs thus give an illusion of multiple servers on a single physical server. The VMs run a Guest OS this OS is different from the underlying layer that may be a hypervisor or hosted OS. The applications running on a VM assume that there is a single OS i.e. the Guest OS running inside the Virtual Machine and an underlying hardware as in a non-virtual server (Virtualization Technology Overview, 2007).
VMware Infrastructure
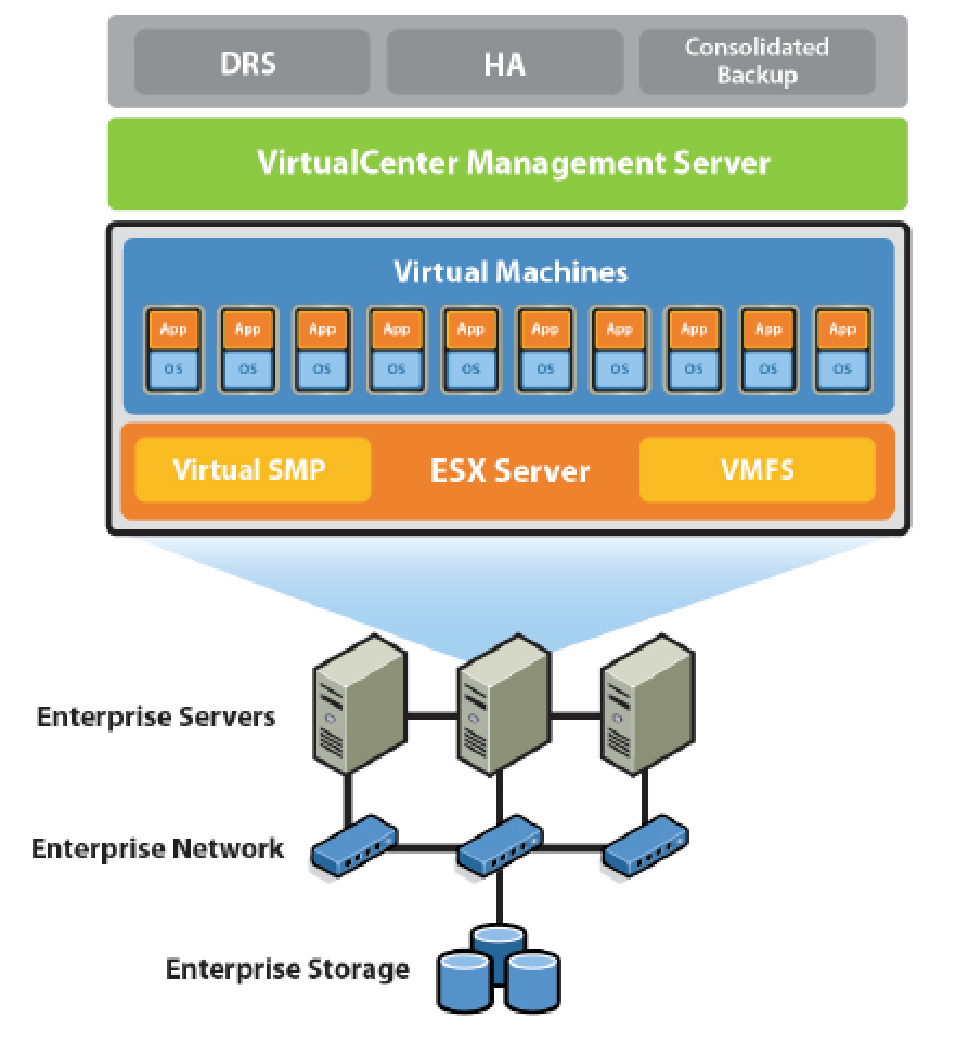
VMware virtualization technology allocates resources to VMs according to the resource requirement policies for the applications running on the Virtual Machine. Each VM has its own resources such as CPU, memory, network bandwidth, auxiliary storage and BIOS resources. The VMware Central Management Server manages ESX servers and the VMs running on these servers. A consolidated database of physical resources of all hosts, host configurations and VM resources is maintained. The control information such as VM statistics, alarms and user permissions are stored in order to ensure that critical applications have required resources at all times. Wizard driven templates provide control for the creation and management of VMs and for automated routine management.
The pool of hardware resources from more than one physical server provides virtual server solution for a data centre; this solution reduces Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and provides better utilization of resources. Virtual Machines and applications running on VMs can be assigned resources from this hardware resource pool thus making virtualization a software and hardware technology. Virtualization is a technique that separates a service from the resources used by the service. The resources may be shared between services. The services may not necessarily be aware about the presence of other services.
A service may assume that available resources are for its exclusive use. The VMware virtual infrastructure that provides an abstract layer between services and resources provides an abstraction of pooled resources that makes it convenient for administrators to manage resources and better utilize organization infrastructure (Virtualization Overview, 2006).
Virtualization Advantages
(Virtualization Overview, 2006; Intel Virtualization Technology, 2006).
Note: * Operational cost is administrative, cooling and power cost of the running system. Maintenance cost is the refurbishment cost due to damages or new requirements.
Dissertation Structure
This report describes the server virtualization technology. VMware virtualization solution is used as a reference to describe the server virtualization technology. The report is organized as follows:
- Chapter 1: Introduction describes server virtualization in brief.
- Chapter 2: Virtualization Techniques describes the hardware and software techniques used to implement server virtualization.
- Chapter 3: VMware ESX Server Architecture describes the processes and features of the VMware ESX server.
- Chapter 4: Fault Tolerance in VMware describes the add-on applications that provide fault-tolerance functionality in the VMware virtualization solution. The applications described in this chapter are: VMware High Availability, Disaster Recovery and VMotion for migration of Virtual Machine and Consolidated Backup for Virtual Machine backup on the secondary storage device.
- Chapter 5: Advantage of Server Virtualization is a descriptive list of benefits of implementing server virtualization in an enterprise.
- Chapter 6: Security in VMware describes how security is implemented in server virtualization.
- Chapter 7: Conclusion is the summary of the report.
Theory – Virtualization Techniques
Hardware Level
The hardware level virtualization is implemented by the sharing of physical server hardware resources between the VMs configured on the server.
Virtual CPU
The challenges to virtualization are:
- sharing of server physical resources
- execution of instructions that cannot be virtualized
The first objective is achieved in the hosted OS or hypervisor methods for virtual server configuration. The physical resources such as I/O interface, memory and CPU are shared amongst the VMs configured on this server. The second requirement is implemented with the following techniques (Understanding Full Virtualization, Para-virtualization, and Hardware Assist, 2007):
Full virtualization using binary translation
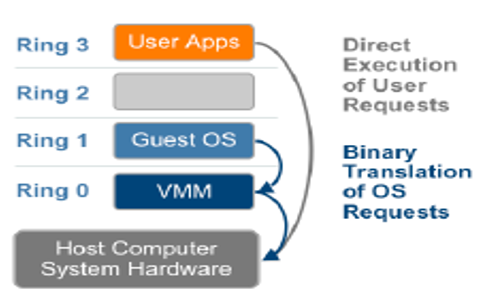
The instructions that cannot be virtualized are replaced with instructions that can be executed in the virtual server. The kernel code with replaced instructions has the same effect on the virtual server hardware resources as the original kernel code would affect non-virtual (native) server hardware resources. The new kernel code is placed in the virtualization layer (hypervisor). This translation of instructions is called binary translation. Full virtualization is achieved with binary translation because the Guest OS is decoupled from the underlying hardware resources and the hypervisor performs the translation of instructions that cannot be executed on virtual resources. The translation is performed on-the-fly, i.e. after the instruction is issued by the VM hypervisor will translate it before it is executed by the CPU.
The non-OS instructions in the user application are executed directly on the host CPU but the OS instructions that require complex transactions such as access to other resources shall require simplification that is achieved by binary translation performed in VMM. VMM provides the decoupling between Guest OS & hardware layer and thus emulates a real CPU as virtual CPU. The advantage of full virtualization is that since translation is performed in the hypervisor and the Guest OS remains unmodified the VM can be ported to any virtual server or native hardware.
OS assisted virtualization or para-virtualization
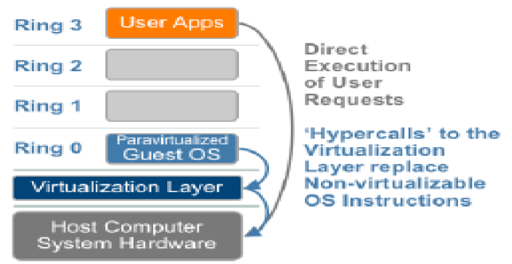
Para-virtualization is also called “alongside virtualization” due to the fact that this method addresses the communication issues between the Guest OS and the hypervisor in order to resolve the instructions that cannot be virtualized. “Para-” is also an English affix that means “alongside” and therefore para-virtualization is a method that is implemented to achieve virtualization. Unlike full virtualization where Guest OS is not modified but instead instructions are translated in the kernel, in para-virtualization hypercalls or wrapper functions are provided between Guest OS and kernel in order to communicate instructions that cannot be virtualized. Kernel may also provide hypercalls for other complex instructions such as for memory management, interrupts and timers. The Guest OS must be modified in order to include these hypercalls.
The modified Guest OS runs in Ring 0 i.e. the layer for the most privileged instructions. Due to the modifications required in the Guest OS and the kernel the para-virtualization method compatibility and portability is poor because the modified Guest OS cannot be ported on to a new virtualization layer (hypervisor) without implementation of hypercalls compatible to the new virtualization layer. For these reasons para-virtualization also adds to the virtual server maintenance cost. Para-virtualization is also used because it is relatively easy to modify Guest OS and virtualization layer rather than achieve full virtualization. Example: in open source Xen project virtual processor and virtual memory are achieved with Linux kernel modification and virtual I/O is achieved with Guest OS device drivers.
Other than virtual CPU para-virtualization is also applied to implement virtual I/O with shared memory between Guest OS and kernel; example: VMware vmxnet.
Hardware assisted virtualization
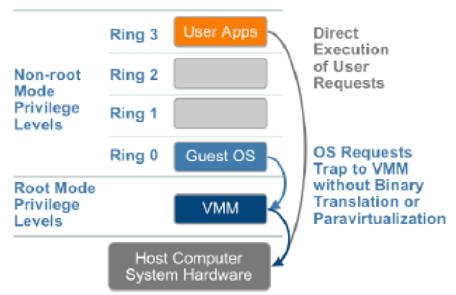
Hardware assisted virtualization is a technique to eliminate software modifications such as binary translation and para-virtualization required for the execution of privileged instructions that cannot be virtualized. This technique therefore requires enhancements in the CPU. The Intel Virtualization Technology (VT-x) and AMD Virtualization (AMD-V) have produced first generation of hardware assisted virtualization solutions. The solution introduces a new CPU execution mode so that the instructions that can not be executed in the virtual server are trapped to the VMM in the hypervisor. These instructions are executed in the new CPU execution mode and the VM state information is stored in Virtual Machine Control Structures (VT-x) or Virtual Machine Control Blocks (AMD-V) of Intel and AMD processor respectively.
VM runs in a non-privileged CPU mode and VMM executes in the privileged CPU mode to trap the OS instructions. The CPU virtualization is achieved by ensuring that all instructions issued by VM are executed on the virtual resources. In the software solution the modifications that are required to execute instructions on the shared hardware resources are performed in the Guest OS and layers beneath the VMs. The new CPU execution mode transition overhead involved in the first generation of hardware assisted virtualization is higher than the VMware binary translation solution for full virtualization.
Virtual I/O
A virtual server that hosts Virtual Machines must also provide a dedicated input/output interface for each VM. The possible solutions must consider the hardware cost of the NIC, the operational and maintenance cost and the affect of the solution on server consolidation. The software-based I/O virtualization and hardware-based I/O virtualization solutions are discussed here (The Future of Ethernet I/O Virtualization is Here Today, 2006):
Software-based virtual I/O
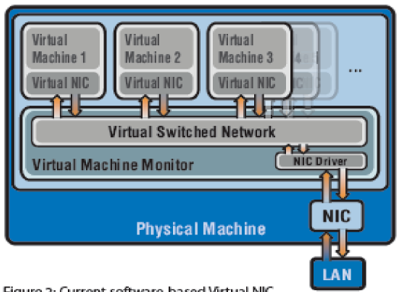
In a virtual server the I/O port is virtualized by the introduction of a virtual NIC per VM. This virtual NIC provides native NIC connection to the VM through a Virtual Switched Network (VSN). The virtual NIC is assigned a MAC address and IP address thus emulating the physical NIC that connects the virtual server to the organization network. The VSN uses shared memory for buffers and asynchronous buffer descriptors for I/O data transfer. The VSN resides in Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM). Since the VSN has to process I/O requests from multiple Virtual NICs the CPU utilization of the virtual server increases. VSN has to ensure that every virtual NIC must get appropriate share of resources such as shared memory buffers, buffer descriptors and network bandwidth in order to ensure native NIC like functionality.
The advantages of software-based virtual I/O are:
CPU utilization – In a virtual server due to the presence of multiple VMs the traffic from these multiple data sources is multiplexed on to the same physical NIC. The multiplexing of data packets from multiple sources results in less idle time for the CPU as the packet queue will remain non-empty for most of the time. In a non-virtual server the traffic from/to single physical source is to be processed therefore the CPU utilization remains low.
Network Bandwidth Utilization – The physical link bandwidth that remains under utilized in a non-virtual server due to the traffic from only one physical data source is better utilized when traffic from multiple VMs is multiplexed onto one physical link in a virtual server.
The disadvantages of software-based virtual I/O are:
Latency – Since there is one VM corresponding to each consolidated server on a virtual server therefore the allocation and de-allocation of shared resources for the multiplexed data from these VMs is performed by VSN. The processing overhead of VSN may add latency to the traffic. The latency factor may hinder the consolidation of servers in a data centre by restricting the number of servers that can be consolidated onto one physical server.
Hardware-based virtual I/O
Hardware based virtual I/O is achieved with an intelligent NIC that implements virtual I/O, TCP/IP and upper layer functionality in the NIC. The main advantage of hardware-based virtual I/O is that it shall remove virtual I/O functionality implemented in Virtual Machine Monitor from the data path and thus eliminate the latency introduced by software-based virtual I/O.
The methods for implementing hardware-based virtual I/O are:
Direct Assignment
Multiple NICs are installed in a virtual server; at least one NIC is configured per Virtual Machine. The virtual I/O functionality implemented in the intelligent NIC eliminates the requirement for data packet processing in the Virtual Monitor.
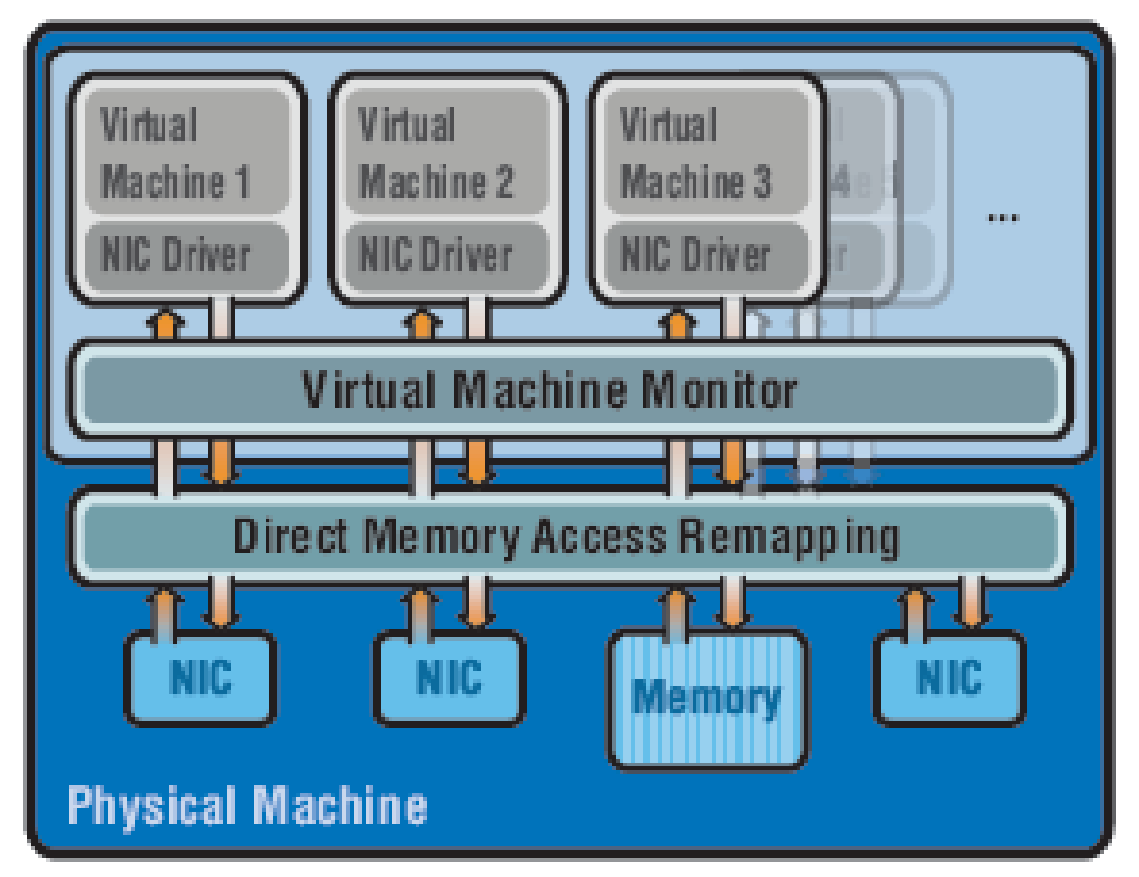
In direct assignment of NIC to Virtual Machine since Virtual Machine Monitor is bypassed there has to be a mechanism in either VM or hardware to associate memory resources used for I/O with specific VM. In order to achieve the memory association with a VM a DMA Remapping function must be implemented in the hardware. This function maps the system memory accessed by the I/O device to the VM specific memory pool, I/O page tables are used for remapping. VMM has a role in controlling the I/O operations of VMs; it isolates the DMA access requests of a VM from another VM, but is not involved in data packet processing.
This situation can be illustrated as follows: There is one DMA engine in the virtual server; the Direct Memory Access Remapping functionality assigns memory M1, M2 and M3 from the memory pool to Virtual Machines VM1, VM2 and VM3 respectively. Virtual Machine Monitor is involved in the configuration of memory pools for VMs in DMA remapping tables in order to isolate one VM from another VM. The VM may then issue the memory transfer command by writing into the DMA Queue.
When a new data packet arrives DMA engine will write the new data packet memory buffer address into the VM Queue. The VMM is not involved in the processing of the data packet to determine the source/destination VM of a data packet (this is shown in the figure as VM to DMA and vice versa path in the background of VMM). The benefit of bypassing the VMM software layer in the data path must be weighed against the advantages and requirements for server consolidation in the data centre. This method of hardware-based virtual I/O has an additional cost of a NIC per VM.
Shared Physical Architecture
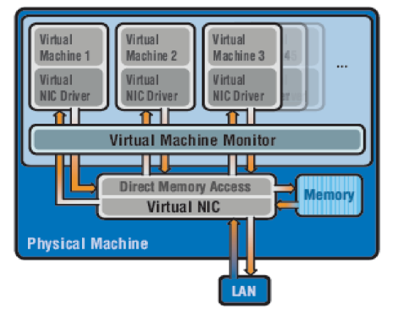
All VMs share the physical NIC device(s) of the physical server and there is no separate physical NIC device for each VM. The shared physical NIC device is called virtual NIC. The DMA remapping is implemented in the virtual NIC hardware, this virtual NIC supports configuration of a separate virtual NIC driver for every configured VM. The virtual NIC is also responsible for the configuration of separate resources for every VM and for the implementation of virtual networking functionality for virtual I/O that is otherwise performed by VMM in the software-based virtual I/O method. Parameters that must be configured are MTU size, TCP segmentation parameters, interrupts and physical link bandwidth allocation configuration. The data packet L2/L3 header processing to determine the destination VM is also implemented in the virtual NIC. The virtual NICs on the server must have a function to interface with the host OS and to enable VMM to configure the virtual NIC.
Enhancements for virtual I/O
The other enhancements proposed to reduce the processing overhead for virtual I/O and to enable inter-operability of virtual I/O devices are:
Support for logical CPU – The processor hardware will support a logical CPU for each configured VM on the physical server. I/O Memory Management Unit will be allocated for every logical CPU and DMA remapping function is included in the logical CPU. The virtual NIC will maintain a DMA I/O Translation Look-aside Buffer in the cache for recently accessed and pre-fetched addresses. These enhancements will bypass the VMM and Guest OS processing required for I/O memory access.
PCI support for I/O Virtualization – PCI Express I/O Endpoints with I/O Virtualization WG specification implementation will enable configuration of virtual servers with shared PCI based I/O devices. These PCIe I/O Endpoints will be able to interoperate with platform specific (such as different CPU or OS) DMA Remapping functions. It will also be possible to share a single PCIe I/O Virtualization Endpoint between multiple VMs on a single virtualized server. Example: Blades in a blade server may host multiple VMs and each blade may have a PCIe I/O Endpoint, this endpoint will be a virtual I/O interface for the VMs on the blade.
Virtual Memory
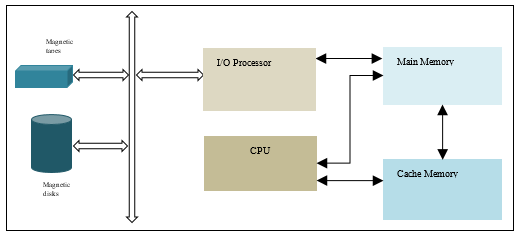
In a computer system programs and data are stored in an auxiliary memory. The program and data are brought into computer main memory as and when required by the CPU. The program and data are transferred between auxiliary and main memory by the I/O processor. The size of main memory is generally smaller than the auxiliary memory; therefore it is possible that complete program and data is not transferred into main memory in one I/O transaction.
The programmer who builds the program and data uses virtual address to refer to a memory location. When the program is executed or data is accessed by the CPU this virtual address is mapped to the main memory physical address. In a computer with virtual memory the virtual address space is larger than main memory physical address space.
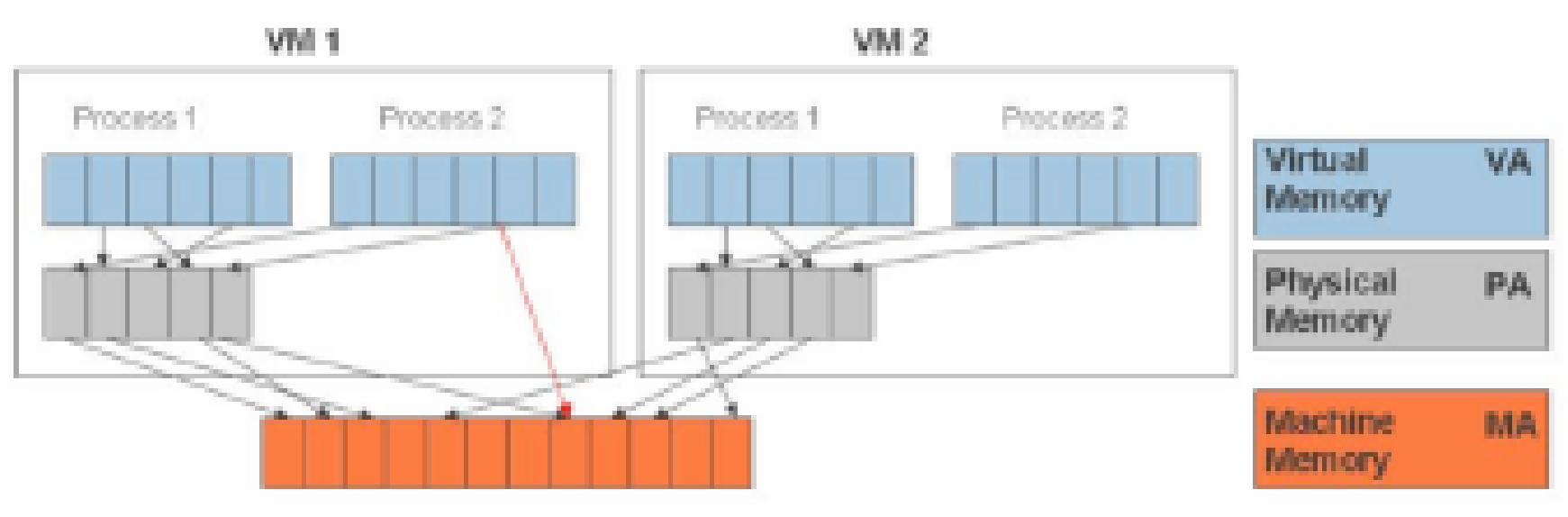
In a virtual server the Virtual Machine Monitor is responsible for mapping the virtual address to the main memory address. The physical memory shown in the figure is the server main memory that is a shared resource and is allocated per VM running on the server. The machine memory is the external memory that could be hard disk or SAN/NAS.
Storage Area Network
Storage Area Network (SAN) is a network of block-memory storage devices. SAN devices appear as a locally attached auxiliary memory to the Operating System of hosts and servers that connect to SAN. The communication protocol used between servers and SAN devices is SCSI protocol. Since SAN can be co-located in the server room or may be distantly located the SCSI cables are not used for the physical interface between the SAN device and the server.
The physical media used to connect the SAN to the servers is the fibre optic cable that runs Ethernet protocol. The SCSI protocol is mapped over TCP/IP Ethernet, the mapping protocol could be iSCSI or HyperSCSI, there are other options also such as iFCP, FICON, etc. The iSCSI protocol requires TCP/IP over Ethernet and the underlying physical layer does not necessarily have to be fibre optic cable. The SAN disk drives are assigned a Logical Unit Number (LUN). The server that has to access the SAN device initiates a TCP/IP session to the target LUN, the established iSCSI session emulates a SCSI hard disk for the server.
The storage area networks are used to provide virtual memory for servers in the data centre. In a virtual server since more than one server is consolidated on to one physical server therefore a larger capacity hard disk is required. Instead of installing multiple hard disk devices inside a virtual server the hard disk devices are consolidated to form a Storage Area Network. These devices are accessible by LUN address and are also called “virtual hard drives”. There are many benefits of providing virtual memory access for Virtual Machines configured on the server:
- Consolidation of hard disks on a SAN eliminates the requirement for installing additional hard disks on the physical virtual server. Data security that would have been achieved with a separate hard disk for every VM can still be achieved with a configuration of separate hard disk on SAN for each VM. However in order to optimize the storage utilization and reduce the power & cooling cost and hardware cost for hard disks partitions may be created on the SAN devices. SAN is also used for containment of hard disks that get scattered due to consolidation of servers as VMs on one physical server.
- Disaster recovery is simplified and system downtime is reduced with SAN connected to the physical servers. The VM image and data is stored on the SAN that is connected to both the active and the passive servers. When a VM has to be migrated for disaster recovery only VM active state data needs to be ported offline or transferred online with VMotion. The new active VM after recovery shall access the SAN disk with the same LUN that the previous VM had used.
- The hard disks that are used by the Consolidated Backup for VM backup may also be configured on the same SAN, these disks may be either co-located or at a distance.
Network Attached Storage
NAS is a file-level storage device connected to a LAN/WAN. NAS devices are used as server appliances that are used only to store data and have a functionality to allow data access and management of data access and storage activities. The hard disks in the NAS system may be arranged as logical & redundant storage devices or as Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks (RAID). NAS is accessible with file-based protocols such as NFS or SMB on UNIX and Windows systems respectively.
The advantage of using NAS over SAN is that the former provides file-system based storage whereas the latter is a block-memory storage that must be supported with a separate file-system. NAS may be used to attach an external memory resource to a virtual server. Secondary storage SAN that stores VM backup may be accessible through NAS.
Blade Server
“A blade server is a server chassis housing multiple thin, modular electronic circuit boards, known as server blades. Each blade is a server in its own right, often dedicated to a single application” (Blade Server, 2008).
“A server blade is a thin, modular electronic circuit board containing one, two, or more microprocessors and memory, that is intended for a single, dedicated application (such as serving Web pages) and that can be easily inserted into a blade server, which is a space-saving rack with many similar servers” (Server Blade, 2005).
Blade servers evolved as a requirement to reduce infrastructure complexity in data centres. The requirement was to increase the processing power and storage space in a single physical system without adding complexity to the infrastructure layout and rise in operational costs for power, cooling and floor space (Blade Server Technology Overview, 2008). A blade server may contain more than one server blade and a server blade can host more than one VM.
Advantages of blade servers are:
- The processing power and memory are directly proportional to the number of server blades contained in the blade server.
- Blade server also reduces the infrastructure space requirements by consolidating more than one computer system in one box, every server blade can be considered as an independent computer system.
- Blade servers also reduce operational and maintenance cost by reducing power requirements and simplifying cabling requirements.
- Other than on-board memory, blade servers may include separate auxiliary memory that is connected to the high-speed bus that connects all the server blades inside the box. Blade server may also connect to Network Attached Storage (NAS) or Storage Area Network (SAN) through iSCSI protocol on network port.
- The advantage of consolidating multiple resources into a single box is that it reduces administrative overhead and all resources can be managed through single management interface.
The blade servers are also referred as high-density server and used for clustering servers that perform similar task in order to achieve server consolidation and containment. Load balancing and fault tolerance features for high availability are also built into the blade server.
Desktop Virtualization
The application and data are stored at a remote server that is accessible from the thin-client user desktop. In client-server architecture a thin client is client computer/software that is used for data input and output from and to the user. The thin client does not store or process the data but provides input data to the remote server for data processing and receives the processed data for output.
In financial services such as banking data security is of utmost importance therefore data is processed and stored on the remote servers and data encryption is used for input & output data transfer. The speed of data input and output operations on the desktop depend on the data processing speed of the backend server and the Input/output interface processing speed of the server. The data processing and I/O interface of the backend server are shared by all desktops connected to the server.
The types of virtual desktop configurations are (Desktop Virtualization, 2008):
- Single Remote Desktop – The desktop PC is accessed from remote location via remote access tools such as GoToMyPC and PCAnywhere etc.
- Shared Desktop – Multiple desktop connect to a server to access shared server resources. A powerful server can handle hundreds of desktop sessions simultaneously, e.g. mainframe computers.
- Virtual Machine Desktop – Desktop connect to a server with multiple VMs.
- Physical PC Blade Desktop – PC blades are used to host multiple user sessions for better utilization of resources. Centralized processing power is provided for user desktop that connect to a PC blade.
In order to better utilize the CPU processing power ClearCube provides a PC blade virtualization solution that enables multiple users to connect to a PC blade (Virtualization Solutions, n.d.).
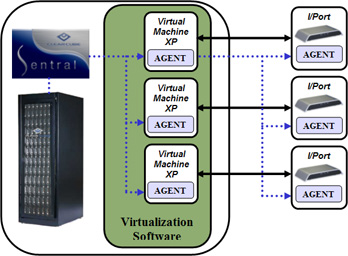
A PC blade is an Intel based computer that consists of all PC components and provides a centralized PC functionality to multiple users thus ensuring optimized utilization of computer resources. ClearCube PC blades provide virtualization with VMware virtualization solution and are manageable via ClearCube Sentral (PC Blades, n.d.).
Intel Virtualization Technology
Diverse operating systems can be installed and executed on the same server. And hence by installing multiple environments on the same server more data processing can be achieved with fewer computer systems thus reducing requirement for large data centre. Multiple environments on a single computer also assist developers and engineers to build and test applications for diverse environments. Small infrastructure also reduces power and cooling cost. The work load and complexity for system administrators is reduced with fewer number of computer systems to manage for same maintenance or administrative operation, such as backup. Virtualization is a software solution that isolates operating systems and their applications from platform hardware resources and from each other (Intel Virtualization Technology, 2006).
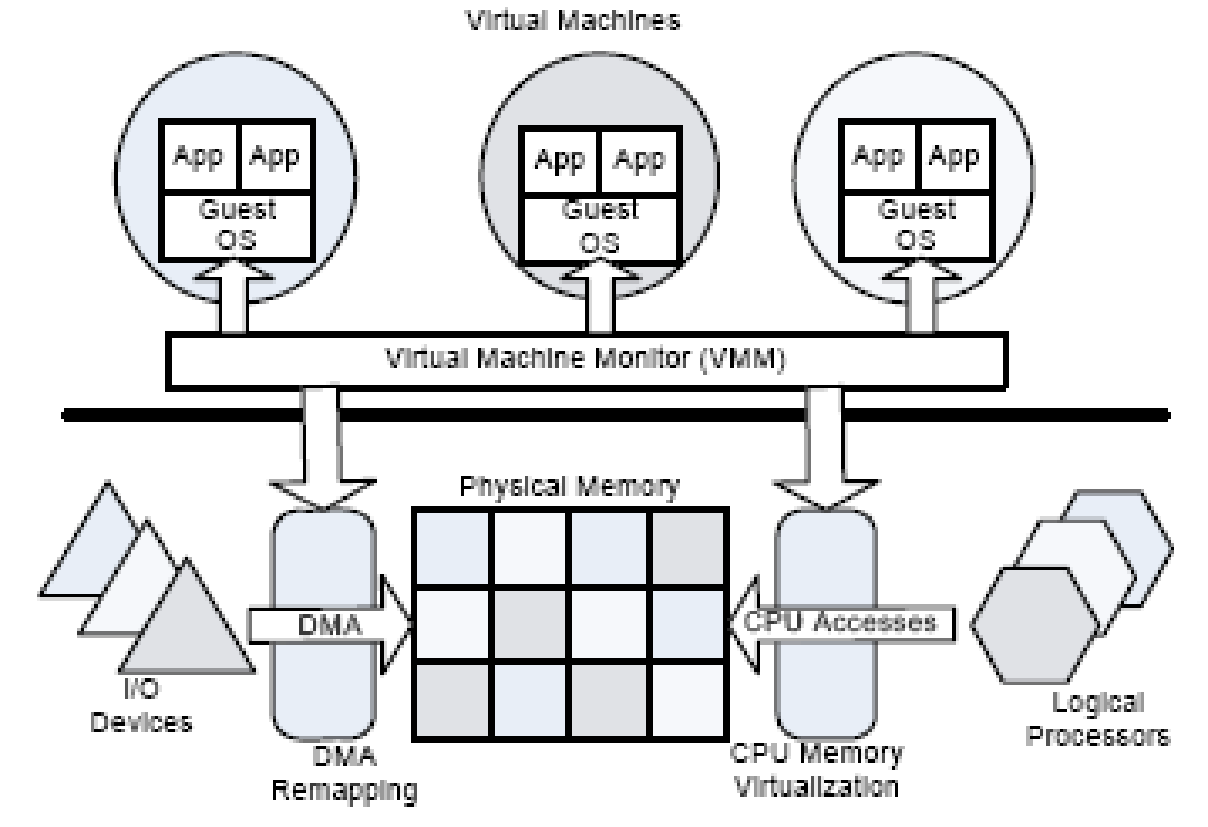
The partition with an OS is called a Virtual Machine (VM) and the applications in this partition run on this VM. The Operating System contained in a VM is called Guest OS. VM has its own security arrangements to secure Guest OS resources, application and data. A VM may operate in an isolated mode without affecting the activities in other VM. Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM) is an interface between VM and the hardware resources. VMM emulates hardware resources for the Guest OS and keeps control of the hardware platform resources. Guest OS assumes that hardware resources that are available to it are not shared and that the Guest OS has direct access to these resources.
The advantage of virtualization is that redundant VMs can be configured on the same hardware to provide system high availability for business continuity. Both test and production environments can be created on the same server in order to reduce cost by elimination of duplicate systems. New software releases can be tested on testing VM and then loaded on production VM at the time of release. Heterogeneous OS on the same server have greater compatibility. Hardware assisted virtualization has greater OS and VMM independence. VMs isolated with hardware assisted virtualization reduce security risks and protect software applications from faults that may propagate through VM and VMM in a software virtualization centre. Intel Virtualization Technology enables 64-bit support for OS and applications.
Hardware-based tasks
The Intel virtualization technology reduces the computation load on VMM by performing compute-intensive operations in the hardware. Without this technology it may be required to pass the platform control to the OS. The types of compute-intensive operations that can be performed in the hardware are memory buffer management such as allocation and de-allocation of buffers from the memory space allocated for a VM. The “dedicated memory space that stores CPU and OS state information (Intel Virtualization Technology, 2006)” is accessible by VMM only to prevent corruption of data.
Software Level
Hosted
In hosted virtual system architecture the VMs run on top of a host Operating System. Thus there are two Operating Systems a Guest OS included in a VM and a native OS that resides between the VM and the hardware resources.
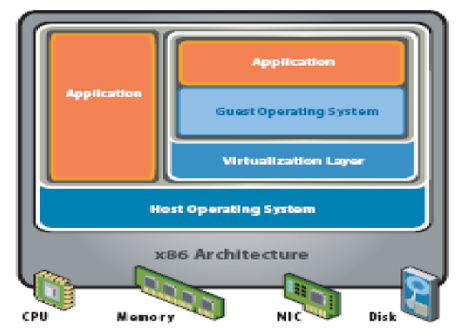
The virtualization layer provides an interface between Guest OS and Host OS. Host OS has direct control of all the underlying hardware resources. A VM is installed and executed as any other application runs on the host OS. The advantage of the hosted architecture is that the VM may contain a Guest OS different from the host OS (Virtualization Overview, 2006). In hosted virtual system architecture the VMs run on top of a host Operating System. Thus there are two Operating Systems a Guest OS included in a VM and a native OS that resides between the VM and the hardware resources.
The virtualization layer provides an interface between Guest OS and Host OS. Host OS has direct control of all the underlying hardware resources. A VM is installed and executed as any other application runs on the host OS. The advantage of the hosted architecture is that the VM may contain a Guest OS different from the host OS (Virtualization Overview, 2006).
Hypervisor
The virtualization software runs on top of the clean x86 system without any underlying OS and therefore hypervisor architecture is also called a “bare-metal” approach.
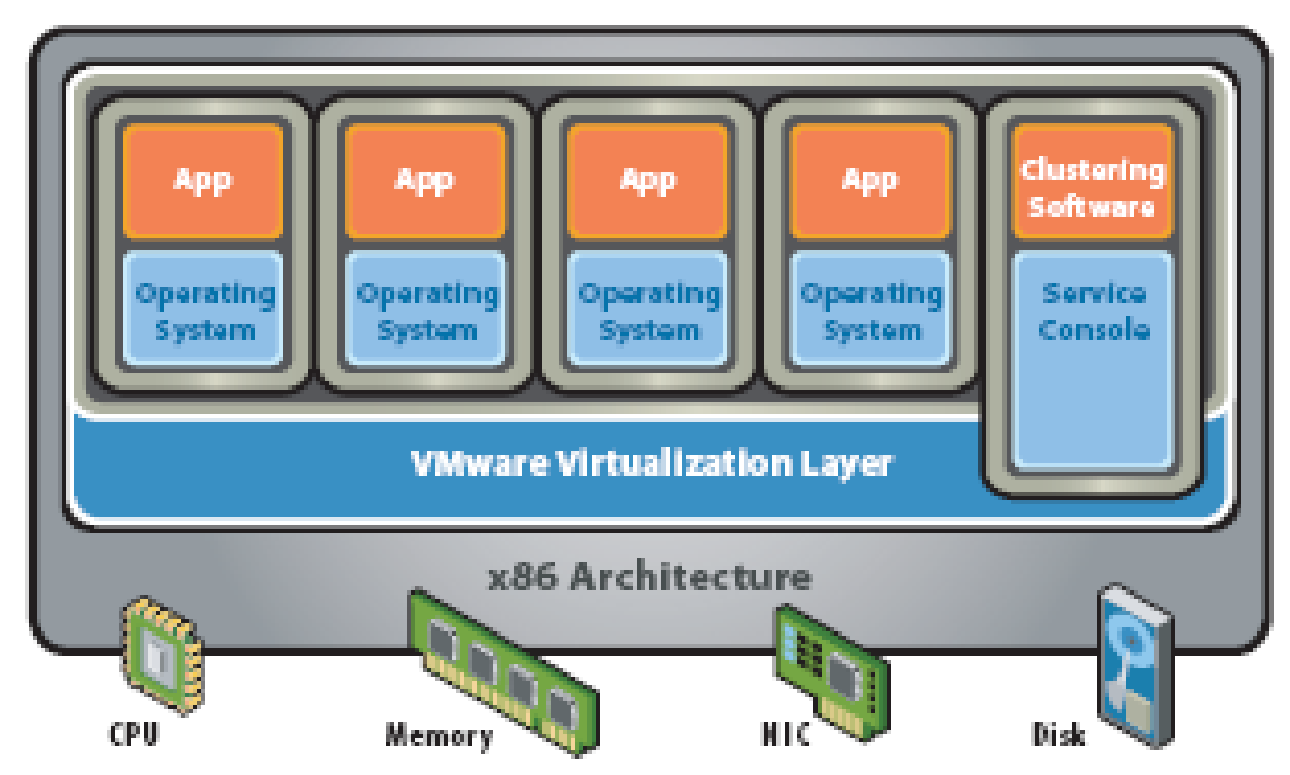
There is neither a separate virtualization layer included in a VM nor a host OS as in hosted architecture. The virtualization layer above clean x86 platform controls the system hardware resources and provides configuration interface for the resources. The Operating System included in the VM acts as a native OS unaware of the virtualization layer beneath it. In VMware hypervisor solution a service console is provided for system resources configuration management. The bare-metal hypervisors may be agnostic to Operating Systems and may therefore provide configuration flexibility by supporting different OS VMs on the same physical server. A hypervisor that is tightly coupled with any one OS will support VMs with this OS only.
A hypervisor may also support more than one but a finite number of OS. Because of direct access to the hardware resources hypervisor provides better resource utilization and hence greater performance and scalability. The absence of host OS reduces failure points and therefore disaster recovery is simple and system is more robust. The VMM in the hypervisor software provides an abstract hardware resource interface for each VM that is supported by the VMM (Virtualization Overview, 2006; Understanding Full Virtualization, Para-virtualization, and Hardware Assist, 2007).
Research Method 1- VMware ESX Server Architecture
VMware ESX server is a hypervisor that consists of VMkernel and applications that run on top of it. The ESX server 3i is either embedded in the server firmware or distributed as software to be installed from the boot disk.
VMkernel is a POSIX-like operating system, the core functionalities provided are (What is POSIX?, n.d.):
- Resource scheduling
- I/O stacks
- Device Drivers
ESX server may be embedded in the firmware or installed on the boot disk of the virtual server. On system boot the VMkernel detects the hardware devices present in the server and installs the device driver for these devices. The default configuration files are created; these are accessible and modifiable with VMware management tools such as VMware VirtualCenter and VI Client. After the system initialization DCUI process is launched.
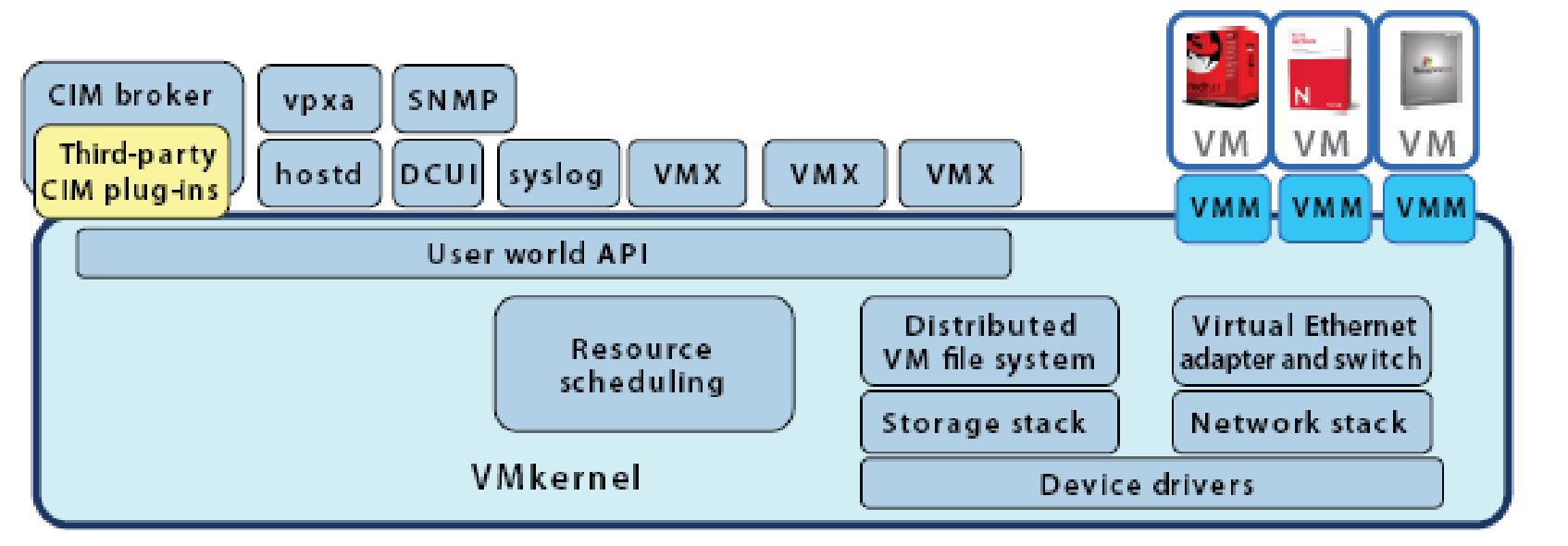
The processes that run on top of VMkernel are:
Direct Console User Interface
This is a menu-driven “local user interface that is displayed only on the console of an ESX server 3i system” (The Architecture of VMware ESX Server 3i, 2007). DCUI provides an interface for initial minimal configuration such as to set root password or to assign IP address in order to connect the server to the network if automatic DHCP configuration does not work. At a later time when network connectivity is available remote management tools may be used. Remote Management tools provided by VMware are VirtualCenter, VI Client and remote command line interface (The Architecture of VMware ESX Server 3i, 2007).
Virtual Machine Monitor
VMM is the process that provides an execution environment such as software and hardware resource control interface for the VM. There is exactly one instance of VMM and the helper process VMX per VM (The Architecture of VMware ESX Server 3i, 2007).
Agents for remote interface with VMware Infrastructure management –
Common Information Model (CIM) system
The CIM system consists of CIM Object Manager called CIM broker and a set of providers that provide access mechanism to computing resources such as device drivers and other hardware resources, these providers are called CIM providers. VMware has CIM providers for virtualization specific resources, storage infrastructure and to monitor server hardware (The Architecture of VMware ESX Server 3i, 2007).
Other User World Processes
The “user world” is the framework to run processes in hypervisor architecture of a virtual server. The native VMkernel applications are run in the “user world” and general purpose arbitrary applications are not run in the “user world”. Some of the management agents that run in the “user world” are (The Architecture of VMware ESX Server 3i, 2007):
- The hostd process provides an interface for user management. It integrates with direct VI Client connections and the VI API.
- The vpxa process is an intermediary process that provides a connection between hostd agent and VirtualCenter.
- The VMware HA agent also runs in the user world.
- The syslog daemon provides the logging facility on local and remote storage. When remote logging feature is enabled the system logs are stored on the remote target.
- The iSCSI target discovery process finds the target iSCSI device and then VMkernel handles the iSCSI traffic.
Open Network Ports
There are some open network ports on ESX server 3i to access important services such as (The Architecture of VMware ESX Server 3i, 2007):
- 80 – To display a static web page.
- 423 – A reverse proxy port for SSL-encrypted communication with services such as VMware Virtual Infrastructure (VI) API.
- 427 – A service location protocol port for locating appropriate VI API for a service.
- 5989 – CIM server port for 3rd party management tools
VI API provides access to services such as RCLI, VirtualCenter Server, VI Client and SDK.
File System
VMkernel has in-memory file system that is different from the VMware VMFS that stores VM. The later may be stored on any external memory. The in-memory files such as log files do not persist on power shut-down and therefore if the files are to be saved they must be stored on an external memory. A syslog daemon exists that stores logs on the remote target and in the local memory. The advantage of storing VMFS on external memory is that if they are stored on NAS or SAN then a local hard disk is not required and hence power is saved and system fault probability due to hard disk failure is reduced.
The file systems in-memory and VMFS are accessible with remote command line interface. The HTTPS get and put access is provided for authenticated users. The user and group authentication information and access privileges are configured on the local server i.e. the server that is the owner of the files. The local server may store these files in local or remote storage (The Architecture of VMware ESX Server 3i, 2007).
User and Groups
The system can distinguish between users that access the server through the Virtual Infrastructure Client, the remote command line interface or the VIM API. Groups are created for the ease of configuration; configurations for multiple users can be set in single step by assigning them to a group. The files /etc/passwd, /etc/shadow and /etc/group store the user and group configuration definitions. These files are present in the in-memory file system and are restored from persistent storage on reboot (The Architecture of VMware ESX Server 3i, 2007).
State Information
The VMkernel stores the system configuration in the in-memory, and since this configuration information is also copied to persistent memory periodically to avoid information loss due to sudden power shutdown, therefore the hard disk is not necessary in the VMware virtual server. The ability to store configuration information on a remote storage facilitates server configuration backup. So if a server or a VM on a server fails the failed server or the VM can be restored to the pre-failure state by downloading the configuration from the backup (The Architecture of VMware ESX Server 3i, 2007).
VI API
The external applications can integrate with VMware infrastructure through Virtual Infrastructure API or command line interface, both provide interface to VirtualCenter that maintains agents and the state of transactions. The ESX server 3i is positioned behind VirtualCenter and remains stateless since no local agents are installed here; therefore all system resources are available for computing. The advantage of this model is that the agents for monitoring and management can be stored and executed on the external system and the ESX server remains independent of any changes to these agents. VI API and CIM thus provide a model for easy maintenance and control of ESX server resources (The Architecture of VMware ESX Server 3i, 2007).
Research Method 2 – Fault Tolerance in VMware
In order to ensure business continuity with minimum Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), minimum system downtime, minimum recovery time and almost no service disruption VMware Virtualization software includes fault-tolerance applications that may be installed as add-on modules.
High Availability
The VMware High Availability (HA) feature ensures business continuity by the detection of system faults and recovery from the system faults. The VMware HA feature monitors the ESX server host for the occurrence of a fault and if the fault results in the failure of a Virtual Machine, the standby VM is restarted on the same or the alternate host. VMware Failure Monitoring functionality in VMware HA monitors both Host OS and Guest OS failures. The Host OS is the Operating System between the VMs and the server hardware resources. The Guest OS is the Operating System that is included in the Virtual Machine. (Refer figure 1) The VMware Failure Monitoring also monitors the VM availability by checking the heartbeat. The VMware Tools on a Virtual Machine sends a heartbeat to VMware Failure Monitoring every second and VMware Failure Monitoring checks the heartbeats every 20 seconds, a defaulting Virtual Machine is declared as failed and is reset.
The VMware Failure Monitoring differentiates between Virtual Machines that are powered off, migrated, suspended or powered-on and sending heartbeats or that has stopped sending heartbeats or is overloaded and therefore has resource starved VMware Tools. Starved VMware tools get less CPU time and hence fewer heartbeats are sent. The heartbeat send frequency, heartbeat monitoring time and stabilization time after start-up are configurable parameters (Virtual Machine Failure Monitoring, 2007).
Disaster Recovery
Traditional disaster recovery methods require redundant hardware equipment and same software configuration on both active and standby systems. This method may require new hardware purchases and operational and maintenance overhead for the redundant hardware. The standby system that is used in recovery scenarios may remain functionally inactive most of the time but shall still occupy floor space and also require cooling and power in order to keep it up-to-date. In addition to this the disaster recovery requires that the active system backup must be taken at regular intervals in order to keep the latest system state information in a secure storage for recovery from a catastrophic failure when both the active and the standby systems may be lost. The backup may be taken offline on tapes or online on a live network connection that shall keep the secondary storage up-to-date at all times.
The disaster recovery process is complex because it is required that in order to minimize disruption in services and to maintain the business continuity the maximum downtime of the system is reduced. To eliminate double fault scenarios such as tape fault or system image fault or both active and standby system fault more stringent disaster recovery mechanisms are required such as methods to avoid physical handling of tapes, simplification of image creation for different system configurations and testing of standby system. Virtualized servers provide solution for the complex disaster recovery methods (Disaster Recovery Solutions from VMware, 2007).
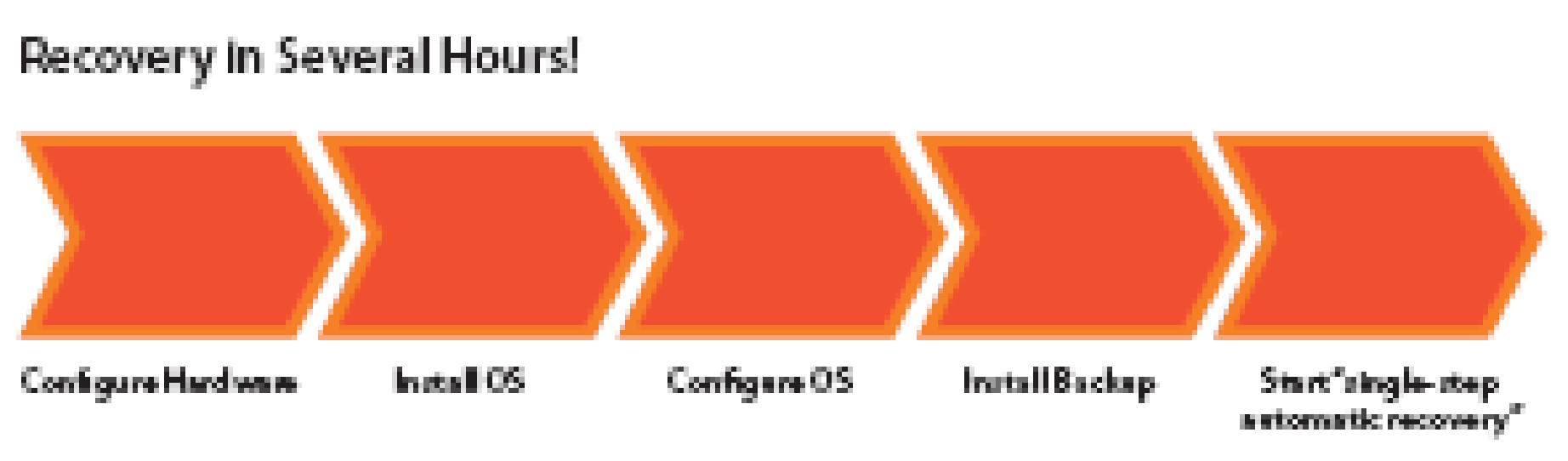
The hardware configuration, OS installation and system configuration are one time initial process that is repeated for every active server in the data centre. The recurring expenses can be reduced by backup of only critical applications that have highest impact on the business continuity and recovery time objectives (RTO). “Recovery time objective (RTO), (which) is the maximum outage duration that your end users can withstand without being disruptive to your business” (Disaster Recovery Solutions from VMware, 2007). Higher RTO values can be defined for other non-critical applications so that frequent backups are not required. The risks involved in this mechanism are that critical applications are mostly coupled with lower-end or non-critical applications therefore the faults in these lower-ends or non-critical application must not propagate to the critical applications and hence the RTO for the critical applications must be carefully defined.
The core properties of VMware infrastructure that are useful in disaster recovery are (Disaster Recovery Solutions from VMware, 2007):
- Partitioning – Virtual Machines (VM) are created by partitioning of server resources. Multiple applications and Operating Systems are consolidated onto one physical system in order to save costs on hardware resources, floor space, cooling and power requirements. Partitioning isolates applications from one another and helps reduce disaster recovery expenditure because of server consolidation.
- Hardware Independence – VMware VM can be installed on any x86 hardware platforms. The hardware independence property of VM makes configuration of virtualized servers simple. The disaster recovery is faster because complexity in creation of system images for different hardware platforms is eliminated and system start-up is simplified. Also, instead of purchasing new hardware for disaster recovery, the VM for disaster recovery can be installed on any server with required hardware resources for the VM.
- Encapsulation – The entire server/VM image including OS, applications, configurations, policies, data and current state information can be stored in a file. The migration to another server machine or VM is simplified by this property. For disaster recovery a simple file transfer is required and there is no need to rebuild the entire system from the scratch.
- Isolation – Since the applications in a VM are isolated from the applications in another VM the system updates, faults and disaster recovery in VMs can be isolated from other VMs.
The recovery process in a virtualized server is illustrated as shown in the figure below:

In comparison to the traditional disaster recovery process as shown in figure 16, the VMware infrastructure recovery process for a virtualized server is simple and short. The physical-to-physical server traditional disaster recovery process would take 40hrs whereas the virtual-to-virtual server disaster recovery process would take only 4 hrs. This reduction in time is due to the fact that the number of tasks involved in the disaster recovery process is reduced in virtual recovery process because a separate hardware configuration and bare-metal configuration are not required for every system.
Tapes are the most common mechanism for system backup; VMware infrastructure provides the following three methods (Disaster Recovery Solutions from VMware, 2007):
Backup from within a VMware Virtual Machine
A third-party backup agent is installed in the VM. If the VM is connected to the network intranet/internet the default backup location can be specified. Also the agent may have additional features to specify frequency of backup and file/folders that must should be backup. A file-level backup can be taken and restored on the VM.
Backup from VMware ESX Server Service Console
From the ESX server console the full system image can be made, the backup agent resides on the server. This is a method that can be used to make a backup file for the VMs on the server. This file can then be used to port or restore the VM. The backup mechanism granularity is not file level but instead a full VM image is made without effecting the applications installed in the VM. The in-machine mechanism described above complements this method and the two together provide a complete backup feature for the VM.
VMware Consolidated Backup
VMware consolidated backup agent can be integrated with a third-party centralized backup application in order to facilitate the backup of VM contents from a central server. Example: Microsoft Windows 2003 proxy server. There are many advantages of consolidated backup:
- Both VM file level and VM image backup can be taken.
- A backup agent is not required on every VM, VMware consolidated backup is included in VMware ESX server.
- Backup traffic on LAN is eliminated because third-party agent can directly attach to the SAN that connects to the VMs on the virtual server. As shown in the figure the backup agent can mount SAN storage disks to make backup disks.
VMware Consolidated Backup is explained in more detail in section 4.4.
VMware infrastructure can work with many types of replication solutions such as host server based, Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks (RAID) and network solutions SAN or NAS. VMware infrastructure also supports the periodic testing of the disaster recovery plan.
VMotion
VMware VMotion technology is used for the migration of VM from one physical server to another physical server or to optimize the server resources dynamically without any disruption in the Guest OS or system downtime. VMotion enhances the data centre efficiency because it provides a non-disruptive solution to maintenance activities. The VM state data is stored on a shared memory that is accessible from both the active and the redundant server. The active state data is then transmitted over a high-speed virtual network for quick migration (VMware VMotion and CPU Compatibility, 2007).
All records of migration activities are maintained in order to comply with audit requirements. VM migration schedule can be pre-configured in order to eliminate the requirement for the administrator presence at the actual time of migration. VMotion also ensures that the shared and virtual resources are available to the mission-critical applications during migration in order to avoid any disruption in the services. While migration of a VM to any hardware platform is supported in VMotion the disruption in services provided by a VM is avoided by first finding the most optimal placement for the VM before migration is initiated. The most optimal placement is the server from where the shared resources are accessible and the required virtual resources such as virtual I/O device, virtual memory and virtual CPU are available.
Requirements for VMotion host and destination are (VMware VMotion and CPU Compatibility, 2007):
- Datastore compatibility – The shared resources on the network may be made available with SAN or iSCSI interface. Alternately VMFS or shared NAS may also be used to share storage disks between the source and the destination of the VMotion.
- Network compatibility – The source and destination servers of VMotion and ESX servers must be connected to the same gigabit Ethernet subnet.
- CPU compatibility – The source and destination host server CPU compatibility is required for VMotion in order to ensure that the virtual CPU functionality in the target VM is supported on the destination server. Refer section 2.1.1 for virtual CPU functionality.
- If all the components of a server are virtualized then the Virtual Machine on the server shall have the state information for virtual BIOS, virtual I/O, virtual CPU and virtual memory. All the VM state data can be encapsulated in a file that can be easily ported on another server for a smooth and fast migration. Following types of migration can be performed:
- Powered Off – Also known as cold migration, the host VM is powered OFF and after file transfer is complete the VM is powered ON on the destination server.
- Suspended – Also known as suspend/resume migration, the host VM is suspended and then resumed on the destination server after the VM state file transfer is complete.
- Powered-on or live – Also known as live migration performed by VMotion, the VM is migrated from the host to destination server without any disruption.
In suspended or live migration since the VM application state is unaffected by the migration therefore these are also known as hot migration. VMotion performs the CPU compatibility check for the destination server before migration in order to ensure that the migrated VM does not crash after it is made live. CPUID instruction is used to determine the host CPU instructions and features. CPUs undergo improvements and ISA is augmented for new instructions.
CPU vendors code new modules in the OS to support new features. If a CPU feature or instruction set extension is present on host server and is used by VM, the same feature and instruction set extension must be made available to VM on the destination server after migration in order to pass the VMotion compatibility test. Example: Intel supports multimedia features with SSE instruction set for compatibility with AMD’s 3DNow!. The compatibility check is performed based on the following features (VMware VMotion and CPU Compatibility, 2007):
- CPU micro-architecture: Different CPU vendors or a processor family with different micro-architecture may support the same Instruction Set Architecture (ISA). Example: Intel Core-based CPU and P4 have different micro-architecture but same x86 ISA is implemented.
- Privileged/non-privileged Code: OS related instructions that execute at the highest privilege level (0) are atomic and cannot be pre-empted. Applications have most non-privileged instructions but may also use OS APIs that are privileged applications. Since the privileged instructions are atomic the execution of an instruction shall be completed without any interruption due to live migration. Migration of a VM from one server to another requires that in hypervisor architecture the Guest OS APIs are mapped to the same privileged instructions in the kernel and in the hosted architecture the host OS supports the Guest OS APIs.
Example: SSE3 instruction set in Intel for faster floating-point operations and 3Dnow! instruction set in AMD for better multimedia processing.
VMware tools for CPU compatibility check
- CPUID instruction – “VMware provides a bootable CPUID image on VMware ESX Server media” (VMware VMotion and CPU Compatibility, 2007). An application may run CPUID instruction at the beginning and based on the result choose to run or not run some features.
- Managed Object Browser – This is a browser on ESX hosts to determine the host CPU features. The browser is launched with web browser.
Consolidated Backup
VMware Consolidated Backup feature performs backup of Virtual Machines, the backup process is made simple, efficient and agile by performing Virtual Machine backup from proxy servers instead of the production ESX host server. The advantages of Consolidated Backup are (VMware Consolidated Backup, 2007):
- Online backup of Virtual Machine snapshot is possible.
- Workload on ESX server hosts is reduced by performing backup from proxy servers.
- A backup agent is not required on every Virtual Machine and backup is performed from centralized backup proxy.
- There is a facility to leverage VMFS snapshot technology in order to backup file snapshot.
- VMware Consolidated Backup can also integrate with any other backup software present on the Virtual Machine.
- Backup of Virtual Machine stored on iSCSI SAN, NAS or ESX server local memory is supported.
- The Virtual Machine backup snapshots can be moved over the LAN and hence SAN based storage can be eliminated. The use of SAN based storage requires that SAN device must be mounted on the system and then it is used as a local hard disk.
- The VMware Consolidated Backup proxy server may be installed and run in a Virtual Machine without the requirement for a tape drive in the Virtual Machine. The backup may be stored on the SAN, NAS or another secondary storage connected to the LAN.
- Consolidated Backup images can be restored with VMware Converter; image may also be customized before restoration. VMware converter is an add-on component of VirtualCenter. It is also used to create a VM template that may be used as a Consolidated Backup image for provisioning multiple Virtual Machines on a virtual server.
- Both 64-bit and 32-bit Windows Server 2003 is supported as proxy server.
Consolidated Backup with iSCSI storage
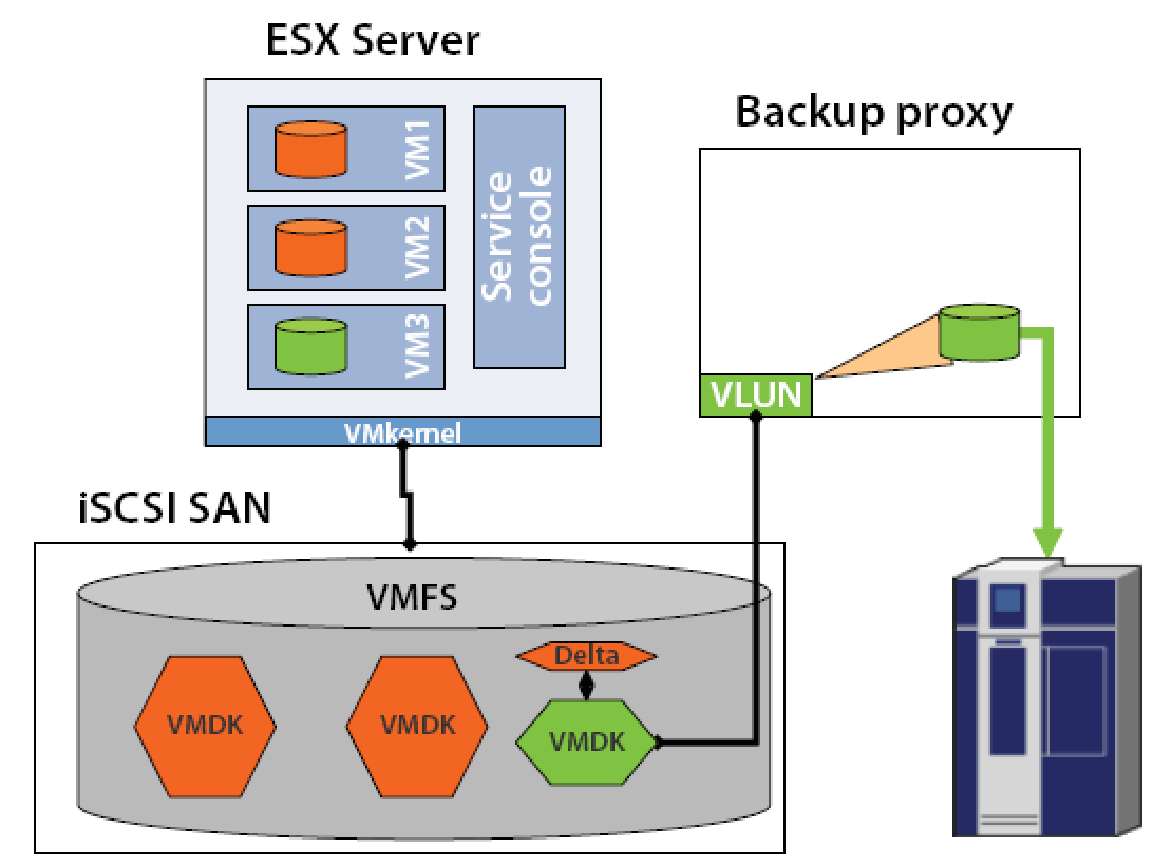
The iSCSI connections are implemented in two ways:
- Software initiator – The iSCSI functionality is emulated in the software and a simple Ethernet adapter is used for network connectivity.
- Hardware initiator – The iSCSI network adapters that act as HBA adapters are used for network connectivity.
In the figure the ESX server host, the iSCSI SAN, and the backup proxy server are all connected via software or hardware iSCSI initiators. With software iSCSI initiator the backup proxy server can also be consolidated into a virtual server as a Virtual Machine and it shall function just like a backup proxy server on a physical host. The green colour shows the Virtual Machine, its data file and the backup path to the storage device. The VLUN driver is installed on the Virtual Machine or a physical host that has a backup proxy server, the VM3 data file VMDK is made available by the driver as a virtual drive for the backup proxy server. The VMDK file is then stored on the secondary storage device connected to the backup proxy server.
LAN-based Data Mover
When the backup proxy server and the Virtual Machine are hosted on a separate physical server the two servers may be connected via LAN interface. The advantage of the LAN based data mover technology is that with Consolidated Backup the online backup of Virtual Machine snapshot can be taken even without block-based storage such as iSCSI SAN or any other shared memory. The other advantages of the LAN based Consolidated Backup feature are (VMware Consolidated Backup, 2007):
- The backup of Virtual Machine stored on a Network Attached Storage (NAS) device or local storage can be done without any disruption.
- The existing infrastructure with storage and Ethernet connections can be leveraged to implement Consolidated Backup of Virtual Machine without a requirement for iSCSI SAN.
- The backup proxy server can be implemented in a dedicated physical server or a Virtual Machine that is connected to the LAN.
- The backup device for a Virtual Machine may be same as the original storage for the Virtual Machine such as the shared local memory on the host virtual server. It is not necessary to install the backup agent on the Virtual Machine in order to take the backup; the backup can be taken from a centralized backup proxy server that is connected to the LAN by mounting the local memory of the target Virtual Machine.
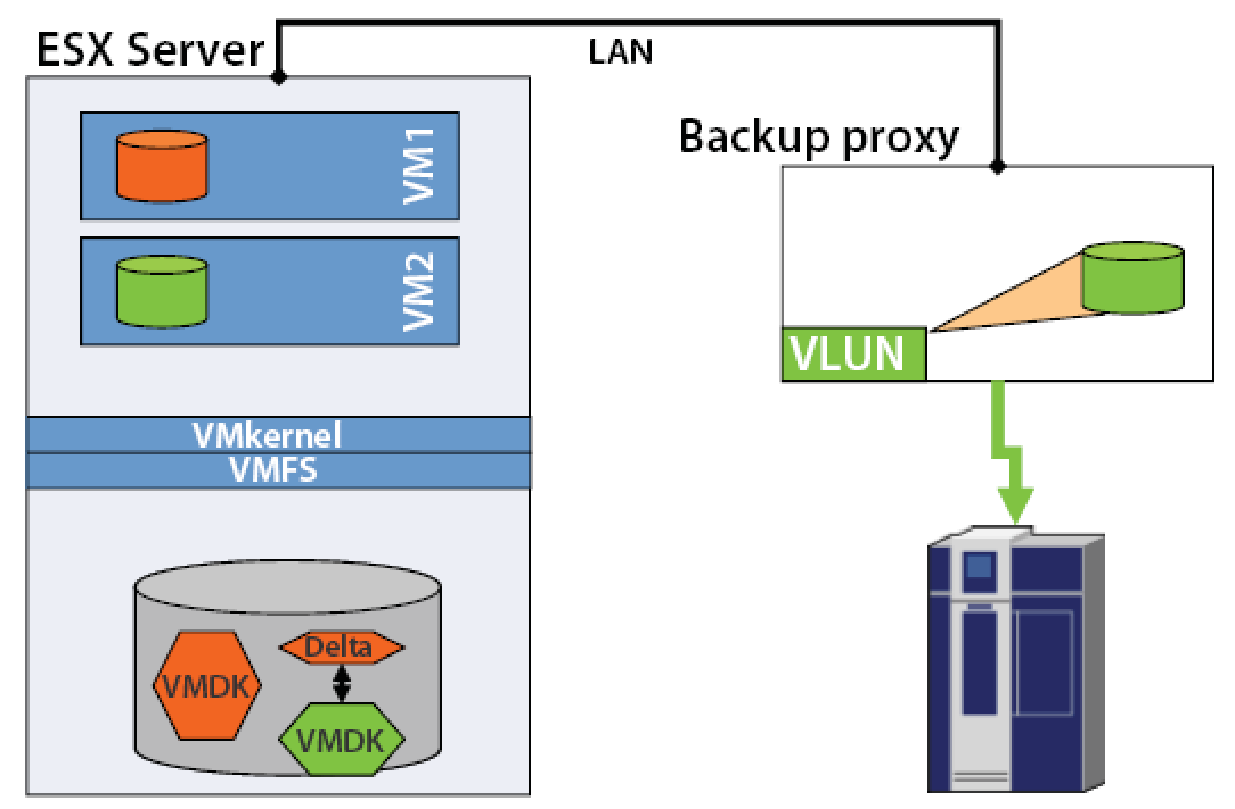
In this figure the green colour is used to highlight the Virtual Machine, local memory resource and the backup path for the Consolidated Backup feature. The backup proxy server creates a snapshot VMDK of the Virtual Machine VM2, this local memory is accessible via the LAN interface that connects the ESX server to the LAN, the VMDK file is mounted on the backup proxy server and copied to the secondary storage device. Since the Virtual Memory local memory is accessible on LAN and the resources such as CPU, network bandwidth and memory buffers are made available by this VM therefore the backup procedure may affect the performance of the other services provided by the VM. Hence in order to ensure best utilization of resources without any disruption in critical services the backup activity must be scheduled in off-peak hours.
Usability of Consolidated Backup
If backup fails the Consolidated Backup performs the cleanup of the failed job and generates notifications. Also graceful exit after cleanup of temporary files and snap shots is provided when the Consolidated Backup procedure is interrupted. Both Consolidated Backup proxy and VirtualCenter Management can be installed on the same host.
Resource Management
The ESX server provides management interface for the following software and hardware resources (ESX Server 2 Systems Management, 2004):
- The Virtual Machine Guest OS and the Virtual Machine applications.
- The configuration and management of multiple Virtual Machines on the virtual server.
- The virtualization of hardware resources such as allocation of CPU, memory, storage and network bandwidth for the Virtual Machines.
- Management of hardware resources on the virtual server.
The ESX server has three type of management interface that can be integrated with other enterprise system management software:
- Web-based graphical user interface for management and monitoring of ESX server and the Virtual Machines running on top of it, called VMware Management Interface.
- Perl and COM APIs are supported to facilitate integration with the proprietary management application of an enterprise.
- ESX Server has a SNMP Management Information Base and an agent to provide configuration and performance information. The SNMP MIB and the agent can be integrated with HP OpenView or IBM Director.
Research Method 3 – Security
The performance of virtual server is affected by the following hardware dependant issues:
Protection exception error
The critical system resources such as some key instructions, memory locations and processor registers may have access restrictions such that only core OS and kernel has access privileges. In a virtual server the Guest OS on the VM may not be provided access to these resources. For this reason the VM may behave differently from actual server and therefore have some feature or behavioural limitations. It is important that the hypervisor or hosted OS restrict the VM Guest OS access to these critical system resources. Unauthorized access to critical system resources may cause “protection error”.
Virtual address space access
The table lookup buffer (TLB) in x86 processor is maintained in the hardware. This makes VM virtual address space management difficult. In order to provide native server like resources for VM it may be required that Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM) maintains a set of memory management tables for all VMs. Since VMM has direct access to the hardware resources, VMM may then perform mapping between VM memory map and the hardware resources and thus keep VM oblivious to the presence of a layer between the VM and the hardware resources.
VMware ESX server has the following security arrangements for the three main components: Virtual Machines, VMware Virtualization Layer and Service Console (ESX Server 2 Security White Paper, 2004):
- All Virtual Machines are isolated from each other and run a dedicated Operating System image, since the Operating System is protected by VM isolation therefore access to OS resources is secured. If the kernel in one Virtual Machine crashes this does not effect other Virtual Machines and they continue to run uninterrupted.
- A Virtual Machine can communicate with other hosts, servers and other devices on the network through the Virtual I/O interface device such as dedicated NIC for a Virtual Machine as in direct assignment of NIC configuration mode or a virtual NIC as in shared physical architecture (Refer section 2.1.2.2.2). If security software such as firewall or antivirus software is installed on a Virtual Machine, the Virtual Machine is protected from external faults in the same manner as it would have been on a native physical server.
- Since Guest OS is included in the Virtual Machine and the virtualization layer lies beneath the Virtual Machines therefore due to this isolation of the Virtual Machines from each other even if a user has system administrator privileges for a Virtual Machine, the user cannot access another Virtual Machine. (Refer figure 1) Access to a Virtual Machine requires system administrator privileges for the Virtual Machine. The login access to the system shell is restricted.
- In order to secure the resource allocation for Virtual Machines to avoid the performance degradation and denial of service due to resource consumption by other Virtual Machines that share the resource fine-grained resource controls are used. The minimum resource allocation is configured for a Virtual Machine to ensure business continuity without any disruption in the services provided by the Virtual Machine. The Virtual Machine kernel that mediates the allocation of the resource allocation does not provide a mechanism to allow a Virtual Machine to access another Virtual Machine resource.
- VMware has a provision for configuring per VM network security policies such as information access privileges for NAS/SAN.
- VMware products are audited by independent 3rd party firms who get access to the source code and support from VMware engineers.
- The promiscuous mode configuration for network adapters is disabled by default. In promiscuous mode a guest network adapter provides its own hardware address for IP-to-physical address mapping for other network adapters that lie behind the guest network adapter. Therefore in promiscuous mode configuration the guest VM shall receive all the packets destined for other network adapters and can “sniff” these packets which can be a security hazard. Promiscuous mode may be used for the configuration of the virtual NIC in shared physical architecture for virtual I/O. In direct assignment architecture for NIC one of the NIC may be configured in promiscuous mode in order to add an additional security layer for other Virtual Machines. The Virtual Machine with this promiscuous mode NIC shall “sniff” and filter the packets destined for other Virtual Machines on the server.
- Troubleshooting information may be logged in files however the size of files must be limited in order to avoid a denial of service attack due to storage resource shortage. The log files may also be saved on the Storage Area Network or Network Attached Storage disks.
Practical Part – Advantages of Server Virtualization
“Server virtualization is an abstraction technology that enables the division of the hardware resources of a given server into multiple execution environments and enables the consolidation of multiple servers and hardware resources into a single computing resource” (Virtualization Technology Overview, 2007).
The advantages of server virtualization are:
- In a virtual server more than one physical server boxes are consolidated into one virtual server box and their workload is virtualized by sharing of the physical resources of this box. The one high-performance computer system thus reduces the number of boxes present in the infrastructure. Further, the operational and maintenance cost is reduced and Return On Investment (ROI) is increased by adding Virtual Machines to the virtual server instead of adding a new box.
- The user gets an illusion of running the service on the legacy hardware, i.e. a dedicated physical server, no modifications are required in the existing service software, hardware resources and the network infrastructure when the service is migrated onto a high performance virtualization enabled machine. The virtual server for migration is selected by matching the service hardware requirements with the availability of the shared hardware resources on the virtual server.
- The virtual server provides increased flexibility in the configuration and the utilization of the existing resources in the data centre due to an ability to run more than one Operating System and applications on a single hardware system simultaneously. Each Virtual Machine that is run on the virtual server has its own Operating System called Guest OS.
- The Virtual Machines of the server are isolated from each other and can communicate either via underlying virtualization layer or through the external network such as LAN. Each VM may be assigned an IP address and a dedicated physical NIC or shared virtual NIC to connect to LAN. This secure configuration of VMs ensures that fault in an application on a VM does not affect applications running on the other VMs and that there is no adverse impact on the system performance and the system downtime is not affected. A standby VM may be configured on the same virtual server or a separate virtual server for disaster recovery in order to ensure business continuity.
- The system provisioning, high availability and system migration of VMs is made simpler with single management interface for similar tasks. In order to achieve this task that constitutes multiple applications and would otherwise be configured on separate legacy servers must be configured on VMs of the same virtual server.
- Virtualization does not restrict a user from working simultaneously on different VMs of a virtual server. Also, more than one user can work simultaneously on the same or different VMs in a virtual server. If a VM crashes it does not impact the other users of the other VM on the server.
In order to benefit from these advantages of a virtual server it is required that the virtual server must provide equal or higher performance than the total performance of all legacy servers that are being replaced by this virtual server. The performance implies processing power, memory, I/O ports, network interfaces, power & cooling requirements, cost and floor space.
On a blade server dynamic load balancing can be achieved by moving an entire VM from overloaded server blade to another server blade with available resources. The dynamism is achieved by the ability in VMware VMotion to move VM run-time based on the application and the system context data. Application context data may be time-of-day when consumer requirement such as web site access or downloads are expected to be at peak. System context data may be CPU utilization and memory buffer thresholds.
Multiple servers required for a testing infrastructure can be replaced with a single blade in a blade server or a virtual server. This replacement and the virtualization technology shall eliminate the cabling requirement, reduce the power and cooling cost and allow multiple users to simultaneously test applications on different VMs without any interference with the other VM or users.
More advantages of server virtualization are described below:
Server Consolidation and Containment
With the VM configuration on a server more than one application is contained on a single server and hence the server resources utilization rate is increased from 5-15% to 60-80%. The consolidation of more than one OS platforms onto a single server eliminates server sprawl problem. The aim of virtualization is not only to enhance system performance but also to reduce the number of servers in the organization infrastructure, i.e. to reduce the ‘box-count’. This reduction in ‘box-count’ also affects the recurring operational cost by reducing power cost and floor space requirement.
The goal of server containment is unification therefore new applications are installed on a VM on existing server rather than purchasing new hardware. Benefits of server consolidation and containment can be measured by Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), i.e. one-time purchasing and setup cost plus recurring operational and maintenance cost. For effective server consolidation and containment automated provisioning of resources such as CPU scheduling, memory allocation, Direct Memory Access for disk read/write operations, iSCSI interface for SAN, network bandwidth allocation, high availability configuration and load balancing between applications on a VM or between the VMs is required.
Test & Development Optimization
The virtual server has a provision to run more than one OS platforms on a single hardware platform. The Guest OS that run on the Virtual Machines can be different. By using virtual server in a test environment the number of server boxes is reduced and hence the development and the test activity is optimized because the administrative and maintenance cost is reduced. Developer/tester may use the VMs on a single server to develop and test the applications that require multiple environments.
Business Continuity
The system downtime is reduced by consolidation of more than one server activities onto a single physical server. The hot standby of the active Virtual Machine can be configured on the same or different virtual server. The hot standby may be configured to use the active VM memory resource and in case of fault or overload condition the standby VM can take the role of an active VM without affecting the system performance. The VMware VMotion technology can be used for migration of the VM to a different server in critical conditions. The critical conditions can be detected by pre-configured threshold values such as CPU utilization percentage, memory buffer usage, latency in network traffic due to congestion because of high user traffic to avail the service provided by the VM, e.g. access to web site.
The VMware High Availability feature may also be used to detect the system condition when either Disaster Recovery or migration is required. In the event of disaster recovery the image of single computer system may be copied to a new server to restore the system. VMware Consolidated Backup may be used to store the VM on the secondary storage for restoration in case of faults such as memory corruption due to application fault or a security breach.
Enterprise Desktop
A virtual desktop can be connected to a backend virtual server with multiple VMs. More than one desktop may be connected to the backend server. A workstation dedicated for a single user has wasted resources due to idle time when the system is not in use or non-optimal use at other times. Virtual Desktop provides the optimized utilization of computing, storage and networking resources. Also the information security risks such as password loss or hard disk theft in a dedicated workstation are mitigated with virtual desktop. The end user autonomy is secured in virtual desktop by including a security policy layer in the VM enclosing software, e.g. user authentication and data access permissions on each VM. The hardware resource for memory is not present at the site of virtual desktop and is kept in more secure server rooms.
Case Study
WWF-UK
A Carbon Footprint is a measure of the impact our activities have on the environment in terms of the amount of greenhouse gases we produce. It is measured in units of carbon dioxide (Carbon Footprint, 2008).
World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF-UK) is a science-based conservation organization that addresses environmental issues such as species & habitat survival, climate change, environmental education and sustainable business. WWF-UK office in Godalming, Surrey has a staff of over 300. As a conservation organization WWF-UK has environmental friendly business practices. Reduction in organization’s carbon footprint was set as an objective as part of organization’s business practices. In order to meet this objective the IT department decided to reduce cooling requirements. To meet this requirement the number of servers used by IT department were to be reduced.
To ensure business continuity and disaster recovery with less number of servers WWF-UK decided to install VMware server virtualization software on the servers. VMware Infrastructure 3 Enterprise was installed by SNS Ltd., a VMware® VIP Enterprise Reseller. VMware components installed included VMware ESX Server 3, VMware VirtualCenter 2 and VMware VMotion.
Result
WWF-UK achieved reduced carbon foot print, small hardware infrastructure and reliable business continuity with VMware server virtualization solution. Networking software, financial system, contact information database of millions of supporters and other HR applications were configured to run on these virtual servers.
Bell Canada
Bell Canada Enterprises (BCE) is Canada’s largest communications company. The main subsidiary, Bell Canada, provides local telephone, long distance, wireless communications, Internet access, data, satellite television and other services to residential and business customers through some 27 million customer connections (Bell Canada & CGI Group, 2006).
To meet the customer support requirements for its large customer base, Bell Canada took an initiative in October 2004 to avoid hardware attrition and reduce the TCO. Bell Canada set a goal to provide customized workstations for its 8,000 call agents in order to facilitate outsourcing and telecommuting.
“Bell Canada came to us with a project to provision, connect and securely deploy 400 desktop environments within three weeks,” says Martin Quigley, CGI senior technical consultant to Bell Canada (Bell Canada & CGI Group, 2006).
Because of space and security restrictions, CGI suggested that Bell Canada use VMware virtualization solution to provide virtual desktops. Bell Canada had specific requirements due to the nature of their business:
Due to the enhanced security requirement from the Bell Canada client it must be possible to create a ‘lockdown environment’ for employees. Due to file sharing no programs could be installed on desktop hard-drive.
VMware desktop virtualization solution could fulfill Bell Canada requirements:
Low Total Cost of Ownership
- Since the server count is reduced and separate CPU unit is not required with the virtual desktop, TCO is reduced.
- Reduced number of hardware units saves floor space and power and cooling cost.
- Operational and maintenance overhead is reduced.
- Eliminates need for site visit by telecommute employee or need to courier desktop hardware for upgrades or incidents.
- Eliminates MAC request.
Telecommute support
The telecommute employees desktop can be controlled from the datacenter because virtual desktop runs as VM on virtual server.
Optimized Development Environment
Multiple desktops could share the hardware resources of a virtual server. A separate Virtual Machine could be configured on a virtual server for each connected desktop. This VM emulates the physical desktop and the user cannot tell the difference between the two configurations.
Centralized Simplified Management
Centralized desktop control. A single VM image shall be configured and then multiple copies can be loaded on virtual server through VMware VirtualCenter.
Rapid Deployment
The centralized and simplified desktop management with VMware VirtualCenter reduces desktop configuration time and hence the time from order to deployment is considerably reduced.
Hardware Independence
Call agents who telecommute may use any desktop hardware if they are not using Bell Canada desktop hardware. The requirement is that Microsoft Windows XP RDP (remote desktop protocol) must be installed on agent desktop in order to connect with Bell Canada virtual server.
Seamless user experience
When employees are moved to different LAN only one network connection of virtual server must be changed.
Disaster recovery and backup
Since all virtual desktop environments are identical VMotion and Disaster Recovery can be used to migrate and restore VMs respectively to different servers.
Result
VMware provides secure desktop environment that is used by Bell Canada internal and external agents to serve the clients. Hardware attrition is eliminated with less number of boxes in the infrastructure and hence TCO is also reduced.
Conclusion
Server virtualization is a technology that is used to reduce the Total Cost of Ownership of hardware and software resources. In a data computing intensive business an enterprise has a requirement for computing, storage and networking resources. In order to gain high Return On Investments it is necessary that optimum utilization of resources is made and operational and maintenance overhead such as floor space, power and cooling requirement is reduced. After the study of VMware virtualization solution for server virtualization it is found that VMware provides necessary software components that can be integrated with hardware solutions to provide the secure and fault-tolerant virtualization solution.
If the enterprise hardware resources do not support hardware assisted virtualization as provided by Intel and AMD, VMware para-virtualization solution can be used to run complex applications that include instructions that cannot be executed on shared hardware resources.
VMware virtualization solution ESX server enables use of Network Attached Storage or Storage Area Network for sharing external memory in order to eliminate hard disk requirement on the virtual server. Desktop virtualization integrated with a virtual server that connects to NAS or SAN provides hardware modularity where user interfaces, computing and storage can be physically isolated without the adverse affect on the quality of service. The advantage of this configuration is that large enterprises can centralize the data storage and have localized computing to ensure data integrity.
Also the VMware fault-tolerance features ensure that system downtime is reduced and resource utilization is optimized with the ability for live migration of a Virtual Machine with VMotion in case of a fault or service requirements such as due to reduced customer traffic on certain days of week less computing resources are required. The ability to create online backup of a Virtual Machine with Consolidated Backup mitigates the risk of damage to physical devices.
VMware provides Web based, API and SNMP interfaces for integration with enterprise system management software to provision the shared resources of a virtual server.
References
A Guide to Harvard Referencing. (2005) Leeds Metropolitan University. Web.
Bell Canada & CGI Group. (2006) VMware Virtual Desktop Infrastructure Connects Bell Canada for Optimized Customer Care. VMware. Web.
Blade Server Technology Overview. (2008) Blade. Web.
Blade Server. (2008) SearchDataCenter. Web.
Carbon Footprint. (2008). Web.
Desktop Virtualization. (2008) Wikipedia. Web.
Disaster Recovery Solutions from VMware. (2007) VMware. Web.
Enhanced Virtualization on Intel Architecture-based Servers. (2006) Intel. Web.
ESX Server 2 Security White Paper. (2004) VMware. Web.
ESX Server 2 Systems Management. (2004) VMware. Web.
Intel Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O. (2007) Intel. Web.
Intel Virtualization Technology. (2006) Intel. Web.
iSCSI. (2008) Wikipedia. Web.
Mano, Morris, M. (1999) Computer System Architecture. 3rd Ed. Prentice Hall.
Network-attached storage. (2008) Wikipedia. Web.
PC Blades. (n.d.) ClearCube. Web.
SCSI. (2008) Wikipedia. Web.
Server Blade. (2005) SearchDataCenter. Web.
Storage area network. (2008) Wikipedia. Web.
The Architecture of VMware ESX Server 3i. (2007) VMware. Web.
The Future of Ethernet I/O Virtualization is Here Today. (2006) Netxen. Web.
Thin Client. (2008) Wikipedia. Web.
Understanding Full Virtualization, Paravirtualization, and Hardware Assist. (2007) VMware. Web.
Virtualization Overview. (2006) VMware. Web.
Virtualization Solutions. (n.d.) ClearCube. Web.
Virtualization Technology Overview. (2007) Blade. Web.
VMware Consolidated Backup. (2007) VMware. Web.
VMware VMotion and CPU Compatibility. (2007) VMware. Web.
What is POSIX? (n.d.) LYNUXWORKS. Web.